Question
In: Physics
A child on a sled is travelling a total distance of 93 m down a dirt...
A child on a sled is travelling a total distance of 93 m down a dirt hill with an angle of 30 degrees from the horizontal from the top of the hill. The mass of the child and sled is 65 kg. The initial velocity is zero and the final velocity is 5.0 m/s. (a) What is the time it takes to travel down the hill? (b) What is the acceleration down the hill? (c) What is the force of friction? (d) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction?
Solutions
Expert Solution
Gravitational acceleration = g = 9.81 m/s2
Angle of the slope =  =
30o
=
30o
Length of the slope = L = 93 m
Height of the slope = H
H = LSin
H = (93)Sin30
H = 46.5 m
Mass of the child = m = 65 kg
Initial velocity of the child at the top of the hill = V1 = 0 m/s
Final velocity of the child at the bottom of the hill = V2 = 5 m/s
Friction force acting on the sled = f
The initial potential energy is converted into kinetic energy plus the work done against friction.
mgH = mV22/2 + fL
(65)(9.81)(46.5) = (65)(5)2/2 + f(93)
f = 310.09 N
Coefficient of kinetic friction = 
Acceleration of the child down the hill = a
Time taken to travel down the hill = T
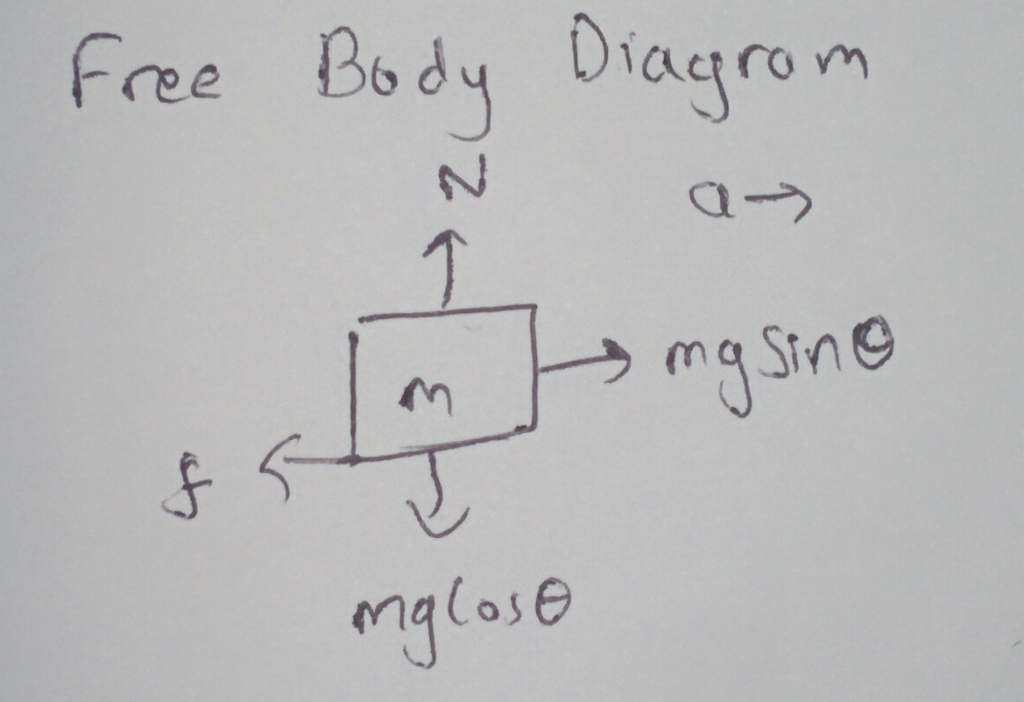
From the free body diagram,
mgCos = N
= N
f =  N
N
f =  mgCos
mgCos
310.09 =  (65)(9.81)Cos(30)
(65)(9.81)Cos(30)
 = 0.561
= 0.561
ma = mgSin - f
- f
(65)a = (65)(9.81)Sin(30) - 310.09
a = 0.134 m/s2
V2 = V1 + aT
5 = 0 + (0.134)T
T = 37.31 sec
a) Time taken to travel down the hill = 37.31 sec
b) Acceleration down the hill = 0.134 m/s2
c) Force of friction = 310.09 N
d) Coefficient of friction = 0.561
Related Solutions
A dog in a weight-pulling competition tugs a 50-kg sled a distance of 5 m across...
Suppose a sled passenger with total mass 51 kg is pushed 26 m across the snow...
A sled slides without friction down a small, ice-covered hill. If the sled starts from rest...
A disk with m=4.4 kg and radius 14.1 cm rolls a distance 4.3 m down a...
A child on a sled starts from rest at the top of a 20.0° slope. 1)...
A child rides down the road on his bike at a speed 4.3 m/s with a...
A child slides down a hill on a toboggan with an acceleration of 1.5 m/s2. Part...
A sled and rider have a total mass of 49.6 kg. They are on a snowy...
What would be the difference in stopping sight distance for two vehicles, each travelling at 65...
1a. An unidentified flying object (UFO) is observed to travel a total distance of 46000 m,...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 genius_generous answered 2 months ago
genius_generous answered 2 months ago