Question
In: Physics
A rock is suspended by a light string. When the rock is in air, the tension in the string is 39.2 N.
A rock is suspended by a light string. When the rock is in air, the tension in the string is 39.2 N. When the rock is totally immersed in water, the tension is 28.4 N. When the rock is totally immersed in an unknown liquid, the tension is 18.6 N. What is the Density of the unknown liquid.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
The concepts used to solve this problem are newton's second law, tension force, and Archimedes principle. First, find the rock's real weight by equating the tension of string in air and force using Newton's second law. Then find the rock's volume by equating the calculated tension in water and subtracted buoyant force from the mass of the rock using the Archimedes principle. Finally, find the density of an unknown liquid by equating the liquid's calculated tension and subtracting the buoyant force of liquid from the rock's mass using Archimedes principle.
Fundamentals
A body experiences an upward force when it is immersed in a liquid. This force will be equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body when it is partially or fully immersed in the liquid. This upward force exerted by the fluid on the body is known as the Buoyant force. When a body is fully immersed in a liquid, the displaced fluid volume is equal to the volume of the body. The buoyant force on a submerged body is in the direction opposite to gravity, and its magnitude is given as \(F_{\mathrm{B}}=\rho_{\mathrm{f}} V g\)
Here, \(\rho_{\mathrm{f}}\) is the density of the fluid, \(\mathrm{V}\) is the volume of the displaced fluid, which is equal to the volume of the submerged body, and \(\mathrm{g}\) is the acceleration due to gravity. An object is in translational equilibrium when the sum of all the forces acting on the object is zero. \(\Sigma F=0\)
When the body is released from the height vertically downward towards the earth's surface, the force of gravitational attraction will exert on the earth's body.
The following figure shows the free body diagram of the rock. A rock of mass m is attached to the string by fixing one end. The string's tension is acting in the upward direction, and the weight of the rock ( W) acts in the downward direction.
![]()
The weight of the rock is given as, \(W=m g\)
Here, \(\mathrm{m}\) is the mass of the rock and \(\mathrm{g}\) is acceleration due to gravity. The net force acting on the rock is, \(\Sigma F=T_{\mathrm{air}}-m g\)
The rock is in translational equilibrium. Thus, the sum of all the forces acting on the rock is zero. \(\Sigma F=0\)
Substitute \(T_{\text {air }}-m g\) for \(\Sigma F\) in the equation \(\Sigma F=0\) and solve for \(m g\).
\(T_{\mathrm{air}}-m g=0\)
$$ m g=T_{\text {air }} $$
Substitute \(39.2 \mathrm{~N}\) for \(T_{a i r}\) in the equation \(m g=T_{\mathrm{air}}\) \(m g=39.2 \mathrm{~N}\)
As the rock is in translational equilibrium, the net force acting on the rock along the vertical direction is zero. Therefore, the tension of the string in the air is equal and opposite to the rock's weight. By substituting the value of tension in the string, the rock's weight can be found.
According to Archimedes' principle, the object partially or completely immersed in a fluid will be buoyed up by force.
The buoyed force will be equal to the fluid displaced by the object.
The following figure shows the free body diagram for the rock when it is totally immersed in water. When the rock is immersed in the liquid, the rock will experience an upward buoyant force. Tension in the string also is acting in the upward direction, and the weight of the rock acts in the downward direction.
