Question
In: Physics
A charged nonconducting rod, with a length of 3.68 m and a cross-sectional area of 2.79...
A charged nonconducting rod, with a length of 3.68 m and a cross-sectional area of 2.79 cm2, lies along the positive side of an x axis with one end at the origin. The volume charge density ρ is charge per unit volume in coulombs per cubic meter. How many excess electrons are on the rod if ρ is (a) uniform, with a value of -2.07 µC/m3, and (b) nonuniform, with a value given by ρ = bx2, where b = -2.89 µC/m5?
Solutions
Expert Solution
Here,
Length of charged nonconducting rod L= 3.68m
cross-sectional area A=2.79cm2 or 
Volume charge density is 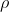
(a) If the charge density on rod is uniform:
Charge on rod is given by  {V is volume of the rod}
{V is volume of the rod}
or  {A is area and L is length}
{A is area and L is length}
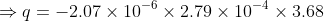
 C
C
Excess of electron 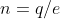
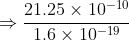
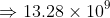
So, This is the number of excess of electron on the rod, Negative
sign was neglected because that show only the nature of
charge.
(b) Charge density is non uniform on the rod:
Now the charge for any specific point where the charge density is
2B(because it is not at every point)
So charge on whole rod is given by-

Because charge density is non uniform so let it covers x portion of
the rod

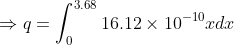
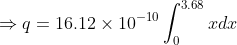


Excess of electron: n=q/e


Related Solutions
A brass rod with a length of 1.23 m and a cross-sectional area of 1.53 cm2...
A cylindrical copper rod of length 1.60 m and cross-sectional area 7.10 cm^2 is insulated to...
The length of a magnetic circuit of a relay is 25 cm and the cross-sectional area...
2) A steel rod with a cross-sectional area of 0.25 sq. in. is stretched between two...
A 1.5 m length of wire has a cross-sectional area of 5.0×10−8 m2. When the potential...
A long solenoid (black coil) with cross-sectional area A and length L is wound with N1...
Question 1 A copper tube having a cross-sectional area of 2000 mm2 and length of 300...
the rod below is a uniformly charged semicircle of arc length .14 m. If the total...
Water is moving with a speed of 11.3 m/s through a pipe with a cross-sectional area...
A cylinder of 10-m-high, and a cross-sectional area of 0.1 m2 , has a piston (that...
- A faulty model rocket moves in the xy-plane (the positive y-direction is vertically upward). The rocket's...
- A charged nonconducting rod, with a length of 3.68 m and a cross-sectional area of 2.79...
- Please list your 3 most favorite brands and say why. 1. 2. 3. Please list your...
- Six years from today you need $10,000. You plan to deposit $1,600 annually, with the first...
- 1. How did IBM become the dominant IT industry leader? 2. What changed that knocked IBM...
- Rental Shop A. Create an abstract class named SummerSportRental that is to be used with for...
- 1-Suppose a Styrofoam cup that weighs 5 grams was used for this experiment in place of...
 genius_generous answered 3 hours ago
genius_generous answered 3 hours ago