Question
In: Biology
three autosomal genes (Z, E and T) in seahorses. Each gene sorts independently and each gene...
three autosomal genes (Z, E and T) in seahorses. Each gene sorts independently and each gene has two alleles. The Z allele forms zebra stripes which are completely dominant over no stripes, z. The E allele codes for crossed eyes which is dominant over uncrossed eyes, e. Lastly, the T allele codes for jellyfish-like tentacles,which are dominant over (t) squid-like tentacles. You have two parents that are completely heterozygous for all traits. What is the probability they have offspring that have:
a.Zebra Stripes, uncrossed eyes, and squid-like tentacles? ________________
b.All dominant traits?_______________________________
c.Have the genotype ZZeeTt?_________________________
d.True breeding for zebra stripes, crossed eyes and squid-like tentacles?______________
e.All dominant alleles or all recessive alleles?________________
f.The first progeny is a male with zebra stripes and the second progeny is a male with no stripes?(assume sex probabilities in zebrafish is similar to humans)
Solutions
Expert Solution
Three genes in seahorse. And each have an allele.
Z = zebra strip -------dominant
z = no strip ----recessive
E = crossed eye -------dominant
e = uncrossed eye ----recessive
T = jelly-fish like tentacles -------dominant
t = squid-like tentacles ----recessive
When parents with complete heterozygous for all traits cross. The progenies will be:
Heterozygous parents genotype = Zz Ee Tt for both parents
Perform the cross ---> ZzEeTt X ZzEeTt
We will use fork-line method to perform the cross. Punnett square can also be made but it's a complex for more number of genes.
Gametes for Zz X Zz
| Z | z | |
| Z | ZZ | Zz |
| z | Zz | zz |
1/4 = ZZ ; 2/4 or 1/2= Zz ; 1/4 = zz
Gametes for Ee X Ee
| E | e | |
| E | EE | Ee |
| e | Ee | ee |
1/4 = EE ; 2/4 or 1/2 = Ee ; 1/4 = ee
Gametes for Tt X Tt
| T | t | |
| T | TT | Tt |
| t | Tt | tt |
1/4 = TT ; 2/4 or 1/2 = Tt ; 1/4 = Tt
Cross is as in image :
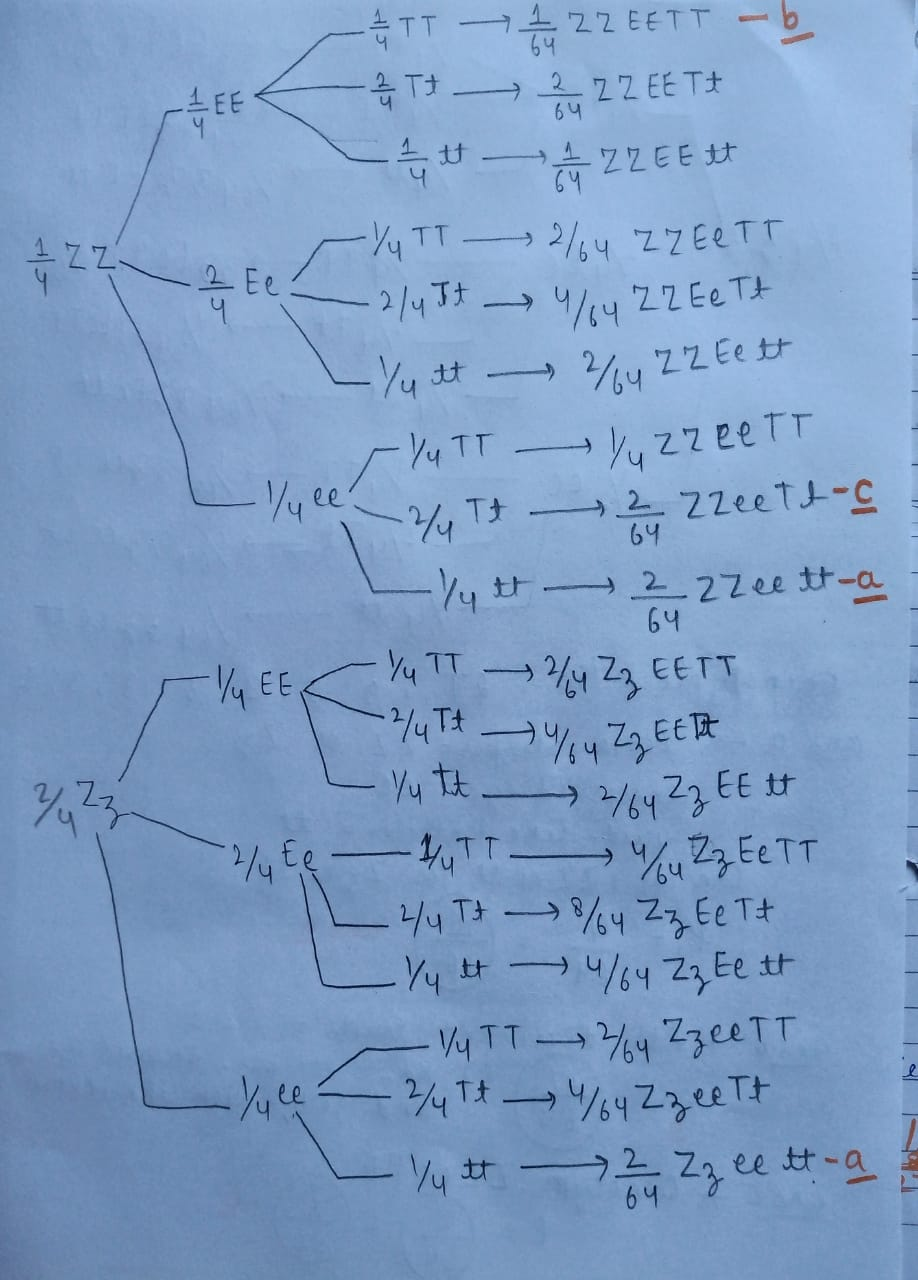

Phenotypic ratio = 27:9:9:9:3:3:3:1
Ans d) true breeding for Zebra stripes, crossed eyes and squid-like tentacles. P = 9/64
Ans e) all dominant allele = 1/64
All recessive allele = 1/64
Thank you...
Expect a ???...
Related Solutions
The genes for A, B, C and E assort independently. If a plant with the genotype...
The genes for A, B, C and E assort independently. If a plant with the genotype...
Drosophila has three linked autosomal genes that determine different traits. These genes are black (b), vestigial...
Hey. Given C = {z | z = z(t) = 10*e^(it), 0 <= t <= 2...
You have three genes on the same chromosome - A, B and C. Each gene has...
You have three genes on the same chromosome - A, B and C. Each gene has...
You have three genes on the same chromosome - A, B and C. Each gene has...
Three genes in fruit flies affect a particular trait, and one dominant allele of each gene...
You are a researcher who is interested in three genes in drosophila: The a gene, the...
You are a researcher who is interested in three genes in drosophila: The a gene, the...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 gladiator answered 1 month ago
gladiator answered 1 month ago