Question
In: Biology
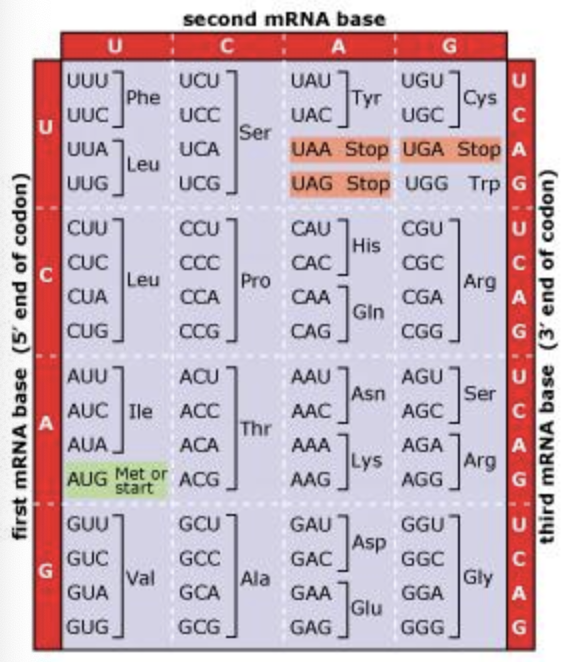
Based on the genetic code chart below, which of the following would be the result of this single base-pair substitution?
The diagram below shows an mRNA molecule that encodes a protein with 202 amino acids. The start and stop codons are highlighted, and a portion of the nucleotide sequence in the early part of the molecule is shown in detail. At position 35, a single base-pair substitution in the DNA has changed that would have been a uracil (U) in the mRNA to an adenine (A).
Based on the genetic code chart below, which of the following would be the result of this single base-pair substitution?
- A. a silent mutation (no change in the amino acid sequence of the protein)
- B. a frameshift mutation causing extensive change in the amino acid sequence of the protein
- C. a missense mutation causing a single amino acid change in the protein
- D. a frameshift mutation causing a single amino acid change in the protein
- E. a nonsense mutation resulting in early termination of translation
Solutions
Expert Solution
If we start from the beginning of the RNA and count nucleotides in groups of three (because this is how many nucleotides make a codon), we start with 1-2-3 which is AUG (the start codon), then 4-5-6, 7-8-9, and so on. Of course, we don't see many of these nucleotides on the diagram, but we know that 28-29-30 makes a codon (because, again, codons come in groups of three nucleotides). Then we have 31-32-33 (which is CUA), and then 34-35-36 (which is UUA). The middle U of UUA is substituted with an A. If we look at the codon diagram, UUA makes leucine, but UAA is the stop codon. Thus, because the RNA encoded more amino acids but the mutation switched the codon to read as a stop codon, this is early termination of protein synthesis and therefore a nonsense mutation.
The answer is E: it becomes a nonsense mutation.
Related Solutions
Based on the ion concentrations provided in the table below, which of the following would result...
13. A) A change to a single base pair in the sequence of a DNA molecule...
1) List four outcomes that can result from a Base Substitution in the middle of a...
In a particular gene in mice, a single base pair change from GC to an AT...
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disease resulting from a single amino acid substitution in the...
Use the genetic code and the table that indicates the base pairing that occurs according to...
Based on the chart below, prepare the following: Prepare the following: -An income statement for 2015...
Which of the following is/are a conjugate acid-base pair? HCN and CN- HNO3 and NO3- HClO4...
A) Six different mutations were derived from base pair substitutions at a single codon. In this...
Which of the following would be the result of increasing the temperature at which GC is...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago