Question
In: Economics
The average resident has a demand for fresh oranges which is a linear function of the...
The average resident has a demand for fresh oranges which is a linear function of the prices of the three goods.
Q=4000 - 200 f + 100 c + 400 p
The subscript ‘f’ denoted fresh oranges, the subscript “c” OJ(orange juice) concentrate, and the subscript “p” peanuts.
Question: Assuming the price of OJ concentrate is fixed at $1 and fresh oranges’ price is fixed at $6, find the cross-price elasticity of demand for fresh oranges relative to peanuts for the average consumer when the price of peanuts is at $2, $8, and $10. What does that tell you about how the average consumer’s views fresh oranges compared to peanuts?
Solutions
Related Solutions
Exercise 1. Monopoly with Linear Costs facing a Linear Demand A monopoly has the cost function...
Exercise 1. Monopoly with Linear Costs facing a Linear
Demand
A monopoly has the cost function c(y)=10y+100, and is facing a
market demand D(p)=100-2p.
a) What is the inverse demand function, p(y)? Having profits
be π = p(y)∙y – c(y), what is the profit maximizing output level?
What is the corresponding market price?
b) Calculate the monopolist’s profit and producer surplus.
What is the consumer surplus? What is the deadweight loss?
c) The government imposes a production tax, tP=10, so...
Q1=40-0.5P1 is the demand function of good 1.Assume (i) That the linear demand function for another...
Q1=40-0.5P1 is the demand function of good
1.Assume
(i) That the linear demand function for another commodity good 2
intersects this function at the point P1=8
(ii) Show that the price elasticity of demand for good 1,ED1 is
half that of good 2 at the point of intersection and express the
demand function for good 2 in algebraic form
Suppose the market demand for a commodity is given by the download sloping linear demand function:...
Suppose the market demand for a commodity is given by the
download sloping linear demand function:
P(Q) = 3000 - 6Q
where P is a price and Q is quantity. Furthermore, suppose the
market supply curve is given by the equation:
P(Q) = 4Q
a) Calculate the equilibrium price, quantity, consumer surplus
and producer surplus.
b) Given the equilibrium price calculated above (say's P*),
suppose the government imposes a price floor given by P' > P*.
Pick any such P'...
The demand curve for a good is given by the linear function Qd = 60 -...
The demand curve for a good is given by the linear function Qd =
60 - P, where P is the price buyers pay for the good and Qd is the
quantity of the good demanded. The supply curve for the good is
given by the linear function Qs = 2P, where P is the price sellers
receive for the good and Qs is the quantity of the good supplied.
If a tax of $12 per unit is levied on...
The average consumer at a firm with market power has an inverse demand function of P...
The average consumer at a firm with market power has an inverse
demand function of P = 10 – Q, and the firm's cost function is TC =
2Q. Assume the firm engages in two-part pricing.
a. What is the optimal fixed fee to charge each consumer?
b. What is the optimal price to charge a consumer for each unit
purchased?
c. How do the firm’s profits arising from two-part pricing compare
to profits arising from the optimal single price?
Assuming the underlying demand for cases of O Be Joyful beverages is a linear function of...
Assuming the underlying demand for cases of O Be
Joyful beverages is a linear function of O Be Joyful
per-case price and state income (000s), use the data to obtain
least squares estimates for each state's beverage demand function
(three separate regressions). Report each estimated demand function
in your memo. Please feel free to attach summary results to your
memo. Your memo should stand alone, however, as communication. Do
not ask the reader to go to attachments to justify any...
Using a linear demand function and constant marginal cost function as illustration, explain the Cournot model...
Using a linear demand function and constant marginal cost
function as illustration, explain the Cournot model with product
differentiation. Derive the sufficient condition that all firms
have no incentive to cheat.
The average weight of a line of oranges is 16 g. Average juice content of the...
The
average weight of a line of oranges is 16 g. Average juice content
of the fruit is 28 ml. farmers one to select for smaller oranges
with a higher juice content. You know that narrow sense
heritability for size is 0.80 and for juice content is 0.60. A tree
producing oranges with an average weight of 12 g in juice content
of 30 A tree producing oranges with an average weight of 12 g in
juice content of 30ml...
Which of the following are linear transformations? Choose Linear Not Linear The function f:ℝ3→ℝ2 defined byf([x y...
Which of the following are linear transformations?
Choose Linear Not Linear The function f:ℝ3→ℝ2 defined
byf([x y z]^T)=[x−y 3y+z]^T.
Choose Linear Not Linear The function a:ℝ→ℝ such that
a(x)=(x−1)+(x−2)^2.
Choose Linear Not Linear The function
g:M2,2(ℝ)→M2,2(ℝ) defined by
g(A)=2A+[1 2
3 4] Here, M2,2(ℝ)) is the vector space of
2×2matrices with real entries.
Choose Linear Not Linear The function h:ℝ2→ℝ defined
by h([xy])=x^2−y^2.
1.Using a linear demand function and constant marginal cost function as illustration, explain the Cournot model...
1.Using a linear demand function and constant marginal cost
function as illustration, explain the Cournot model with product
differentiation. Derive the sufficient condition that all firms
have no incentive to cheat.
2.In the context of a static duopoly model explain why the
joint profit maximizing solution is unstable. Discuss some factors
that may engender collusion.
3.Using a quadratic net birth function, and linear total cost
and catch functions as illustration, derive the supply function of
fishery. Why this supply function...
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
ADVERTISEMENT

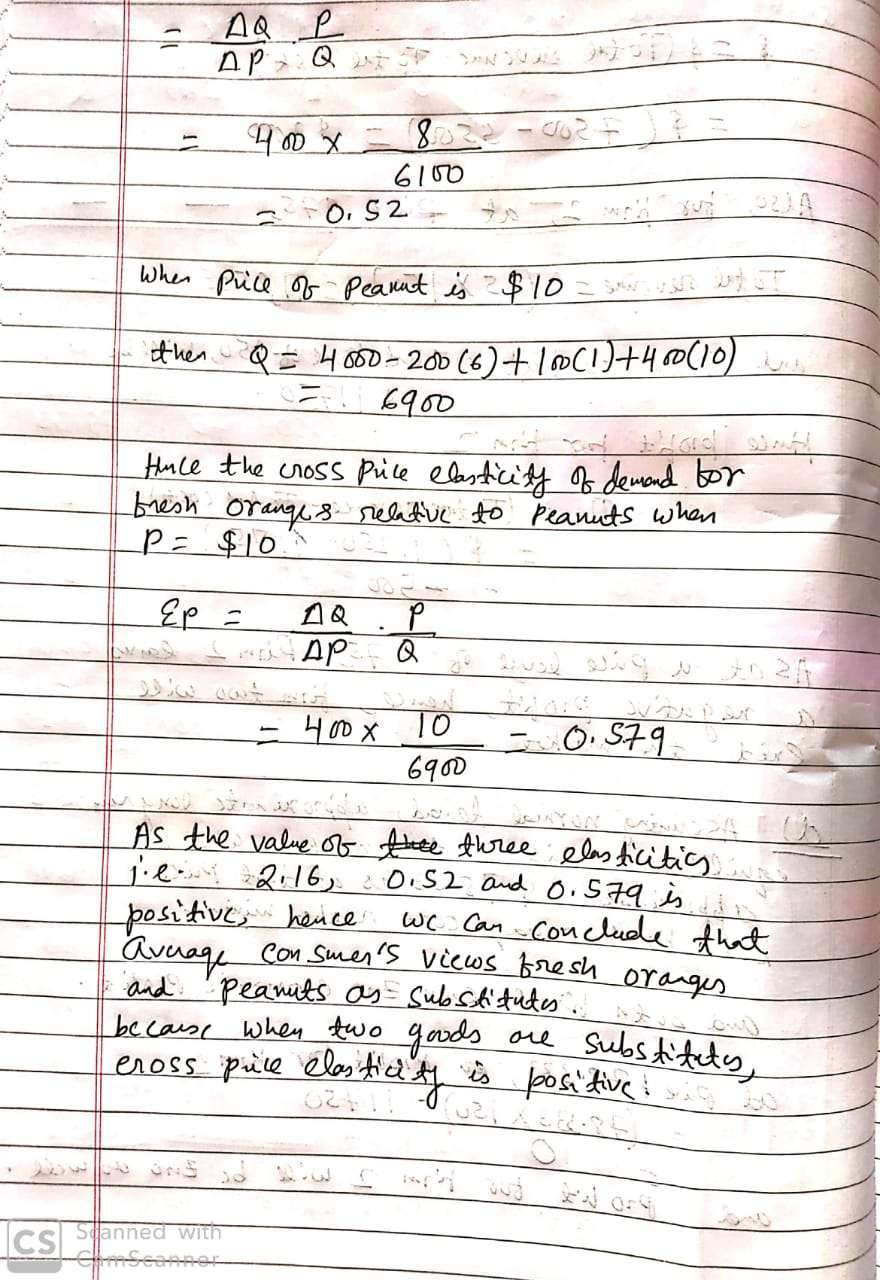
 Rahul Sunny answered 1 month ago
Rahul Sunny answered 1 month ago