Question
In: Physics
Explain why the diffraction pattern of a human hair appears in the direction that it does.
Explain why the diffraction pattern of a human hair appears in the direction that it does.
Solutions
Related Solutions
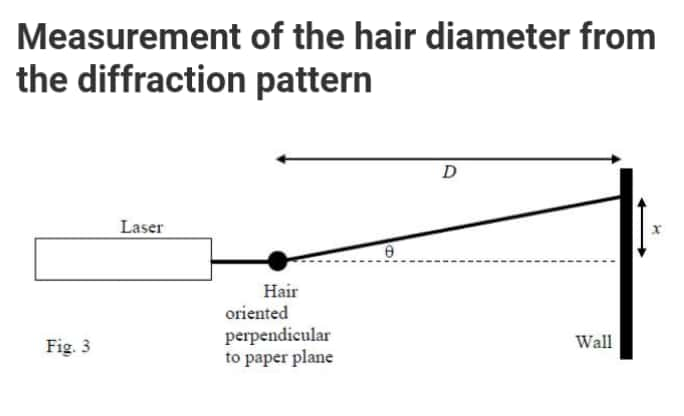
Explain why the diffraction pattern of the hair appears in the horizontal direction that it does.
Explain why the diffraction pattern of the hair appears in the
horizontal direction that it does.
How does the single-slit diffraction pattern look in comparison to the double-slit interference pattern? Is it...
How does the single-slit diffraction pattern look in comparison
to the double-slit interference pattern? Is it possible to have a
double-slit pattern without the single-slit pattern overlaid?
1/ Explain how the aperture geometry relates to the diffraction pattern. 2/ Predict how changing the...
1/ Explain how the aperture geometry
relates to the diffraction pattern.
2/ Predict how changing the wavelength
or aperture size affects the diffraction pattern.
In the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern of a double slit, it is found that the fourth secondary...
In the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern of a double slit, it is
found that the fourth secondary maximum is missing. What is the
ratio of slit width b to slit separation h?
If possible please cite the equations used.
No fringes are seen in a single-slit diffraction pattern if ..... the distance to the screen...
No fringes are seen in a single-slit diffraction pattern if
.....
the distance to the screen is greater than the slit width
the wavelength is less than the distance to the screen
the wavelength is greater than the slit width
the screen is far away
the wavelength is less than the slit width
A single-slit diffraction pattern is formed on a distant screen. If the width of the single...
A single-slit diffraction pattern is formed on a distant screen.
If the width of the single slit through which light passes is
reduced, what happens to the width of the central bright fringe?
Assume the angles involved remain small.
The
central bright fringe becomes
wider.
The
central bright fringe remains the same
size.
The
effect cannot be determined unless the distance between the slit
and the screen is
known.
The
central bright fringe becomes narrower.
The intensity pattern formed by a diffraction grating of N slits is where θ is the...
The intensity pattern formed by a diffraction grating of N slits
is
where θ is the angle of diffraction. The radiation reaches the
grating at normal incidence.
Using the formula above and m = 0, ±1, ±2 ... and p = an
integer ≠ mN
show that
the interference maxima occur for β = mπ
and minima occur for β = pπ/N .
show that the orders m=pd/a (of interference) are missing if
d/a is an integer .
What is the result of increasing the number of slits on the resulting diffraction pattern? What...
What is the result of increasing the number of slits on the
resulting diffraction pattern? What is a diffraction grating? What
are they used for? Assuming you have light incident on a
diffraction grating, at what angle do you except the second-order
diffraction maximum to appear?
Why does VIX futures usually show a contango pattern?
Why does VIX futures usually show a contango pattern?
A double-slit diffraction pattern is formed on a distant screen. If the separation between the slits...
A double-slit diffraction pattern is formed on a
distant screen. If the separation between the slits decreases, what
happens to the distance between interference fringes? Assume the
angles involved remain small.
The distance between interference fringes
remains the same.
The effect cannot be determined unless the
distance between the slits and the screen is known.
The distance between interference fringes
also decreases.
The distance between interference fringes
increases.
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- A ball is launched straight up into the air with an initial velocity=40m/s. a) How much...
- Define 1- Obligate anaerobes 2- Obligate aerobes 3- Mesophilic 4- Thermophiles 5-Coenzyme 6-Chemoautotrophs 7-Ribozyme 8-Proton motive...
- What is liberation to a Hindu? Is it the same as "heaven"? Why or why not?...
- ASSIGNMENT 10 Problem 10-1: Post transactions from General Journal to General Ledger. Robert Carpenter began business...
- The distribution of wait times for a movie to load on Hulu is normally distributed with...
- block 1 of mass m1 slides from rest along a frictionless ramp from height h =...
- An ion can produce an emission spectrum according to the Bohr model. A group of lines...
ADVERTISEMENT

 genius_generous answered 3 weeks ago
genius_generous answered 3 weeks ago