Question
In: Chemistry
Molecular geometry of IF2^-1 and lewis structure?
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
The problem is based on the concepts of VSEPR theory and Lewis structure. This is used to tell the geometry molecules taking electron pairs surrounding their central atoms into consideration. Both bond pairs and lone pairs are contributing to determining the geometry of molecules.
Fundamentals
There are certain rules for writing Lewis structure of a molecule. These rules are as follows:
1. First, draw the molecule's skeleton, keeping more electronegative atoms at the terminal position and less electronegative at the center.
2. Count the total number of valance electrons by taking the sum of each atom's valence electron.
3. Distribute electrons in such a way that the octet of every atom is complete.
4. Electrons that are not taking part in bonding are represented as dots and are known as lone pairs of that atom.
In \(\mathrm{IF}_{2}^{-}\), both iodine and fluorine belongs to the halogen family and have 7 electrons in the outermost valence shell. Since fluorine is more electronegative than iodine, iodine will be at the center. There are 7 valence electrons in iodine also 1 negative charge adds one more electron; thus, the total number of electrons surrounding iodine will be 8 as follows: ![]()
Two fluorine atoms can share 2 of the 8 electrons resulting \(s p^{3} d\) hybridization as follows:![]()
According to VSEPR theory, \(s p^{3} d\) hybridization corresponds to trigonal bipyramidal geometry (TBP), which is represented as follows: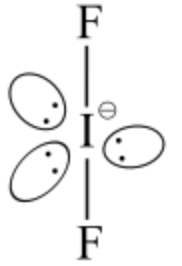
But molecular geometry describes the shape of the molecule, which is linear in this case because the effect of lone pairs cancels each other. Resultant molecular geometry is represented as follows:![]()
Molecular geometry of \(\mathrm{IF}_{2}^{-}\) is Linear
In \(\mathrm{IF}_{2}^{-},\) hybridization is \(s p^{3} d\) therefore, according to VSEPR theory geometry is trigonal bipyramidal. The cancellation of lone pairs' resultant shape of the molecule or molecular geometry is linear.
Draw the Lewis structure by showing lone pairs on each atom so that the octet of all the atoms is complete. Therefore, Lewis structure of \(\mathrm{IF}_{2}^{-}\) is as follows:
In the Lewis structure, atoms are arranged so that more electronegative atom is at the terminal position. Terminal atoms are arranged around the central atom to form bonds that can be single, double, or triple. Non-bonding electrons are represented as dots on atoms and are known as lone pairs of electrons.
Related Solutions
1. Draw the Lewis structure, determine the molecular geometry and electronic geometry, hybridization, and bond angles...
The Lewis structure for SF4 is shown. What is the electron-pair geometry and the molecular geometry...
what is I3- lewis structure and molecular geometry with bond angles?
What is the Lewis Dot Structure, hybridization, and molecular geometry of HBr?
For the molecules below, draw the Lewis structure, determine the electron groups geometry, the molecular geometry,...
Draw the lewis structure for ICl3 (iodine trichloride). What is the electron geometry and molecular geometry...
What is the Lewis Structure, valid resonance structures, electron geometry, molecular geometry, polarity, and hybridization of...
a) number of valence electrons, lewis structure, electron geometry, molecular geometry, bond angles, polar or non...
Write the best Lewis structure, and determine the molecular geometry, hybridization, and polarity for each of...
Hi, I need the Lewis Structure, the Molecular Geometry, and polarity of these compounds: CH2Cl2 BH3...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago