Question
In: Biology
Cells require a constant exchange of solutes (ions and small molecules) with the outside of the cell.
Cells require a constant exchange of solutes (ions and small molecules) with the outside of the cell. Many of these solutes undergo passive transport across the membrane. Passive transport occurs without the input of cellular energy. Some solutes are transported into the cell while others are transported out of the cell.
Part A - Diffusion
All molecules have energy that causes thermal motion. One result of thermal motion is diffusion: the tendency of substances to spread out evenly in the available space. Although the motion of each individual molecule is random, there can be directional motion of an entire population of molecules. Consider a chamber containing two different types of dye molecules, purple and orange. The chamber is divided into two compartments (A and B) by a membrane that is permeable to both types of dye. Initially (left image), the concentration of the orange dye is greater on side \(\mathrm{A},\) and the concentration of the purple dye is greater on side B. With time, the dye molecules diffuse to a final, equilibrium state (right image) where they are evenly distributed throughout the chamber.
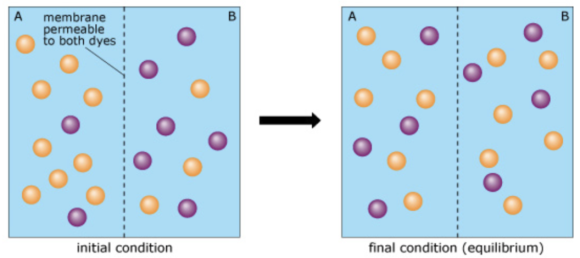
Drag the labels onto the table to indicate when each statement is true. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all.

Part B - Permeability of the lipid bilayer
Some solutes are able to pass directly through the lipid bilayer of a plasma membrane, whereas other solutes require a transport protein or other mechanism to cross between the inside and the outside of a cell. The fact that the plasma membrane is permeable to some solutes but not others is what is referred to as selective permeability.
Which of the following molecules can cross the lipid bilayer of a membrane directly, without a transport protein or other mechanism? Select all that apply.
- ions
- oxygen
- water
- proteins
- sucrose
- carbon dioxide
- lipids
Part \(\mathrm{C}\) - Facilitated diffusion via channels and carrier proteins
The majority of solutes that diffuse across the plasma membrane cannot move directly through the lipid bilayer. The passive movement of such solutes (down their concentration gradients without the input of cellular energy) requires the presence of specific transport proteins, either channels or carrier proteins. Diffusion through a transport protein in the plasma membrane is called facilitated diffusion.
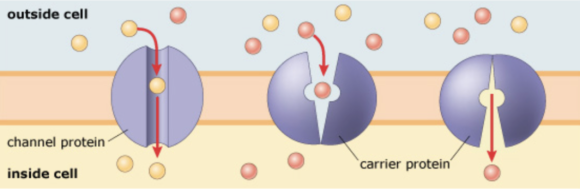
Sort the phrases into the appropriate bins depending on whether they are true only for channels, true only for carrier proteins, or true for both channels and carriers.
Solutions
Related Solutions
How do protein pumps move ions and small molecules across a cell membrane?
If a cell has less concentration of solutes inside than outside, it is in a(n) ___________...
Tight junctions: a. allow communication between cells and an exchange of ions b. cause cell membranes...
In most resting cells, the concentration of sodium ions is higher outside of cells compared with...
Which cell-cell connection allows for the formation of a gradient of 2nd messengers, small molecules or...
in autorthythmic cells, influx of these two ions bring the cell threahold? A) sodium B) calcium...
Living cells "pump" singly ionized sodium ions, Na+, from the inside of the cell to the...
18.) Molecules (like adrenaline or epinephrine) that signal from outside the cell use receptors because: a....
Animal cells generally have a higher concentration of Na+ outside of the cell than inside the...
1. Specific extracellular signal molecules require a cell surface receptor. What about the chemistry of these...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...

 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago