Question
In: Biology
There are two properties that affect the conduction speed of an action potential along an axon
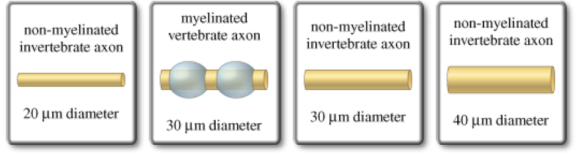
There are two properties that affect the conduction speed of an action potential along an axon: the axon's diameter and whether or not the axon is myelinated. Rank the axons from slowest to fastest conduction speed. If two axons have the same conduction speed, place one on top of the other.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Fastest - myelinated vertebrate axon 30μm
Next - non-myelinated invertebrate axon - 40μm
Next - non-myelinated invertebrate axon - 30μm
Slowest - non-myelinated invertebrate axon -20μm.
The size of the axon and myelin insulation increase the speed of conduction of action potential.
Related Solutions
Describe how an action potential propagates along a myelinated and an unmyelinated axon, including how the...
Describe how an action potential propagates along a myelinated
and an unmyelinated axon, including how the potential is spread
along the membrane. How are these two processes similar and how are
they different? What two benefits do myelinated axons have over
unmyelinated ones? Provide one way in which a myelinated axon is
similar to an electrical wire and one way in which an axon is
different than a wire. Why does multiple sclerosis (MS) prevent
transmission in myelinated axons (that...
22. Choose the correct sequence of action potential conduction along the conductive tissues of the heart:...
22. Choose the correct sequence of action potential
conduction along the conductive tissues of the heart:
a. SA node → AV node →
Bundle of His → Purkinje fibers → Bundle branches
b. SA node → AV node →
Bundle of His → Bundle branches → Purkinje fibers
c. SA node → AV node →
Bundle branches → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibers
d. SA node → AV node →
Purkinje fibers → Bundle of His → Bundle branches...
Explain the need for saltatory conduction and how myelination and axon diameter affect rate of conduction...
Explain the need for saltatory conduction and how myelination
and axon diameter affect rate of conduction – you can do this as an
illustration. Make sure in your answer you include: axon, axon
hillock, axon terminal, original action potential, new action
potential, Schwann cell, myelin, node of Ranvier, depolarization,
refractory DO NOT DEFINE THESE TERMS INDIVIDUALLY
please type the answer.
When one action potential is traveling along an unmyelinated axon from cell body side and another...
When one action potential is traveling along an unmyelinated
axon from cell body side and another action potential is traveling
along the axon from synaptic terminal side, these two action
potentials are going to collide with each other at the center of
the axon. What is going to happen to these action potentials after
the collision?
The speed of signal propagation along an axon strongly depends on its two characteristics or parameters....
The speed of signal propagation along an axon strongly depends
on its two characteristics or parameters. What are they?
A impulse conduction, explain how a nerve impulse was initiated and transmitted along the axon. Illustrate...
A impulse conduction, explain how a nerve impulse was initiated
and transmitted along the axon. Illustrate answer with an action
potential diagram to explain the membrane potential changes due to
movement of ions in the gated channels.
Describe the importance of voltage-gated channels in the conduction of an action potential.
Describe the importance of voltage-gated channels in the conduction
of an action potential.
List the sequence of action potential generation of the heart's intrinsic conduction system:
List the sequence of action potential generation of the heart's
intrinsic conduction system:
1. Which of the following DOES NOT influence the conduction velocity of an action potential A)...
1. Which of the following DOES NOT influence the conduction
velocity of an action potential
A)
Diameter of the axon
B)
Permeability of the axon
C)
Density of Ca channels
D)
Myelination (answer not D or A)
2. The relationship of an action potential (AP) to the stimulus
that generates it is best described as:
A)
Stimulus intensity is correlated with the frequency of the
AP
B)
Stimulus intensity is proportional to the amplitude of the
AP
C)
Stimulus intensity...
Describe how an action potential is propagated through an axon, and how neurotransmitters are released in...
Describe how an action potential is propagated through an axon,
and how neurotransmitters are released in response to the action
potential reaching the synaptic terminal
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
ADVERTISEMENT
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago