Question
In: Chemistry
Explain how the induced, orientation, and dipersion interactions trend between HCl, HBr, and HI. Why do...
Explain how the induced, orientation, and dipersion interactions trend between HCl, HBr, and HI. Why do the dipersion interactions increase from HCl to HI? Why do the orientation interactions decrease from HCl to HI? Why are induced interactions greatest in HCl and lowest in HI?
Solutions
Expert Solution
The first explanation of the attraction between noble gas atoms was given by Fritz London in 1930.[2][3][4] He used a quantum-mechanical theory based on second-order perturbation theory. The perturbation is the Coulomb interaction V between the electrons and nuclei of the two monomers (atoms or molecules) that constitute the dimer. The second-order perturbation expression of the interaction energy contains a sum over states. The states appearing in this sum are simple products of the stimulated electronic states of the monomers. Thus, no intermolecular antisymmetrization of the electronic states is included and the Pauli exclusion principle is only partially satisfied.
London developed the method perturbation V in a Taylor series in
 , where
, where 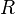 is the distance between the nuclear centers of mass of the
monomers.
is the distance between the nuclear centers of mass of the
monomers.
This Taylor expansion is known as the multipole expansion of V because the terms in this series can be regarded as energies of two interacting multipoles, one on each monomer. Substitution of the multipole-expanded form of V into the second-order energy yields an expression that resembles somewhat an expression describing the interaction between instantaneous multipoles (see the qualitative description above). Additionally, an approximation, named after Albrecht Uns
Related Solutions
Circle the weakest acid in each group. Explain why. a) HClO3 HClO2 HClO b) HI HBr...
Circle the weakest acid in each group. Explain why. a) HClO3 HClO2 HClO b) HI HBr...
Explain the differences between solidification cracking, HAZ cracking, hydrogen induced cracking, and lamellar cracking. Why is...
Reaction: 1 PbBr2 + 2 HCl --> 2 HBr + 1 PbCl2 How many moles of...
Describe the types of interactions that occur between species and explain how predation affects the population...
Describe the types of interactions that occur between species and explain how predation affects the population...
Physiology of Exercise: 1. Explain hormone receptor interactions. How do they work? 2. Explain protein to...
Explain why quantum numbers stop following the expected trend for elements at potassium, while they do...
Explain why preferences ≽ that are induced by a utility function are always complete, reflexive, and...
Explain the Difference between a simple trend model and a causal model
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 2 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 2 years ago