Question
In: Chemistry
We will abbreviate Malonic acid, CH2(CO2H)2 as H2M. Find the pH and concentrations of H2M, HM-,...
We will abbreviate Malonic acid, CH2(CO2H)2 as H2M. Find the pH and concentrations of H2M, HM-, and M^2- in a) .1 M H2M b) .1 M NaHM c) .1 M Na2M
Solutions
Related Solutions
We will abbreviate malonic acid, CH2(CO2H)2, as H2M. Find the pH and concentrations of H2M, HM+
We will abbreviate malonic acid, CH2(CO2H)2, as H2M. Find the pH and concentrations of H2M, HM+, and M2+ in (a) 0.100 M H2M; (b) 0.100 M NaHM; (c) 0.100 M Na2M.
Malonic acid (FW = 104.06) is a diprotic acid of the form CH2(COOH)2, with pKa1 =...
Malonic acid (FW = 104.06) is a diprotic acid of the form
CH2(COOH)2, with pKa1 = 2.847
and pKa2 = 5.696. Assume all solutions are
ideal.
(a) If 15.000 g of malonic acid is added to 100 mL of pure water,
what will the pH of the
solution be?
(b) You add 18 mL of 5 M NaOH to the solution in part (a). What
will the new pH be?
(c) You then add 5.000 g of sodium malonate (Na2CH2(COO),...
A 25.00 mL sample of 0.120 M of the diprotic malonic acid, HOOC-CH2-COOH, was titrated with...
A 25.00 mL sample of 0.120 M of the diprotic malonic acid,
HOOC-CH2-COOH, was titrated with 0.250 M NaOH. If the following
results were obtained, calculate Ka1 and Ka2.
mL NaOH added: 5.00 6.00 10.00 12.00 15.00 18.00 20.00 24.00
pH: 2.68 2.83 3.53 4.26 5.21 5.69 6.00 9.24
What is the pH of a solution that is 0.0924 M in malonic acid? What will...
What is the pH of a solution that is 0.0924 M in malonic acid?
What will be the equilibrium concentration of each of the three
malonic acid species? pKa1 = 2.85 pKa2 = 5.70
pH: _________________
[H2A]: ____________________ [HA-]: _________________ [A2-]:
_________________
The net equation for the Briggs-Rauscher reaction is: IO3- + 2H2O2 + H+ + CH2(CO2H)2 ------->...
The net equation for the Briggs-Rauscher reaction is:
IO3- + 2H2O2 +
H+ + CH2(CO2H)2
-------> ICH(CO2H)2 + 2O2 +
3H2O
From the exact concentrations and amounts of reagents you
created and worked with (i.e the volumes when performing the
reaction), calculate the grams of oxygen that have been formed when
the reaction is complete. What reagent is limiting? Show all work.
(NOTE: Volume of Malonic Acid 10mL, volume of Manganese Sulfate
Monohydrate 10mL, Potassium Iodate 10mL, 1mL of starch).
Calculate the pH and concentration of all species of malonic acid (C3H4O4) in each of the...
Calculate the pH and concentration of all species of malonic
acid (C3H4O4) in each of the follwing solutions.
K1=1.42*10^-3, K2=2.01*10^-6
0.100 M NaC3H3O4 solution
0.100 M Na2C3H2O4 solution
Initial pH: 2.54 malonic acid (C3H4O4) sodium malonate (NaC3H3O4) Addition of HCl (drop in pH) mL...
Initial pH: 2.54
malonic acid (C3H4O4)
sodium malonate (NaC3H3O4)
Addition of HCl (drop in
pH)
mL of HCl added
ΔpH
4.12
-0.51
6.93
-0.69
11.59
-0.89
25.63
-1.09
49.9
-1.24
Addition of NaOH (increase in pH)
mL of NaOH added
ΔpH
1.91
2.77
2.61
3.00
3.56
3.21
4.43
3.48
4.98
3.69
5.39
3.96
5.87
4.25
6.36
4.51
6.9
4.71
Clearly outline how you made your assigned buffer with its
target pH.
Assuming no volume change, how many mL of 0.1...
Phosphoric acid, H3PO4(aq), is a triprotic acid. Calculate the pH and concentrations of H3O + (aq),...
Phosphoric acid, H3PO4(aq), is a triprotic acid. Calculate the
pH and concentrations of H3O + (aq), H3PO4(aq), H2PO4 − (aq), HPO4
2− (aq), PO4 3− (aq), and OH− (aq) in a 0.100-M phosphoric acid
solution at 25°C.
Consider the diprotic acid h2a with k1=1.00x10-4 and k2=1.00x10-8. find the pH and concentrations of h2a,...
Consider the diprotic acid h2a with k1=1.00x10-4 and
k2=1.00x10-8. find the pH and concentrations of h2a, ha-, and a2-
in (a) 0.100 M H2A (b) 0.100 M NaHA (c) 0.100 M Na2A
a. What is the pH of a 0.25 M lactic acid (CH3(CH2)COOH) solution? Known: pKa =...
a. What is the pH of a 0.25 M lactic acid (CH3(CH2)COOH)
solution? Known: pKa = 3.85
I set the equation up as CH3(CH2)COOH –> CH3(CH2)COO- + H3O+. My
final answer I got was pH = 3.99.
b. Assume you had enough solid sodium lactate (NaCH3CH(OH)COO)
to cause the lactate ion (CH3CH(OH)COO-) concentration in the
solution to increase to 0.20 M. what is the pH of the solution
after the addition of sodium lactate to lactic acid?
I have no...
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
ADVERTISEMENT


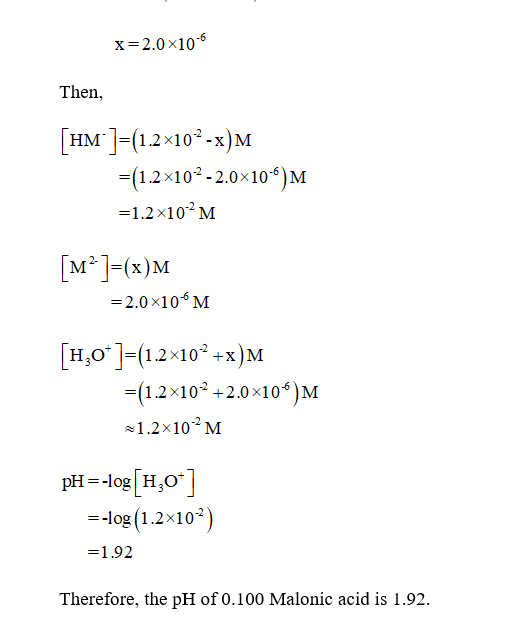
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 weeks ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 weeks ago