The net force acting on the rock is, \(\Sigma F=T_{\text {water }}+F_{\mathrm{B}}-m g\)
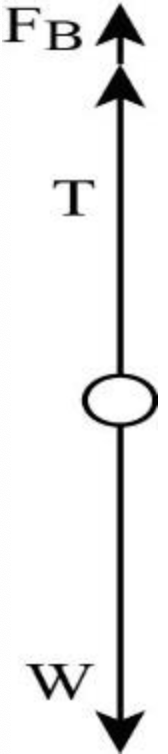
Here, \(F_{\mathrm{B}}\) is the buoyant force acting on the rock. The rock is in translational equilibrium. Thus, the sum of all the forces acting on the rock is zero. \(\Sigma F=0\)
Substitute \(T_{\text {water }}+F_{\mathrm{B}}-m g\) for \(\Sigma F\) in the equation \(\Sigma F=0\) and solve for \(T_{\text {water }}\)
$$ T_{\text {water }}+F_{\mathrm{B}}-m g=0 $$
\(T_{\text {water }}=m g-F_{\mathrm{B}}\)
Substitute \(V_{\text {rock }} \rho_{\text {water }} g\) for \(F_{\mathrm{B}}\) in the equation \(T_{\text {water }}=m g-F_{\mathrm{B}}\) and solve for \(V_{\text {rock }}\)
\(T_{\text {water }}=m g-V_{\text {rock }} \rho_{\text {water }} g\)
$$ V_{\text {rock }}=\frac{m g-T_{\text {water }}}{\rho_{\text {water }} g} $$
Here, \(V_{\text {rock }}\) is the volume of the rock and \(\rho_{\text {water }}\) is the density of water. Substitute \(39.2 \mathrm{~N}\) for \(m g, 28.4 \mathrm{~N}\) for \(T_{\text {water }}, 1000 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\) for \(\rho_{\text {water }},\) and \(9.8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\) for \(g\) in the equation \(V_{\text {rock }}=\frac{m g-T_{\text {water }}}{\rho_{\text {water }} g}\)
\(V_{\text {rock }}=\frac{39.2 \mathrm{~N}-28.4 \mathrm{~N}}{\left(1000 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\right)\left(9.8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)}\)
$$ V_{\text {rock }}=1.102 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~m}^{3} $$
When the rock is immersed in water, the sum of the tension force and buoyant force is equal to the rock's weight. The buoyant force is the upward force on the rock, and it is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the rock.
(3) The expression for the tension in unknown liquid is, \(T_{\text {liquid }}=m g-F_{B \text { ,liquid }}\) Here, \(F_{B \text { ,liquid }}\) is the buoyant force on the rock when it is immersed in an unknown liquid. Substitute \(V_{\text {rock }} \rho_{\text {liquid }} g\) for \(F_{B \text { ,liquid }}\) in the above equation and solve for \(\rho_{\text {liquid }}\).
\(T_{\text {liquid }}=m g-V_{\text {rock }} \rho_{\text {liquid }} g\)
$$ \rho_{\text {liquid }}=\frac{m g-T_{\text {liquid }}}{V_{\text {rock }} g} $$
Substitute \(39.2 \mathrm{~N}\) for \(m g, 18.6 \mathrm{~N}\) for \(T_{\text {liquid }}, 1.102 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~m}^{3}\) for \(V_{\text {rock }},\) and \(9.8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\) for \(g\) in the equation \(\rho_{\text {liquid }}=\frac{m g-T \text { liquid }}{V_{\text {rock }} g}\)
\(\rho_{\text {liquid }}=\frac{39.2 \mathrm{~N}-18.6 \mathrm{~N}}{\left(1.102 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~m}^{3}\right)\left(9.8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)}\)
$$ \rho_{\text {liquid }}=1.91 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3} $$
The density of unknown liquid is \(1.91 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\)
When the rock is immersed in an unknown liquid the sum of the tenion force and buoyant force is equal to the weight of the rock. Buoyant force is the upward force on th rock and it is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the rock.
The density of unknown liquid is \(1.91 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3} .\)
Related Solutions
A rock is suspended by a light string. When the rock is in air, the tension...
A rock is suspended by a light string. When the rock is in air, the tension...
An ore sample weighs 17.50 N in air. when the sample is suspended
A large crate is suspended by a light string. A bullet is fired horizontally into the...
A 8.9 kg rock whose density is 4500 kg/m3 is suspended by a string such that...
A rock has mass 1.80 kg. When the rock is suspended from the lower end of...
A rock weighing 25-N is thrown vertically into the air from ground level. when it reaches...
A thin film suspended in air is 0.400 µm thick and is illuminated with white light...
A violin string 20.0 cm long with mass 4.8 g and tension 48 N, fixed at...
Light attempts to move from cubic zirconia (n=1.61) to air. In a nearby experiment, light is...
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago