Question
In: Computer Science
In C++ I just need a MAIN that uses the steps and uses the functions and...
In C++ I just need a MAIN that uses the steps and uses the functions and class given below.
Implement the BinarySearchTree ADT in a file BinarySearchTree.h exactly as shown below.
// BinarySearchTree.h
// after Mark A. Weiss, Chapter 4, Dr. Kerstin Voigt
#ifndef BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_H
#define BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_H
#include
#include
using namespace std;
template
class BinarySearchTree
{
public:
BinarySearchTree( ) : root{ nullptr }
{
}
~BinarySearchTree( )
{
makeEmpty();
}
const C & findMin( ) const
{
assert(!isEmpty());
return findMin( root )->element;
}
const C & findMax( ) const
{
assert(!isEmpty());
return findMax( root )->element;
}
bool contains( const C & x ) const
{
return contains( x, root );
}
bool isEmpty( ) const
{
return root == nullptr;
}
void printTree( ) const
{
if( isEmpty( ) )
cout << "Empty tree" << endl;
else
printTree( root );
}
void makeEmpty( )
{
makeEmpty( root );
}
void insert( const C & x )
{
insert( x, root );
}
void remove( const C & x )
{
remove( x, root );
}
private:
struct BinaryNode
{
C element;
BinaryNode* left;
BinaryNode* right;
BinaryNode( const C & theElement, BinaryNode* lt, BinaryNode* rt )
: element{ theElement }, left{ lt }, right{ rt } { }
};
BinaryNode* root;
// Internal method to insert into a subtree.
// x is the item to insert.
// t is the node that roots the subtree.
// Set the new root of the subtree.
void insert( const C & x, BinaryNode* & t )
{
if( t == nullptr )
t = new BinaryNode{ x, nullptr, nullptr };
else if( x < t->element )
insert( x, t->left );
else if( t->element < x )
insert( x, t->right );
else
; // Duplicate; do nothing
}
// Internal method to remove from a subtree.
// x is the item to remove.
// t is the node that roots the subtree.
// Set the new root of the subtree.
void remove( const C & x, BinaryNode* & t )
{
if( t == nullptr )
return; // Item not found; do nothing
if( x < t->element )
remove( x, t->left );
else if( t->element < x )
remove( x, t->right );
else if( t->left != nullptr && t->right != nullptr ) // Two children
{
t->element = findMin( t->right )->element;
remove( t->element, t->right );
}
else
{
BinaryNode* oldNode = t;
t = ( t->left != nullptr ) ? t->left : t->right;
delete oldNode;
}
}
// Internal method to find the smallest item in a subtree t.
// Return node containing the smallest item.
BinaryNode* findMin( BinaryNode* t ) const
{
if( t == nullptr )
return nullptr;
if( t->left == nullptr )
return t;
return findMin( t->left );
}
// Internal method to find the largest item in a subtree t.
// Return node containing the largest item.
BinaryNode* findMax( BinaryNode* t ) const
{
if( t != nullptr )
while( t->right != nullptr )
t = t->right;
return t;
}
// Internal method to test if an item is in a subtree.
// x is item to search for.
// t is the node that roots the subtree.
bool contains( const C & x, BinaryNode* t ) const
{
if( t == nullptr )
return false;
else if( x < t->element )
return contains( x, t->left );
else if( t->element < x )
return contains( x, t->right );
else
return true; // Match
}
void makeEmpty( BinaryNode* & t )
{
if( t != nullptr )
{
makeEmpty( t->left );
makeEmpty( t->right );
delete t;
}
t = nullptr;
}
void printTree( BinaryNode* t) const
{
if( t != nullptr )
{
printTree( t->left);
cout << t->element << " - ";
printTree( t->right);
}
}
};
#endif
:Program your own file lab07.cpp in which your main() function will test the new data structure.
- The main function is contained in the file lab07.cpp.
- Declare an instance of BinarySearchTree (short: BST) suitable to hold integer values.
- Prompt user to enter a random sequence of integer values, insert these values into the data structure (the entered values should NOT be in sorted order).
- Call the printTree() member function in order to print out the values of the BST structure.
- Prompt user to enter a random sequence of integer values, remove these values from your BST. Print out the reduced BST.
- Add the following member function in your BinarySearchTree
class template.
public: void printInternal() { print_Internal(root,0); } private: void printInternal(BinaryNode* t, int offset) { if (t == nullptr) return; for(int i = 1; i <= offset; i++) cout << "..."; cout << t->element << endl; printInternal(t->left, offset + 1); printInternal(t->right, offset + 1); } - Go back to your program lab07.cpp and call printInternal. Compile and run your program, and see what you get.
