Question
In: Chemistry
Explain the concept of resonance using Lewis structure model and molecular orbital model
Explain the concept of resonance using Lewis structure model and molecular orbital model
Solutions
Expert Solution
In chemistry, resonance is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis structure.
A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical structures)
Example
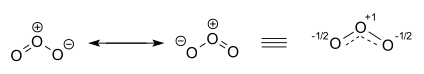
The ozone molecule is represented by two resonance structures. In reality the two terminal oxygen atoms are equivalent and the hybrid structure is drawn on the right with a charge of − 1⁄2 on both oxygen atoms and partial double bonds with a full and dashed line
Consider the Lewis structure of the carbonate ion, CO32-. The Lewis structure for this ion has a carbon-oxygen double bond, and two carbon-oxygen single bonds. Each of the singly bonded oxygen atoms bears a formal charge of 1-. But which of the three oxygens forms the double bond? There are three possibilities:
Concept of resonance through molecular orbital model
Molecular orbitals provide what initially looks like a very
different picture.
They are intrinsically delocalized descriptions, and much of the qualitative picture we get from resonance forms is tied up in the numerical results: MO energies, atomic charges.
However, the shapes of the HOMO (Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital) and the LU MO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) along with the ESP map provide a qualitiative presentation of molecular properties and reactivity. It helps to make some comparisons of the descriptions from both directions.

Note a couple things in the MO shapes: the HOMO is largest on
the nitrogen--the most reactive electrons are there (or, the pi
bond is polarized toward nitrogen). This corresponds to what the
right-hand resonance form describes.
The LU MO is oriented toward the carbon. Anything with electrons
will interact at this end of the pi bond.
The delocalization of the pi bond is consistent with the left-hand
resonance form: this molecule will have a barrier to rotation about
C-N (and this should be about 80 kcal/mol).
Because this molecule has a positive charge, the LU MO offers the
more relevant picture of reactivity: it will react with things that
have (at least partial) negative charge--and therefore
electrons--which will interact with the LUMO to form a new set of
MOs
Related Solutions
Molecular Orbital Theory 1.1 Which model, the Lewis electron dot structure or the MO energy level...
Benzene is a very stable compound. Explain why using resonance and molecular orbital theory. For each...
What is the Lewis Structure, valid resonance structures, electron geometry, molecular geometry, polarity, and hybridization of...
Molecular Orbital Theory -- Homodiatomics Use the molecular orbital model to fully describe the bonding in...
In which one of the following is the best Lewis structure a resonance structure? (central atoms...
Which one of the following will have a resonance structure as the best Lewis structure? SO3...
[6] (a) Explain the structure and spectra of hydrogenic atoms? (b) Explain the molecular orbital theory...
Molecular geometry of IF2^-1 and lewis structure?
Resonance structures are Lewis structures drawn for a molecule when more than one Lewis structure is...
3) for one resonance structure of a nitrate(NO3-) provide the: a) Lewis structure b) formal charge...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago