Question
In: Finance
Suppose you observe the following situation: Security Beta Expected Return Pete 1.60 12.9% Repete 0.97 9.5%...
Suppose you observe the following situation:
|
Security |
Beta |
Expected Return |
|
Pete |
1.60 |
12.9% |
|
Repete |
0.97 |
9.5% |
Assume these securities are correctly priced. Based on the CAPM,
what is the expected return on the market? What is the risk-free
rate?
Shows all the step and formula. Don't round off until you get the
answer.
Solutions
Related Solutions
(4) Suppose you observe the following situation: Security Beta Expected Return Pete Corp. 1.15 12.90% Repete...
(4) Suppose you observe the following situation:
Security Beta Expected Return
Pete Corp. 1.15 12.90%
Repete Co. 0.84 10.20%
Assume the two securities are correctly priced. Based on CAPM, what
is the expected return on the market? What is the risk-free rate?
(15 points)
Suppose you observe the following situation: Security Beta Expected Return Assume these securities are correctly priced....
Suppose you observe the following situation:
Security Beta Expected Return
Assume these securities are correctly priced. peat co. 1.20
11.0
Repeat co. 0.65 9.9
Based on the CAPM, what is the expected return on the market?
What is the risk-free rate? (Do not round intermediate
calculations. Enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal
places.)
Expected return on market %
Risk-free rate %
Suppose you observe the following situation: Security Beta Expected Return Cooley, Inc. 1.6 19% Moyer Co....
Suppose you observe the following situation:
Security
Beta
Expected Return
Cooley, Inc.
1.6
19%
Moyer Co.
1.2
16%
If the risk-free rate is 8 %, are the securities correctly
priced? What would the risk-free rate have to be if they are
correctly priced?
Suppose you observe the following situation: Standard Deviation Beta Expected Return Stock A 33% 1.2 0.13...
Suppose you observe the following situation:
Standard Deviation
Beta
Expected Return
Stock A
33%
1.2
0.13
Stock B
38%
0.8
0.12
Stock C
30%
1.1
0.11
T-Bill
-
-
0.03 + 0.5×9
Which one(s) has the highest
systematic risk? (Stock A, Stock B, Stock C, Hard to
Say)
Which one(s) has the highest
unsystematic risk? (Stock A, Stock B, Stock C, Hard to
Say)
If Stock C is correctly priced, what
is the reward-to-risk ratio (Sharpe ratio) for Stock A...
Suppose you observe the following situation: Rate of Return If State Occurs State of Probability...
Suppose you observe the following situation:
Rate of Return If State Occurs
State of
Probability of
Economy
State
Stock A
Stock B
Bust
.30
−.10
−.08
Normal
.50
.11
.11
Boom
.20
.46
.26
a.
Calculate the expected return on each stock. (Do not
round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers as a percent
rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.)
Expected return
Stock A
%
Stock B
%
b.
Assuming the capital asset pricing model holds and Stock...
Suppose you observe the following situation: Rate of Return If State Occurs State of Probability...
Suppose you observe the following situation:
Rate of Return If State Occurs
State of
Probability of
Economy
State
Stock A
Stock B
Bust
.25
−.07
−.05
Normal
.45
.14
.14
Boom
.30
.49
.29
a.
Calculate the expected return on each stock. (Do not
round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers as a percent
rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.)
Expected return
Stock A
%
Stock B
%
b.
Assuming the capital asset pricing model holds and Stock...
Suppose you observe the following situation: State of Economy Probability of State Return if State Occurs...
Suppose you observe the following situation:
State of
Economy
Probability
of State
Return if State Occurs
Stock A
Stock B
Bust
.15
−.08
−.10
Normal
.60
.11
.09
Boom
.25
.30
.27
a.
Calculate the expected return on each stock.
(Do not round intermediate calculations
and enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2
decimal places, e.g., 32.16.)
b.
Assuming the capital asset pricing model holds and Stock A’s
beta is greater than Stock B’s beta by...
Evaluating risk and return. Stock X has an expected return of 9.5 percent, a beta coefficient...
