Question
In: Civil Engineering
Determine the lightest W14 section to carry LRFD factored compression load of 900 kips and LRFD...
Determine the lightest W14 section to carry LRFD factored compression load of 900 kips and LRFD factored strong axis moment of 600 foot-kips.
Solutions
Expert Solution
LRFD solution:
Step 1:
Pu=900 Kips
Mux=600 ft-kips
Muy=0
Step 2:
Assume a length of 16 ft for the column as it is not given
Start with a W14 sectionwith Pu/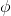 Pn>0.2
and less than 1, try with a W14x99 Section
Pn>0.2
and less than 1, try with a W14x99 Section
Pu/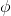 Pn=900/1080=0.833
Pn=900/1080=0.833
p=1/1080=9.25x10-4
bx=8/9Mcx
bx=8/9(646 ft-kips)
bx=0.001357
Step 3:
Check for stability
pPu+bxMux+byMuy
=9.25x10-4x900+0.001357x600+0
=0.833+0.81=1.643>1, so this section will not be adequate, Try for another section
Step 4:
Try with a W14X120 section
p=1/1309=7.63x10-4
Mx=8/9x795=0.0011
Check for stability
pPu+bxMux+byMuy
=7.63x10-4x900+0.0011x600=1.347>1
so this section will not be adequate, Try for another section
Step 5:
Select a W14X132 section
p=1446 Kips
pPu=900/1446=0.62
bx=0.001
pPu+bxMux+byMuy
=900/1446+0.001x600
=1.22>1, Not Good
Step 6:
Consider a W14X159 section
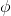 Pn=1777
Kips
Pn=1777
Kips
p=1/1777=5.62x10-4
pPu=0.5
bx=8/9Mcx
bx=8/9x1080
bx=8.14x10-4
pPu+bxMux+byMuy
=0.5+8.14x10-4x600
=0.98<1
The lightest section which can carry the given load and moment is W14X159 section
Related Solutions
Determine the lightest section W14 available to carry a service dead load of 150 kips and...
Select the lightest W14 section to carry an axial compression of P = 100 kips dead...
1) Select the lightest section to support a axial load (DL=700 kips y LL= 300 kips)....
Design a circular column, using approximate methods, for a factored load of 80 Kips and a...
Select double angle tension member to resist a factored load of 100 kips. Member is connected...
For bending only, determine the lightest-weight W-shape to carry a uniform dead load of 4.5 kip/ft...
Design a short square tied column to carry a factored axial load of 1300k and a...
Design a short square tied column to carry a factored axial load of 1300k and a...
Select the lightest W section to support a uniform distributed load WD=0.5 kip/ft, W=1.4 kip/ft in...
Q4: Experiments were conducted to determine the safe buckling load on columns with T-section 100 mm...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Ally Wells answered 2 years ago
Ally Wells answered 2 years ago