Question
In: Statistics and Probability
7.3 (1 point) A package delivery service wants to compare the proportion of on-time deliveries for...
7.3 (1 point) A package delivery service wants to compare the proportion of on-time deliveries for two of its major service areas. In City A, 343 out of a random sample of 403 deliveries were on time. A random sample of 264 deliveries in City B showed that 209 were on time.
1. Calculate the difference in the sample proportion for the delivery times in the two cities.
?̂ ?????−?̂ ?????p^CityA−p^CityB =
2. What are the correct hypotheses for
conducting a hypothesis test to determine whether the proportion of
deliveries that are on time in City A is different from than the
proportion in City B?
A. ?0:??=??, ??:??>??
B. ?0:??=??, ??:??≠??
C. ?0:??=??, ??:??<??
3. Calculate the pooled estimate of the sample proportion.
p^ =
4. Calculate the test statistic for this hypothesis test.
z/t/X^2/F =
5. Calculate the p-value for this hypothesis test.
p-value =
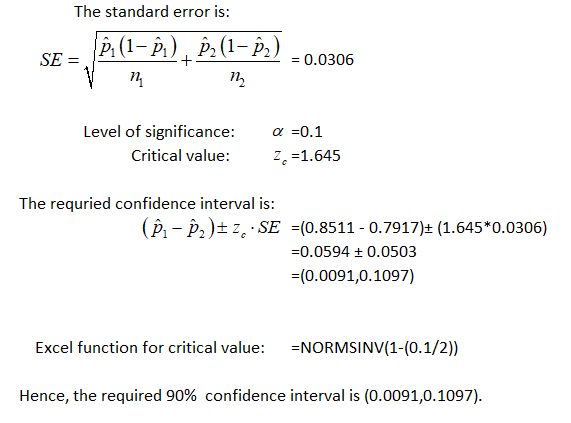
6. Compute a 90% confidence interval for the difference ?̂ ?????−?̂ ?????.
( , )
Solutions
Expert Solution
Let city A shows sample 1 and city B shows sample 2.
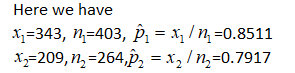
1:
The difference in the sample proportion for the delivery times in the two cities is

2:
Hypotheses are:
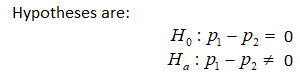
B. ?0:??=??, ??:??≠??
3:
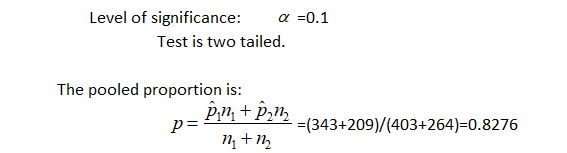
4:
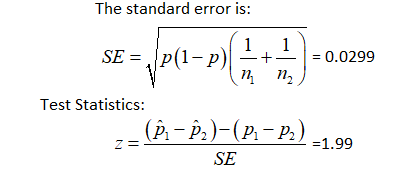
5:


6:
Related Solutions
1 point) A package delivery service wants to compare the proportion of on-time deliveries for two...
7) (1 point) A package delivery service wants to compare the proportion of on-time deliveries for...
A package delivery service wants to compare the proportion of on-time deliveries for two of its...
A package delivery service wants to compare the proportion of on-time deliveries for two of its...
A package delivery service wants to compare the proportion of on-time deliveries for two of its...
A package delivery service wants to compare the proportion of on-time deliveries for two of its...
Suppose that the weight of a package in a package delivery service is right-skewed with mean...
300 deliveries 1. If you are unable to change the standard deviation of the delivery time,...
In service companies, revenue is recognized either at a point in time, or over time. Compare...
a package delivery service claims that 55% of all package arrive at the address late. Assuming...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
 orchestra answered 3 years ago
orchestra answered 3 years ago