Question
In: Economics
Consider the following: C= 116 + 0.8 (Y - T) - 1000r I= 140 - 2000r...
Consider the following: C= 116 + 0.8 (Y - T) - 1000r
I= 140 - 2000r G= 165 T= 30 + 0.25Y
EX= 100; IM= 110 + 0.2Y
L= 5Y - 100000r M= 60000 P= 100 rrr= 0.2
IS: Y = 1/0.6 (387 - 3000r) Y = 645 - 5000r
LM: Y = 1/5 (600 + 100000r) Y = 120 + 20000r
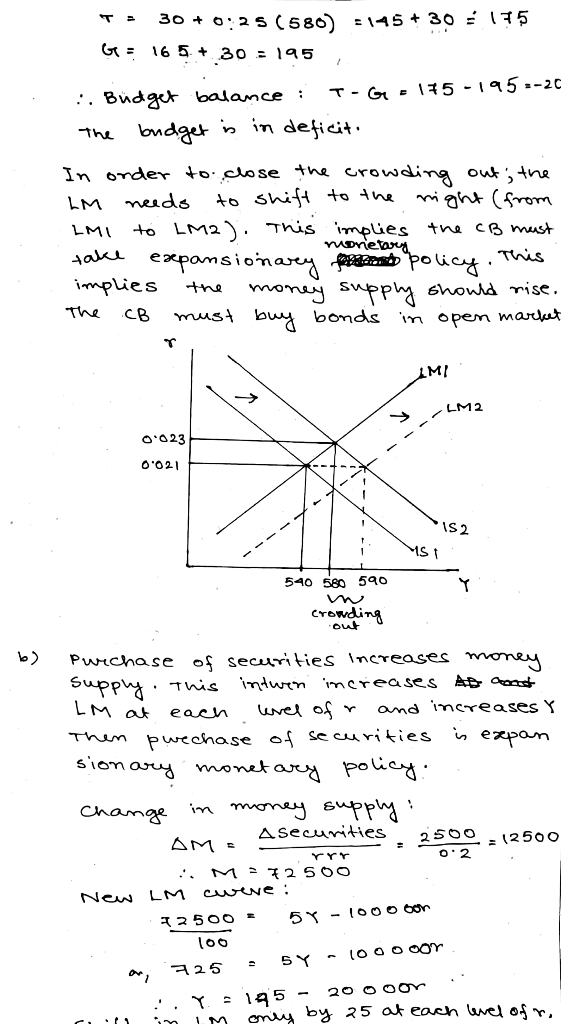
a) If G increases by 30, is it an expansionary, or a contractionary (pick one) fiscal policy? By how much does the IS and LM curves shift and by how much does Y change?
How much is the crowding out effect? Is the budget balanced? If Fed monetizes the additional budget deficit to eliminate crowding out, do they need to buy bonds, or sell bonds?
b) If the Fed purchases securities worth of 2500; is it an expansionary, or a contractionary (pick one) monetary policy? If there is no leakage of excess reserves, then by how much does it change the money supply? By how much do the IS and LM curves shift and by how much does Y change?
Solutions
Related Solutions
Consider the following macroeconomic model: C(t) + I(t) = Y (t) I(t) = 0.8 dC(t) dt...
18. Consider the following closed economy: C = 60 +0.8(Y-T) I = 150-1000i G = 250...
c = 100 + 0.8 (y - t) i = 500 - 50r g = 400...
Consider a hypothetical economy where: • C(Yd) = 105 + 0.8 × (Y − T) •...
Consider a hypothetical economy where: • C(Yd) = 105 + 0.8 × (Y − T) •...
An economy is described by the following equations: C = 40 + 0.8 (Y – T)...
An economy is described by the following equations: C = 100 + 0.8 (Y – T)...
. Consider the following model: C = 500 + .3(Y − T) I = 150 +...
Given the following economy: Y = C(Y - T) + I(r) + G C(Y - T)...
Let the following equations characterize an economy: C = 400 + 0.8*(Y-T) G = 300 T...
- Peter and Blair recently reviewed their future retirement income and expense projections. They hope to retire...
- Byzantine Generals Problem and Solutions Based on the proposed solutions use any code you want to...
- All of these problems involve preparation and use of a vaccine solution that contains an active...
- Consider the following: C= 116 + 0.8 (Y - T) - 1000r I= 140 - 2000r...
- 0.80 grams of KHP is titrated with 20 mL of the unknown NaOH solution. What is...
- We have discussed three methods of horizontal gene transfer. Correctly match the method with its name....
- Investigation B, The Braun Electroscope The Braun electroscope consists of a metal disc at the...


 Rahul Sunny answered 3 hours ago
Rahul Sunny answered 3 hours ago