Question
In: Biology
Describe primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure and differentiate among the structures based on Stabilization by...
Describe primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure and differentiate among the structures based on
- Stabilization by intramolecular covalent bonds
- Stabilization by hydrogen bonds
- Stabilization by hydrophobic effect
- Function in binding ligand
- Regulation of function by allostery
Solutions
Expert Solution
Solution
- Primary Structure of Proteins - stabilized by
covalent interaction
Secondary Structure of Proteins- stabilized by hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding-electrostatic interactionThe primary structure is the sequence of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain. 20 different amino acids are found in proteins. The exact order of the amino acids in a specific protein is the primary sequence for that protein. 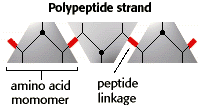
Protein secondary structure refers to regular, repeated patterns of folding of the protein backbone. The two most common folding patterns are the alpha helix and the beta sheet. Alpha Helix
In an alpha helix, the polypeptide backbone coils around an imaginary helix axis in clockwise direction.In this illustration, only the N-C-CO backbone atoms are shown. Note the coiling of the backbone around an imaginary axis down the center of the helix.

Beta sheet
In the beta sheet secondary structure, the polypeptide backbone is nearly fully extended. The R-groups (not shown) are alternately pointed above and then below the extended backbone.
Quaternary Structure of Proteins- are stabilized by hydrophobic interaction, hydrogen bonding
Many proteins are formed from more than one polypeptide chain. The quaternary structure describes the way in which the different subunits are packed together to form the overall structure of the protein. For example, the human hemoglobin molecule shown below is made of four subunits. -
Tertiary Structure of Proteins- are stabilized by salt bridges, disulphide bonds.
Tertiary structure refers to the overall folding of the entire polypeptide chain into a specific 3D shape. The tertiary structure of enzymes is often a compact, globular shape.
Related Solutions
Describe primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure and differentiate among the structures based on Stabilization by...
Describe primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure
and differentiate among the structures based on
Stabilization by intramolecular covalent bonds
Stabilization by hydrogen bonds
Stabilization by hydrophobic effect
Function in binding ligand
Regulation of function by allostery
Explain the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of the proteins.
Explain the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of the proteins.
Distinguish between, primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of a protein and provide a picture of...
Distinguish between, primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary
structures of a protein and provide a picture of each.
What is the difference between the primary, secondary, tertiary,
and quaternary structures within a protein? Could you also provide
pictures of these?
Talking about the protein "TITIN" Describe the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. Include sequences, images,...
Talking about the protein "TITIN"
Describe the primary, secondary, tertiary, and
quaternary structure. Include sequences, images,
secondary/tertiary/quaternary structures, and data from online
resources (properly citing them).
Biochemistry question: Describe the four levels of proteins structure (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary). Make sure...
Biochemistry question:
Describe the four levels of proteins structure (primary,
secondary, tertiary and quaternary). Make sure to describe the role
of non-covalent interactions involving the main chain or side
chains of the amino acids that form to stabilize the structure.
Compare and contrast the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures of Myoglobin(Mb) and Hemoglobin(Hb). You can...
Compare and contrast the primary, secondary, tertiary
and quaternary structures of Myoglobin(Mb) and Hemoglobin(Hb). You
can create a Venn diagram or do columns listing the similarities
and differences. BE SPECIFIC
Drag each label into the appropriate bin depending on whether it applies to primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure
Drag each label into the appropriate bin depending on whether it applies to primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure
Discuss the structure of β-keratin in detail by referring to the primary, secondary and tertiary structures...
Discuss the structure of β-keratin in detail by referring to the
primary, secondary and tertiary structures of the protein?
PLEASE TYPE OUT YOUR WORK 1A)Explain the difference between primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of...
PLEASE TYPE OUT YOUR WORK
1A)Explain the difference between primary, secondary,
tertiary, and quaternary structure of proteins, including
similarities and differences in hydrogen bonding of EACH STRUCTURE
WITH ONE ANOTHER
1 B) Distinguish between parallel and
antiparallel BETA-sheets
1C) which kinds of forces stabilize proteins at different levels
of structure, i.e., what stabilizes secondary structure, what
causes protein chains to fold into tertiary structure, what holds
oligomers together?
1D) which bonds can rotate in proteins, and WHAT ARE the names...
BIO&160 QUESTIONS: 3. Explain how the various levels of structure of proteins (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary)...
BIO&160 QUESTIONS:
3. Explain how the various levels of structure of proteins
(primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary) are responsible for
protein's very important role as enzymes.
In your answer, use the following terms correctly - induced fit,
substrate, active site.
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
ADVERTISEMENT


 gladiator answered 2 years ago
gladiator answered 2 years ago