Question
In: Physics
A sinusoidal voltage Δv = 42.5 sin(100t), where Δv is in volts and t is in...
A sinusoidal voltage Δv = 42.5 sin(100t), where Δv is in volts and t is in seconds, is applied to a series RLC circuit with L = 180 mH, C = 99.0 µF, and R = 51.0 Ω.
(a) What is the impedance (in Ω) of the circuit? Ω
(b) What is the maximum current (in A)? A
(c) Determine the numerical value for ω (in rad/s) in the equation i = Imax sin(ωt − ϕ). rad/s
(d) Determine the numerical value for ϕ (in rad) in the equation i = Imax sin(ωt − ϕ). rad
(e) What If? For what value of the inductance (in H) in the circuit would the current lag the voltage by the same angle ϕ as that found in part (d)? H
(f) What would be the maximum current (in A) in the circuit in this case? A
Solutions
Expert Solution
For this particular question, I have uploaded an image Please go through this first-
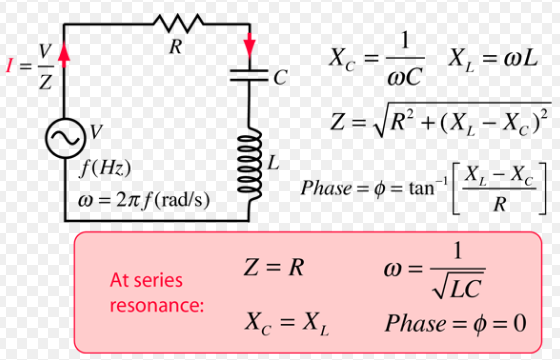
Now, Part A)-
XL =  * L
* L
XL = 100* 0.180 = 18 ohm
XC = 1/( *C)
*C)
= 1/ (100*99*10-6)
XC = 101.01 ohm
Z = 
Z = 
Z = 97.425 ohm
Part B)-
For Imax , Z)total should be minimum which is equal to Z)min = R = 51 ohm
Imax = V/Zmin
I max = 42.5 / 51 = 0.834 Amp
Part C)-
Value of frequency will never change for a circuit or its
components i.e  will remain same
in every equation and equal to input frequency = 100 rad/sec
will remain same
in every equation and equal to input frequency = 100 rad/sec
Part D)-
phase =  = tan-1
[(XL - XC ) / R]
= tan-1
[(XL - XC ) / R]
=tan-1 [(18 - 101.01 ) / 51]
= −1.019 rad = -58.43 degree
Part E)-
For current laging phase =  should be +ve same
value
should be +ve same
value
tan(58.43) = [(XL - XC ) / R]
1.62* 51 = (XL - 101.01 )
XL = 183.63 ohm
Part F )- Max value of current does depend only on value of circuit resistance so this value will not change and reamin same as part B
Thankyou !!! Have Fun
Please Rate High.
Related Solutions
A voltage of 10 sin(3t) volts is impressed on a series circuit containing a 20Ω resistor,...
At time t = -250/6 μs a sinusoidal voltage is zero and is increasing. The next...
At time t = -250/6 μs a sinusoidal voltage is zero and is increasing. The next...
The voltage in a circuit is 115 volts. A particular technique for measuring the voltage gives...
The voltage in a circuit is 115 volts. A particular technique for measuring the voltage gives...
1. A voltage is given by v(t) = 10 sin(1000?t + 30o). a. Use a cosine...
An RLC circuit consists of an AC voltage source with a maximum voltage of 122 Volts...
An RLC circuit consists of an AC voltage source with a maximum voltage of 135 Volts...
7 If a carrier signal vc(t) = 10 sin (20000πt+π/2) volts is amplitude modulated by message...
A. According to Equation 20.7, an ac voltage V is given as a function of time t by V = Vo sin 2ft, where Vo is the peak voltage and f is the frequency (in hertz).
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 genius_generous answered 1 month ago
genius_generous answered 1 month ago