Question
In: Nursing
Search and review the assigned model of culture/transcultural/health and briefly describe the basic premise of the...
Search and review the assigned model of culture/transcultural/health and briefly describe the basic premise of the model. Give an example based on the model of how you can effectively use what you have learned to improve your cultural sensitivity and linguistics when interacting with patients of different cultures/ethnicities.
1.)Campinha-Bacote Model of Cultural Competence in psychiatric mental health nursing
Solutions
Expert Solution
DEFINITIONS
Transcultural Nursing
- Transcultural nursing is a comparative study of cultures to understand similarities (culture universal) and difference (culture-specific) across human groups (Leininger, 1991).
Culture
- Set of values, beliefs and traditions, that are held by a specific group of people and handed down from generation to generation.
- Culture is also beliefs, habits, likes, dislikes, customs and rituals learn from one’s family.
- Culture is the learned, shared and transmitted values, beliefs, norms and life way practices of a particular group that guide thinking, decisions, and actions in patterned ways.
- Culture is learned by each generation through both formal and informal life experiences.
- Language is primary through means of transmitting culture.
- The practices of particular culture often arise because of the group's social and physical environment.
- Culture practice and beliefs are adapted over time but they mainly remain constant as long as they satisfy needs.
Religion
- Is a set of belief in a divine or super human power (or powers) to be obeyed and worshipped as the creator and ruler of the universe.
Ethnic
- refers to a group of people who share a common and distinctive culture and who are members of a specific group.
Culturally competent care
- is the ability of the practitioner to bridge cultural gaps in caring, work with cultural differences and enable clients and families to achieve meaningful and supportive caring.
Nursing Decisions
Leininger (1991) identified three nursing decision and action modes to achieve culturally congruent care.
- Cultural preservation or maintenance.
- Cultural care accommodation or negotiation.
- Cultural care repatterning or restructuring.
INTRODUCTION
- Madeleine Leininger is considered as the founder of the theory of transcultural nursing.
- Her theory has now developed as a discipline in nursing.
- Transcultural nursing theory is also known as Culture Care theory.
- Theoretical framework is depicted in her model called the Sunrise Model (1997).
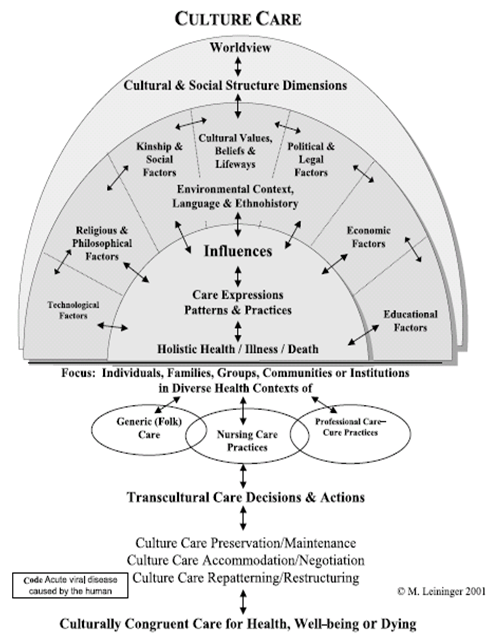
MAJOR CONCEPTS [Leininger (1991)]
- Illness and wellness are shaped by a various factors including perception and coping skills, as well as the social level of the patient.
- Cultural competence is an important component of nursing.
- Culture influences all spheres of human life. It defines health, illness, and the search for relief from disease or distress.
- Religious and Cultural knowledge is an important ingredient in health care.
- The health concepts held by many cultural groups may result in people choosing not to seek modern medical treatment procedures.
- Health care provider need to be flexible in the design of programs, policies, and services to meet the needs and concerns of the culturally diverse population, groups that are likely to be encountered.
- Most cases of lay illness have multiple causalities and may require several different approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and cure including folk and Western medical interventions..
- The use of traditional or alternate models of health care delivery is widely varied and may come into conflict with Western models of health care practice.
- Culture guides behavior into acceptable ways for the people in a specific group as such culture originates and develops within the social structure through inter personal interactions.
- For a nurse to successfully provide care for a client of a different cultural or ethnic to background, effective intercultural communication must take place.
APPLICATION TO NURSING
- To develop understanding, respect and appreciation for the individuality and diversity of patients beliefs, values, spirituality and culture regarding illness, its meaning, cause, treatment, and outcome.
- To encourage in developing and maintaining a program of physical, emotional and spiritual self-care introduce therapies such as ayurveda and pancha karma.
HEALTH PRACTICES IN DIFFERENT CULTURES
Use of Protective Objects
- Protective objects can be worn or carried or hung in the home- charms worn on a string or chain around the neck, wrist, or waist to protect the wearer from the evil eye or evil spirits.
Use of Substances .
- It is believed that certian food substances can be ingested to prevent illness.
- E.g. eating raw garlic or onion to prevent illness or wear them on the body or hang them in the home.
Religious Practices
- Burning of candles, rituals of redemption etc..
Traditional Remedies
- The use of folk or traditional medicine is seen among people from all walks of life and cultural ethnic back ground.
Healers
- Within a given community, specific people are known to have the power to heal.
Immigration
- Immigrant groups have their own cultural attitudes ranging beliefs and practices regarding these areas.
Gender Roles
- In many cultures, the male is dominant figure and often they take decisions related to health practices and treatment. In some other cultures females are dominant.
- In some cultures, women are discriminated in providing proper treatment for illness.
Beliefs about mental health
- Mental illnesses are caused by a lack of harmony of emotions or by evil spirits.
- Problems in this life are most likely related to transgressions committed in a past life.
Economic Factors
- Factors such as unemployment, underemployment, homelessness, lack of health insurance poverty prevent people from entering the health care system.
Time orientation
- It is varies for different cultures groups.
Personal Space
- Respect the client's personal space when performing nursing procedures.
- The nurse should also welcome visiting members of the family and extended family.
NURSING PROCESS AND ROLE OF NURSE
- Determine the client's cultural heritage and language skills.
- Determine if any of his health beliefs relate to the cause of the illness or to the problem.
- Collect information that any home remedies the person is taking to treat the symptoms.
- Nurses should evaluate their attitudes toward ethnic nursing care.
- Self-evaluation helps the nurse to become more comfortable when providing care to clients from diverse backgrounds
- Understand the influence of culture, race ðnicity on the development of social emotional relationship, child rearing practices & attitude toward health.
- Collect informationabout the socioeconomic status of the family and its influence on their health promotion and wellness
- Identifiy the religious practices of the family and their influence on health promotion belief in families.
- Understanding of the general characteristics of the major ethnic groups, but always individualize care.
- The nursing diagnosis for clients should include potential problems in their interaction with the health care system and problems involving the effects of culture.
- The planning and implementation of nursing interventions should be adapted as much as possible to the client's cultural background.
- Evaluation should include the nurse's self-evaluation of attitudes and emotions toward providing nursing care to clients from diverse sociocultural backgrounds.
- Self-evaluation by the nurse is crucial as he or she increases skills for interaction. .
CONCLUSION
- Nurses need to be aware of and sensitive to the cultural needs of clients.
- The practice of nursing today demands that the nurse identify and meet the cultural needs of diverse groups, understand the social and cultural reality of the client, family, and community, develop expertise to implement culturally acceptable strategies to provide nursing care, and identify and use resources acceptable to the client (Andrews & Boyle, 2002).
Related Solutions
Review the website: A Culture of Health, and respond to the following questions for discussion: Describe...
Describe the basic elements of culture.
Consider this theory: Papadopoulous and Taylor Model for Transcultural Nursing and Health and in a 2-4...
Consider this theory: Papadopoulous and Taylor Model for Transcultural Nursing and Health and in a 2-4...
(1) Basic EOQ: You need to briefly describe the basic EOQ model with modeling assumption, the...
Briefly describe the theory of intersectionality? Give an example using institutional discrimination as the premise
Describe the basic differences between the "scientific culture" and the "military culture" that were forced to...
Please describe the main characteristics of honor culture, dignity culture, and victimhood culture. And briefly compare...
Describe CATS model search strategies and results
Review on various theories utilized in health promotion: The Health Belief Model, The Transtheoretical Model, Social...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.

 Nightingale answered 3 years ago
Nightingale answered 3 years ago