Evaluating risk and return. Stock X has an expected return of
9.5 percent, a beta coefficient of 0.9, and a 30 percent standard
deviation of expected returns. Stock Y has a 13 percent expected
return, a beta coefficient of 1.3, and a 20 percent standard
deviation. The risk-free rate is 5 percent, and the market risk
premium is 5.5 percent.
a) Calculate the coefficient of variation of each stock.
b) Which stock is riskier for diversified investors? Which stock
is...
Stock X has a 9.5% expected return, a beta coefficient of 0.8, and a 30% standard...
Stock X has a 9.5% expected return, a beta coefficient of 0.8,
and a 30% standard deviation of expected returns. Stock Y has a
12.0% expected return, a beta coefficient of 1.1, and a 25.0%
standard deviation. The risk-free rate is 6%, and the market risk
premium is 5%.
Calculate each stock's coefficient of variation. Round your
answers to two decimal places. Do not round intermediate
calculations.
CVx =
CVy =
Which stock is riskier for a diversified investor?
For...
Stock X has a 9.5% expected return, a beta coefficient of 0.8, and a 40% standard...
Stock X has a 9.5% expected return, a beta coefficient of 0.8,
and a 40% standard deviation of expected returns. Stock Y has a
12.0% expected return, a beta coefficient of 1.1, and a 25%
standard deviation. The risk-free rate is 6%, and the market risk
premium is 5%.
Calculate each stock's coefficient of variation. Do not round
intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal
places.
CVx =
CVy =
Which stock is riskier for a diversified investor?
For...
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- This week, we are focusing on Management and Motivation (Chapter 3). Be sure to read chapter...
- A 2.00 m long horizontal uniform beam is supported by a wire as shown in the...
- State two reasons why it is advisable to place the transaction log on a separate disk...
- ( Posting the same question for third time. Can I please get answer in C++.( and...
- Write a Java program to do the following with your name. This can all be done...
- When preparing government-wide statements, which of the following is not true? Multiple Choice Entries are necessary...
- Hawaiian Location (e.g., what can be grown there because of the climate, soils, etc.) Culture (e.g.,...
ADVERTISEMENT


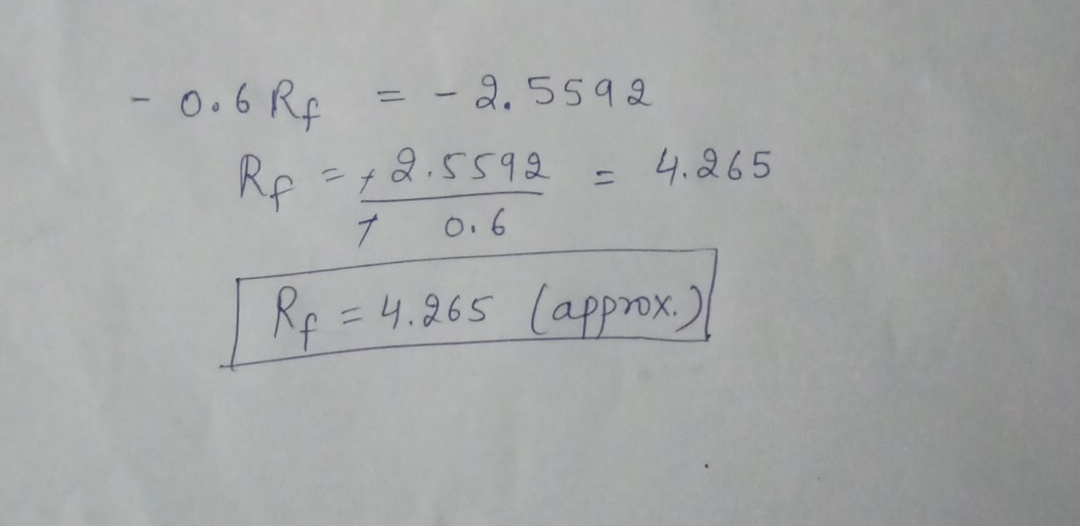
 jeff jeffy answered 3 weeks ago
jeff jeffy answered 3 weeks ago