Question
In: Physics
A) Describe what you think will happen if two cars of equal mass collide with each...
Solutions
Expert Solution
The conservation of the total momentum demands that the total momentum before the collision is the same as the total momentum after the collision, and is expressed by the equation

Likewise, the conservation of the total kinetic energy is expressed by the equation

These equations may be solved directly to find vi when ui are known or vice versa. An alternative solution is to first change the frame of reference such that one of the known velocities is zero. The unknown velocities in the new frame of reference can then be determined and followed by a conversion back to the original frame of reference to reach the same result. Once one of the unknown velocities is determined, the other can be found by symmetry.
Solving these simultaneous equations for vi we get:

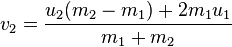
or

 .
.
No it does not matter what their speeds are.
B)
| Collisions in which the kinetic energy is also conserved, i.e. in which the kinetic energy just after the collision equals the kinetic energy just before the collision, are called elastic collision. In these collisions no ordered energy is converted into thermal energy. Collisions in which the kinetic energy is not conserved, i.e. in which some ordered energy is converted into internal energy, are called inelastic collisions. If the two objects stick together after the collision and move with a common velocity vf, then the collision is said to be perfectly inelastic. | |
Note: In collisions between two isolated objects momentum is always conserved. Kinetic energy is only conserved in elastic collisions. We always have m1v1i +
m2v2i =
m1v1f +
m2v2f. |
|
Related Solutions
Two cars collide at an intersection. Car A, with a mass of 2000 kg , is...
Two cars collide at an intersection. Car A, with a mass of 2000 kg , is...
Two cars collide at an intersection. Car A, with a mass of 1900 kg , is...
Two cars collide at an intersection. Car A, with a mass of 1900 kg , is...
For each event, describe what you think would happen to the premium for both an at-the-...
Two asteroids of equal mass in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter collide with a...
For each event, describe what you think would happen to the premium for both an at-the-money...
For each event, describe what you think would happen to the premium for both an at-the-money...
Given the mass of two blocks that collide, and the velocities of each block before and...
When two objects collide, the impulse each delivers to the other is equal and opposite. But...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 genius_generous answered 2 years ago
genius_generous answered 2 years ago