Question
In: Chemistry
Reaction of HBr with 3-methylcyclohexene yields a mixture of four products
Reaction of HBr with 3-methylcyclohexene yields a mixture of four products: cis-and trans-1-bromo-3-methylcyclohexane and cis-and trans-1-bromo-2-methylcyclohexane. The analogous reaction of HBr with 3-bromocyclohexene yields trans-1, 2-dibromocyclohexane as the soleproduct.
Draw structures of the possible intermediates, and then explain why only a single product is formed in this reaction.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Given chemical reactions,
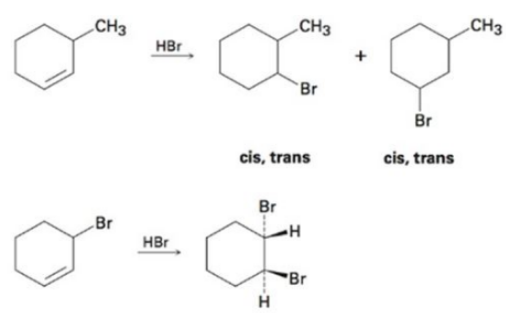
Reaction of HBr with 3-methylcyclohexene,
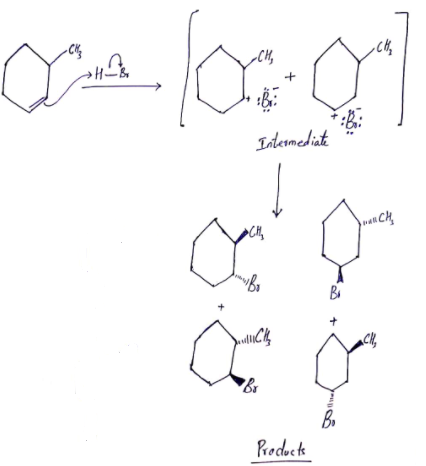
The attack of the electrons of the double bond in 3-methyl cyclohexene on the positively polarized hydrogen of HBr yields two carbocations of almost equal stabilities. These carbocations being planar can be attacked by the bromide ion from top to bottom faces to yield four different products.
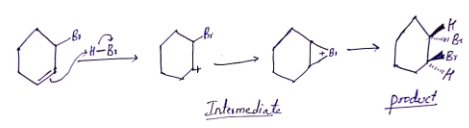
Reaction of HBr with 3-bromocyclohexene,
The attack of the electrons of the double bond in 3-bromocyclohexene on the positively polarized hydrogen of HBr yields two carbocations but one carbocation is unstable. This led to the formation of cyclic bromonium ions. then bromide ion attacked from opposite side leads to the formation of trans 1,2 di-bromocyclohexane.
Answers can be found in the Explanation section.
Related Solutions
Products: 1-methylcyclohexene, 3-methylcyclohexene, methylenecyclohexane 1a) Which kind of mechanism can better account for the product mixture...
2 step reaction: 1-methylcyclohexene to 1,6-heptandiol
What is the expected alkyl bromide product from reaction: 3-methyl-1-butanol with HBr
1-Write the reaction of acidic water with the followings: a-1-Methylcyclopentene b-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexene c-isobutene 2.Draw and name a...
LP 3. A manufacturer wants to maximize the profit of two products. Product X yields a...
3) A reaction vessel at 27 ∘C contains a mixture of SO2(P= 3.10 atm ) and...
In a reaction involving the ionization of acetone, the following reaction reaction mixture was used: 5.00mL...
Reaction: H2O + C3H7Br --- > C3H7OH + HBr Table 1.0 Reaction Trial Grams of H2O Grams...
What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? HBr
A.) The equilibrium constant for the reaction A(g) ⇌ B(g) is 102 . A reaction mixture...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
 DogeShow answered 4 years ago
DogeShow answered 4 years ago