Question
In: Physics
A 510-turn solenoid has a radius of 8.00 mm and an overall length of 14.0 cm....
A 510-turn solenoid has a radius of 8.00 mm and an overall length of 14.0 cm. (a) What is its inductance? (b) If the solenoid is connected in series with a 2.50-?(ohm electrical symbol) resistor and a battery, what is the time constant of the circuit?
Solutions
Expert Solution
Step 1:
Definition:
Inductance: is the property of a conductor by which a change in current flowing through it induces (creates) a voltage (electromotive force) in both the conductor itself (self-inductance), and in any nearby conductors (mutual inductance).
These effects are derived from two fundamental observations of physics: First, that a steady current creates a steady magnetic field (Oersted's law), and second, that a time-varying magnetic field induces voltage in nearby conductors (Faraday's law of induction). According to Lenz's law, a changing electric current through a circuit that contains inductance induces a proportional voltage, which opposes the change in current (self-inductance). The varying field in this circuit may also induce an e.m.f. in neighbouring circuits (mutual inductance).
Step 2:
A solenoid is a long, thin coil,
i.e. a coil whose length is much greater than the diameter. Under
these conditions, and without any magnetic material used, the
magnetic flux density 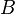 within the coil is practically constant and is given by
within the coil is practically constant and is given by

where 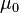 is the magnetic constant,
is the magnetic constant, 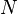 the number of turns,
the number of turns, 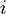 the current and
the current and 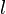 the length of the coil. Ignoring end effects, the total magnetic
flux through the coil is obtained by multiplying the flux density
the length of the coil. Ignoring end effects, the total magnetic
flux through the coil is obtained by multiplying the flux density
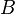 by the cross-section area
by the cross-section area  :
:

When this is combined with the definition of inductance,

it follows that the inductance of a solenoid is given by:

Step 3:
(a) What is its inductance?
ANSWERS:
Carry 14 centimeters to meters


Carry 8 milimeters to meters





(b) If the solenoid is connected in
series with a 2.50  (ohm electrical
symbol) resistor and a battery, what is the time constant of the
circuit?
(ohm electrical
symbol) resistor and a battery, what is the time constant of the
circuit?
The time constant for circuit R-L is:


If you have any questions please let me know in the comments
Related Solutions
A 320 turn solenoid with a length of 19.0 cm and a radius of 1.20 cm...
A solenoid of radius 3.5 cm has 800 turns and a length of 25 cm. (a)...
A solenoid of radius 3 cm, 2900 turns, and a length of 8 cm is carrying...
A 410-turn solenoid, 21 cm long, has a diameter of 4.0 cm . A 12-turn coil...
A 450-turn solenoid, 24 cm long, has a diameter of 2.2 cm . A 10-turn coil...
A 450-turn solenoid, 26 cm long, has a diameter of 2.1 cm . A 12-turn coil...
A solenoid has N=1000 turns, length l=20 cm, and radius r=1.0 cm. (a) What is its...
Question text Consider a long solenoid of length = 1m, radius = 3.0 cm and 800...
If the radius of a cylindrical resistor is 8.4 mm and its length is 4.6 cm,...
A wire with a radius R = .89 mm and length 45 cm is made of...
- C PROGRAMMIMG I want to check if my 2 input is a number or not all...
- In long paragraphs answer the questions below: Discuss the key components (where, when, what) and causes...
- Sinkal Co. was formed on January 1, 2018 as a wholly owned foreign subsidiary of a...
- Larry’s best friend, Garfield, owns a lasagna factory. Garfield’s financial skills are not very strong, so...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
 genius_generous answered 2 years ago
genius_generous answered 2 years ago