Question
In: Computer Science
Consider a binary classification problem where each example (observation) x has n features and class label...
Consider a binary classification problem where each example
(observation) x has n features and class label y can take one of
the two possible values: y = 1 (positive class label) and y = 0
(negative class label). Suppose a Logistic Regression model is
trained using a training set and θ ∈ Rn is the learned parameter
vector of this trained model. Show that given an unseen example x ∈
Rn having n features, the trained Logistic Regression model will
predict its class label to be 1, if θ⊤x > 0 and class label to
be 0 otherwise.
Solutions
Expert Solution
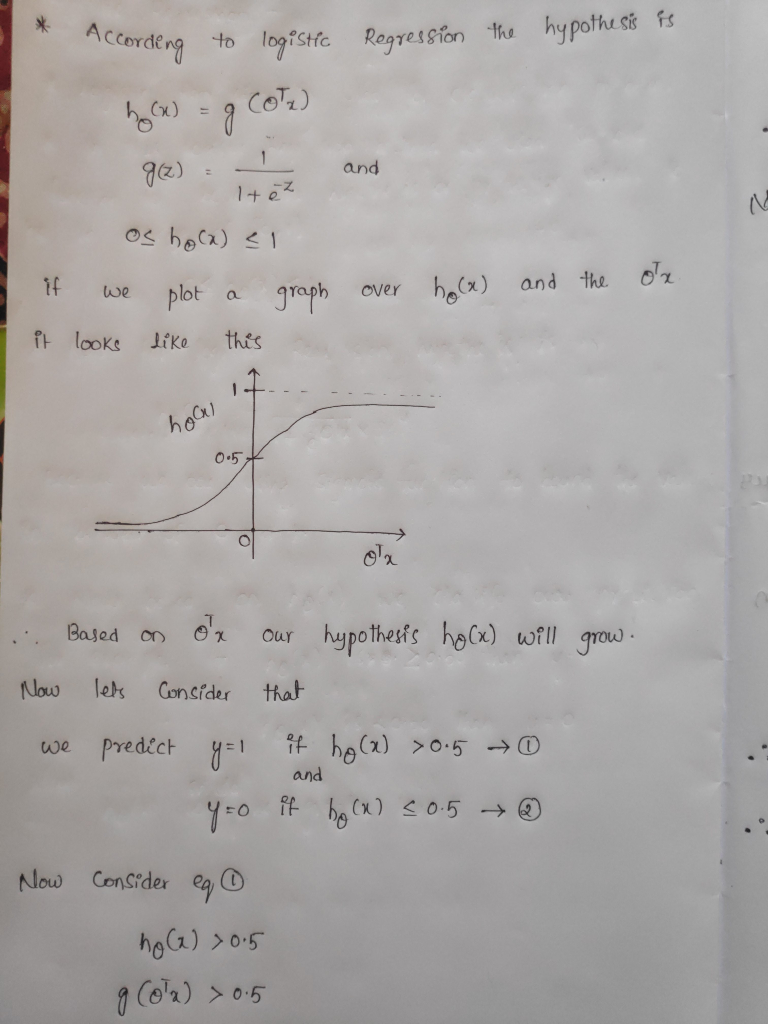
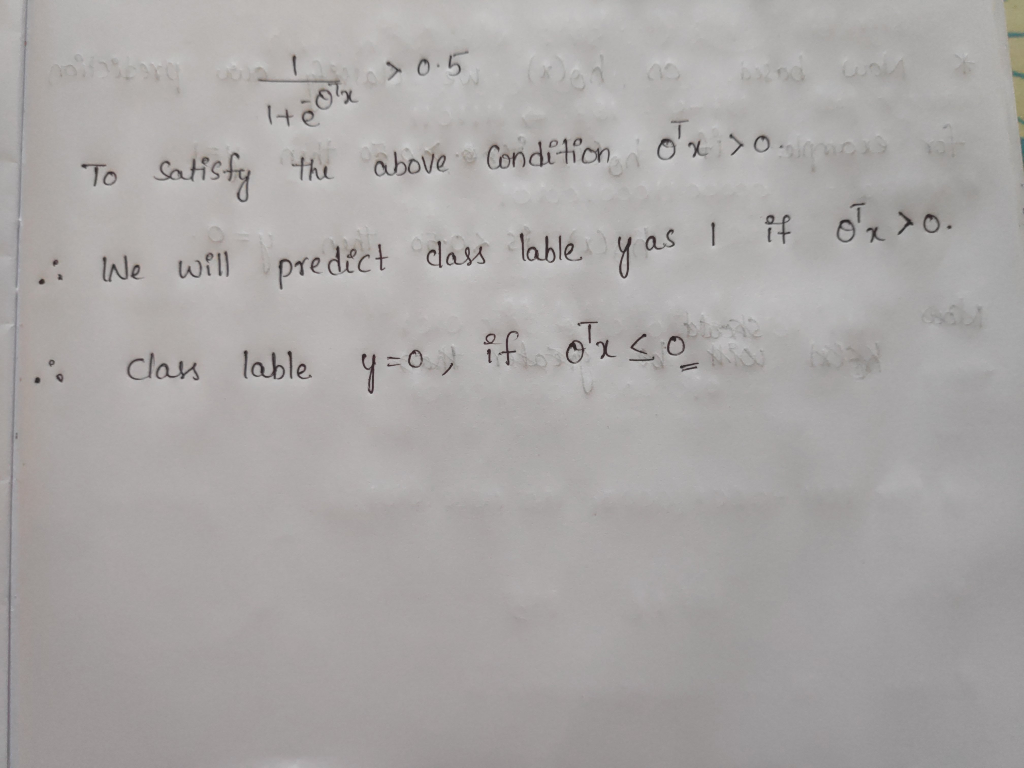 Here the function
Here the function  is predicting the values of class lable.This values should be in
[0,1].
