Question
In: Computer Science
The Language is Java. Sample Output: There is no given sample Output IsEqualToTest (30) Write a...
The Language is Java.
Sample Output:
There is no given sample Output
IsEqualToTest (30)
Write a simple generic version of method isEqualTo that compares its two arguments with the equals method and returns true if they’re equal and false otherwise. Use this generic method in a program that calls isEqualToTest with the built-in types Integer, String, Double and Object. The main reads in two Integer, and two Double values with autoboxing, as well as two String and calls the method. For Object just create two Object objects with no parameters. The method doesn’t need to include any correctness tests.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Please find the code below.
class isEqualToTest<T1, T2>
{
T1 obj1; // An object of type T1
T2 obj2; // An object of type T2
isEqualToTest(T1 obj1, T2 obj2) // Constructor of the class
'isEqualToTest'
{
this.obj1 = obj1;
this.obj2 = obj2;
}
// It will return the boolean value after comparison
public boolean isEqualTo()
{
if (obj1.equals(obj2)){
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
}
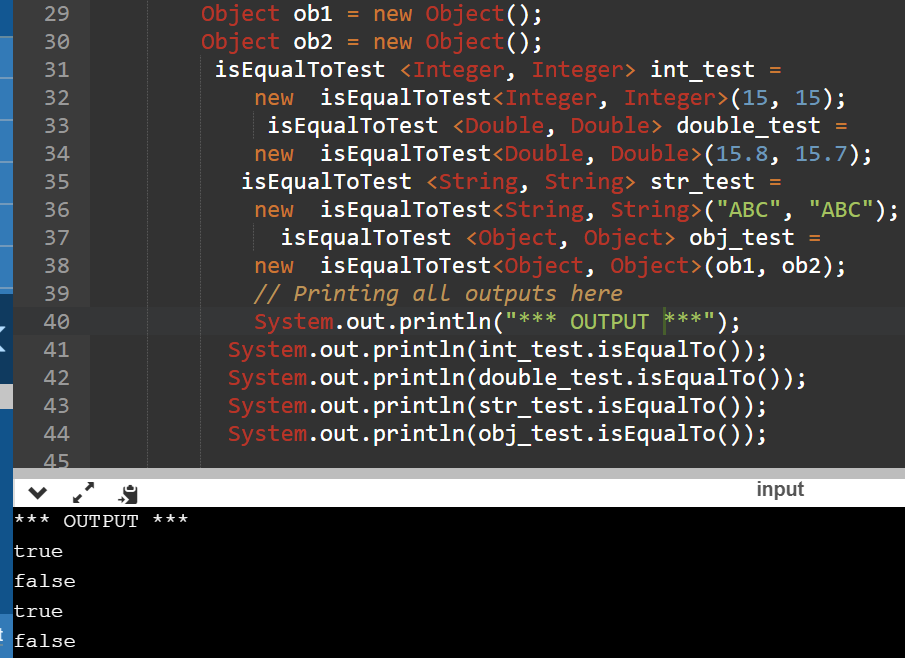
class Main
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
Object ob1 = new Object();
Object ob2 = new Object();
isEqualToTest <Integer, Integer> int_test =
new isEqualToTest<Integer, Integer>(15, 15);
isEqualToTest <Double, Double> double_test =
new isEqualToTest<Double, Double>(15.8, 15.7);
isEqualToTest <String, String> str_test =
new isEqualToTest<String, String>("ABC", "ABC");
isEqualToTest <Object, Object> obj_test =
new isEqualToTest<Object, Object>(ob1, ob2);
// Printing all outputs here
System.out.println("*** OUTPUT ***");
System.out.println(int_test.isEqualTo());
System.out.println(double_test.isEqualTo());
System.out.println(str_test.isEqualTo());
System.out.println(obj_test.isEqualTo());
}
}
OUTPUT:
Related Solutions
Write a program to perform the following actions: the language is Java – Open an output...
Language for this question is Java write the code for the given assignment Given an n...
Write Lexical Analyzer program in C language. Below is the sample input and ouput. /* output...
In JAVA answer has to be able to do exact Sample Output shown Write a do-while...
PROGRAM SIMULATION. Understand the given JAVA program and write the output. 1. public class Places {...
**Please write in Java, in a very simple/beginner coding style/language - thank you!** Directions: Given a...
Write a machine language program to output your name on the output device. The name you...
Language is Java Design and write a Java console program to estimate the number of syllables...
Java programming language Write a Java application that simulates a test. The test contains at least...
Write Java statements that will Create an UnorderedLinkedList Given List: 75 48 78 45 30 18...
- The Language is Java. Sample Output: There is no given sample Output IsEqualToTest (30) Write a...
- what is the correct name of the glycosidic bond in maltose?
- According to the Law of One Price, assuming there are no transport costs and freecompetition exists,...
- Two 2.0 cm -diameter disks face each other, 3.0 mm apart. They are charged to ±11nC....
- Write a decrease-conquer algorithm to solve the following problem: input: a nonempty unsorted array A[lo..hi] of...
- PLEASE DO THIS WITH PYTHON 3 Lab 4-2: Computing Tax The United States federal personal income...
- Peter and Blair recently reviewed their future retirement income and expense projections. They hope to retire...
 venereology answered 2 hours ago
venereology answered 2 hours ago