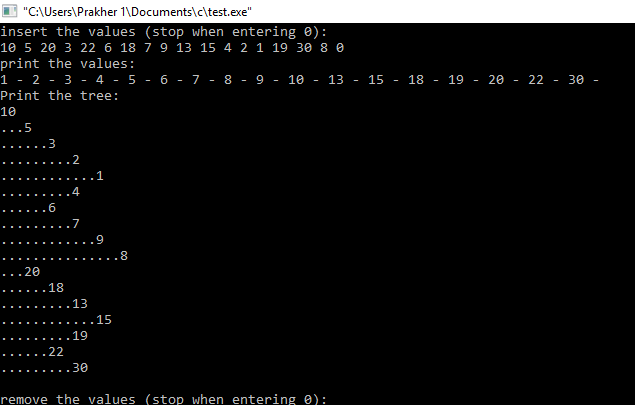
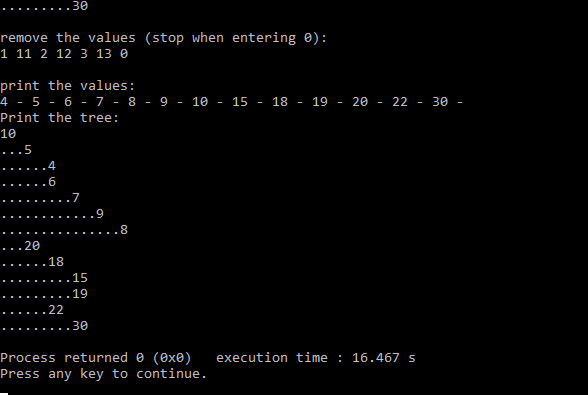
The expected result:
insert the values (stop when entering 0): 10 5 20 3 22 6 18 7 9 13 15 4 2 1 19 30 8 0 print the values: 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 - 9 - 10 - 13 - 15 - 18 - 19 - 20 - 22 - 30 - Print the tree: 10 ...5 ......3 .........2 ............1 .........4 ......6 .........7 ............9 ...............8 ...20 ......18 .........13 ............15 .........19 ......22 .........30 remove the values (stop when entering 0): 1 11 2 12 3 13 0 print the values: 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 - 9 - 10 - 15 - 18 - 19 - 20 - 22 - 30 - Print the tree: 10 ...5 ......4 ......6 .........7 ............9 ...............8 ...20 ......18 .........15 .........19 ......22 .........30
Solutions
Expert Solution
Below is the C++ code I hope that i have provided sufficient comments for your better understanding Note that I have done proper indentation but this code is automatically left alligned on this interface
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include "BinarySearch.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
BinarySearchTree <int>tree;
string s,num;
stringstream ss;
int temp;
cout<<"insert the values (stop when
entering 0):\n";
getline(cin,s); //Take input in string
format
int prev=-1,ind=-1;
while(1)
{
prev=ind;
ind=s.find(" ",prev+1);
//find index of next space
if(ind==-1) //we reached
last word
break; //exit from loop
num=s.substr(prev+1,ind-prev-1); //num contains number in string
format
//convert num from
string to integer
ss<<num;
ss>>temp;
ss.clear();
tree.insert(temp); //add
number to tree
}
cout<<"print the values:\n";
tree.printTree();
cout<<"\nPrint the tree:\n";
tree.printInternal();
cout<<"\nremove the values (stop when
entering 0):\n";
getline(cin,s); //Take input in string
format
prev=-1,ind=-1;
while(1)
{
prev=ind;
ind=s.find(" ",prev+1);
//find index of next space
if(ind==-1) //we reached
last word
break; //exit from loop
num=s.substr(prev+1,ind-prev-1); //num contains number in string
format
//convert num from
string to integer
ss<<num;
ss>>temp;
ss.clear();
tree.remove(temp); //add
number to tree
}
cout<<"\nprint the values:\n";
tree.printTree();
cout<<"\nPrint the tree:\n";
tree.printInternal();
return 0;
}
Below is the screenshot of output
I have tried to explain it in very simple language and I hope that i have answered your question satisfactorily.Leave doubts in comment section if any.
Related Solutions
In C++ prototype functions above "main" and define them below "main"; Write a program that uses...
IN C++, ONE FILE Also include the main class that just runs these functions, thanks. Write...
(i just need an answer for question 4) (i just need an answer for just question...
C++ Need to add the following functions to my templatized class linked list. (main is already...
IN JAVA PLEASE ASAP !!! I just need the main and mergesort function Ask the user...
I need to know the steps of solution for part (b,c,d) I have been trying for...
Assume the following functions have already been defined, write a main() using c++ that uses them...
i just need the national saving rate for the last two, b and c, I answered...
Can someone explain a,b and c? The answers are correct I believe but I just need...
Write this in java please. I use Eclipse Write the following two functions. main doesnt need...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 venereology answered 3 months ago
venereology answered 3 months ago