is predicting the values of class lable.This values should be in
[0,1].
Now we consider y-lable as 1 if the  >0.5 and
>0.5 and
y-lable as 0 if  <= 0.5
<= 0.5
Let's consider that our prediction  > 0.5 then y-lable is 1.
> 0.5 then y-lable is 1.
But  >0.5 if and only if
>0.5 if and only if  is >0 and
is >0 and  is >= 1 if
is >= 1 if  >0
>0
Related Solutions
Imagine you have a 6-class classification problem, where the dataset contains 9 input features. You decide...
Imagine you have a 6-class classification problem, where the
dataset contains 9 input features. You decide to build a classifier
using a “mixture of mixtures”, i.e. using a Gaussian mixture model
for each likelihood (p(x|θ)). 3 mixture components are used with
diagonal covariance matrices for each mixture model. Calculate the
total number of model parameters in the classifier (do not consider
priors).
Suppose that X is a single observation from a Binomial(n, p) distribution where n is known...
Suppose that X is a single observation from a Binomial(n, p)
distribution where n is known and 0 < p < 1 is unknown.
Consider three estimators of p:
pˆ = X /n “sample proportion”
pˆA = (X + 2)/ (n + 4) “plus four estimator”
pˆB = (X + (√n/4))/( n + √ n ). “constant MSE estimator”
(a) Find the bias functions for all three estimators.
(b) Find the variance functions of all three estimators.
(c) Find the...
Suppose that X is a single observation from a Binomial(n, p) distribution where n is known...
Suppose that X is a single observation from a Binomial(n, p)
distribution where n is known and 0 < p < 1 is unknown.
Consider three estimators of p: pˆ = X /n “sample proportion” pˆA =
(X + 2)/ (n + 4) “plus four estimator” pˆB = (X + (√n/4))/( n + √ n
). “constant MSE estimator” (a) Find the bias functions for all
three estimators. (b) Find the variance functions of all three
estimators. (c) Find the...
Decision Trees: Consider a data set described by n binary features. Does n place a limit...
Decision Trees: Consider a data set described by n binary
features. Does n place a limit on the depth of the tree? Justify
your answer.
Provide an example for each industry classification group based on 1) where they are in their...
Provide an example for each industry classification group based
on 1) where they are in their life cycle, and 2) how the react to
the economy's business cycle
Consider an example where X person has planned a trek in Himalayas. Suppose you are to...
Consider an example where X person has planned a trek in
Himalayas. Suppose you are to assist in the decision-making of
whether X should go ahead with the plan or not. Which model would
you employ under the uncertainty management?
Consider the TA assignment problem where n Teaching Assistants (TAs) are to be assigned to n...
Consider the TA assignment problem where n Teaching
Assistants
(TAs) are to be assigned to n courses with one course having
exactly
one TA. Each course ranks all of the TAs, and each TA ranks all
the
courses, from most to least desirable.
Can you provide an example of an assignment and preference lists
such
that every TA and course forms an unstable pair? (Yes/No). If
Yes,
present the assignment. If No, justify your answer.
note: gale shapley algorithm
Consider the following scheduling problem. There are n jobs and a single machine. Each job has...
Consider the following scheduling problem. There are n jobs and
a single machine. Each job has a length ℓi and a weight wi . The
weight wi represents the importance of job i.
a) Let fi be the finishing time of job i. Design a greedy
algorithm to minimize the weighted sum of the completion times ∑n
i=1 wifi . Your algorithm should run in time O(n log n) and output
an ordering of the jobs.
b) Prove the correctness...
Problem 1 1.1 If A is an n x n matrix, prove that if A has...
Problem 1
1.1 If A is an n x n matrix, prove that if A has n linearly
independent eigenvalues, then AT is diagonalizable.
1.2 Diagonalize the matrix below with eigenvalues equal to -1
and 5.
0
1
1
2
1
2
3
3
2
1.3 Assume that A is 4 x 4 and has three different eigenvalues,
if one of the eigenspaces is dimension 1 while the other is
dimension 2, can A be undiagonalizable? Explain.
Answer for all...
Redraw the diagram presented in Problem 2. Label each element in the diagram and briefly describe its role and key features.
Redraw the diagram presented in Problem 2. Label each element in the diagram and briefly describe its role and key features.
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
ADVERTISEMENT
 venereology answered 1 month ago
venereology answered 1 month ago