Question
In: Computer Science
Please read the whole program (all the way to the bottom), Thanks in advance! Develop car...
Please read the whole program (all the way to the bottom), Thanks in advance!
Develop car rental application may use to produce a receipt. A receipt will be formatted as follows:
E Z – R I
D E R
Rental Receipt
Customer : John
Jones
Driver License : PA 12343
Telephone : 724-555-8345
Credit Card : VISA 12345678012
Vehicle : Mercedes
350E
Tag # : PA
342399
Rent Class : Luxury Sedan
Daily Rate : $ 95.00
Weekly Rate : $ 545.00
Date/Time Out : 01/10/2017 at 10:45
Date/Time In : 01/20/2017 at 11:44
Rental Charge : $ 830.00
Airport Tax : $ 150.00
Sales Tax : $ 49.80
Total : $
1029.80
For this application create four main classes for customer, rental
class, vehicle, and rental agreement. The customer class should
have six pieces of information (i.e. instance variables) including
customer name (as a String), driver’s license state (as a String),
driver’s license number (as an int), telephone number (as a
String), credit card type (as a String), and credit card number (as
a long). A rental class represents the rental terms for a class of
vehicle. For example Compact, Mid-Size, Full Size, Sport etc. are
classifications of cars with each time having different rental
terms. A rental class should have three pieces of information: a
rental class name (as a String), a daily rate (as a double) and a
weekly rate (as a double). A vehicle should have four pieces of
information: a make/model (as a String), state issuing a tag (as a
String), a tag number (as a String) and a rental class (as a rental
class). Lastly a rental agreement is the agreement of a customer to
rental a given vehicle together with the rental terms, date/time
out and date/time in. Thus a rental agreement has 4 pieces of
information: the customer, the vehicle, date/time out (as a
LocalDateTime) and date/time in.
For your customer class, provide a constructor accepting values for all instance variables. Provide getter methods for all instance variables except account number, but setter methods for only the telephone, credit card type and credit card number variables.
For rental class class, provide a constructor accepting values for all instance variable. Provide getter methods for all instance variables. Likewise for the vehicle class.
For your rental agreement class provide a constructor accepting values for all instance variables except date/time in as it is intended that this field will be given a value only when the customer returns the vehicle. Provide only getter methods for all instance variables. Provide a setter method for only the date/time in variable.
To represent a date/time use Java’s LocalDateTime class. For this class, however, do not use new to create instances. Instead use the of method:
LocalDateTime dateTimeOut = LocalDateTime.of(2017,1,10, 8, 45);
The above example creates a LocalDateTime for 1/10/2017 at 8:45.
In the rental agreement provide getRentalCharge(), getAirportTax(), getSalesTax() and getTotal() methods. The getRentalCharge() is to return the number of days rented times the daily rental rate. The getAirportTax() is to return the number of days rented times $ 15.00. The getTax() is to return the rental change times 6%. The getTotal() is to return the sum of rental charge, airport tax, and tax.
In addition to the special get methods, provide a print receipt method that will print the receipt according to the above format.
A day is a 24 hours period. However, there is a one hour grace in returning a car. That is if a car is returned after 24 hours and 59 minutes, then only one day is used in the computations. To compute the number of days between dateTimeOut and dateTimeIn, use the following code:
int noDays = Duration.between(dateTimeOut,dateTimeIn).plusMinutes(23 * 60);
BONUS 5 points: have the computation of rental charge use weekly
rate to the best benefit of the customer. The data in the example
is using the weekly rate. That is one week charge plus three days
at the daily rate. The weekly rate should be used where
it benefits the customer even in cases where it is better than the
daily rate. For example if in the example the vehicle was rented 6
days and 1 week rental charges should be used.
In addition, develop another class to test your classes by printing
three separate, and different, recepts. This class will have a main
method. In the main method, create instances of your
classes in order to print the three separate receipts. Thus, you
will hard code inside the main the values to be used when
instantiating your classes. With the exception of the fixed values
given in the computations above (for example .06 for sales tax
rate), do not hard code any other data within your classes. For
each receipt instance, call the print method to print the receipt.
Make sure to call setDateTimeIn appropriately after creating an
instance of a rental receipt and before printing.
NOTE: You do not need, and therefore should not, code any routines to input the values from the user or from files. Your test class is sufficient to demonstrate that your classes are working correctly. If you do the bonus, make sure to have data that will test the logic.
Make sure the instance variables are private. Provide javadoc for each class and methods. Abide by good programming practices.
Solutions
Expert Solution
1) customer.java
package package1;
public class Customer {
String name;
int licenseNo;
String telephoneNo;
long creditCardNo;
String creditCardType;
String licenseState;
/*
* Constructor to initalize Customer object
*/
Customer(String name,int lisno,String telno,String
credittype, long creditno, String state)
{
this.name = name;
this.telephoneNo =telno;
this.licenseNo = lisno;
this.creditCardNo = creditno;
this.creditCardType =
credittype;
this.licenseState = state;
}
/*
* getter method to get License state
*/
public String getLicenseState() {
return licenseState;
}
/*
* getter method to get Customer Name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/*
* getter method to get license number
*/
public int getLicenseNo() {
return licenseNo;
}
/*
* getter method to get Telephone number
*/
public String getTelephoneNo() {
return telephoneNo;
}
/*
* getter method to get Credit card number
*/
public long getCreditCardNo() {
return creditCardNo;
}
/*
* getter method to set Credit card number
*/
public void setCreditCardNo(long creditCardNo) {
this.creditCardNo =
creditCardNo;
}
/*
* getter method to set customer telephone number
*/
public void setTelephoneNo(String telephoneNo) {
this.telephoneNo =
telephoneNo;
}
/*
* getter method to set credit card type
*/
public void setCreditCardType(String creditCardType)
{
this.creditCardType =
creditCardType;
}
/*
* getter method to get credit card type
*/
public String getCreditCardType() {
return creditCardType;
}
}
2) RentalClass.java
package package1;
public class RentalClass {
String name;
double dailyRate;
double weeklyRate;
/*
* construcot to initialize renal class object
*/
RentalClass(String name, double dailyrate, double
weekrate){
this.name = name;
this.dailyRate = dailyrate;
this.weeklyRate = weekrate;
}
/*
* getter method to get rental class name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/*
* getter method to set rental class name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/*
* getter method to get daily rate
*/
public double getDailyRate() {
return dailyRate;
}
/*
* getter method to set daily rate
*/
public void setDailyRate(double dailyRate) {
this.dailyRate = dailyRate;
}
/*
* getter method to get weekly rate
*/
public double getWeeklyRate() {
return weeklyRate;
}
/*
* getter method to set weekly rate
*/
public void setWeeklyRate(double weeklyRate) {
this.weeklyRate = weeklyRate;
}
}
3) Vehicle.java
package package1;
public class Vehicle {
String model;
String statetag;
String tagno;
RentalClass rentalClass;
/*
* constructor to initialize vehicle object
*/
Vehicle(String model, String tagState, String tagno,
RentalClass obj){
this.model = model;
this.statetag = tagState;
this.tagno = tagno;
this.rentalClass = obj;
}
/*
* getter method to get vehicle model
*/
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
/*
* getter method to set vehicle model
*/
public void setModel(String model) {
this.model = model;
}
/*
* getter method to get state tag
*/
public String getStatetag() {
return statetag;
}
/*
* getter method to get state tag
*/
public void setStatetag(String statetag) {
this.statetag = statetag;
}
/*
* getter method to get tag number
*/
public String getTagno() {
return tagno;
}
/*
* getter method to set tag number
*/
public void setTagno(String tagno) {
this.tagno = tagno;
}
public RentalClass getRentalClass() {
return rentalClass;
}
public void setRentalClass(RentalClass rentalClass)
{
this.rentalClass =
rentalClass;
}
}
4) RentalAgreement.java
package package1;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class RentalAgreement {
LocalDateTime timeout;
LocalDateTime timein;
Customer c ;
Vehicle v;
/*
* constructor to initialize rental agreement
object
*/
public RentalAgreement(LocalDateTime timein, Customer
cObj, Vehicle vObj) {
this.timein = timein;
this.c = cObj;
this.v = vObj;
}
/*
* getter method to get time out of vehicle
*/
public LocalDateTime getTimeout() {
return timeout;
}
/*
* getter method to get time in of vehicle
*/
public LocalDateTime getTimein() {
return timein;
}
public Customer getC() {
return c;
}
public Vehicle getV() {
return v;
}
/*
* getter method to set time out of vehicle
*/
public void setTimeout(LocalDateTime timeout) {
this.timeout = timeout;
}
/*
* getter method to set time in of vehicle
*/
public void setTimein(LocalDateTime timein) {
this.timein = timein;
}
/*
* getter method to get rental charge
*/
public int getRentalCharge(){
//System.out.println(noOdDays());
//System.out.println(v.rentalClass.getDailyRate());
int RentalChage =
(int)(Integer.parseInt(noOdDays().toString()) *
v.rentalClass.getDailyRate());
return RentalChage;
}
/*
* getter method to get Airport charge
*/
public int getAirportCharge(){
int airportCharge =
(int)(Integer.parseInt(noOdDays().toString())*15);
return airportCharge;
}
/*
* getter method to get sales tax
*/
public int getSalesTax(){
int salestax = (int)
(getRentalCharge() * 0.6);
return salestax;
}
/*
* getter method to get total Charge
*/
public int getTotal(){
return (getRentalCharge() +
getSalesTax() + getAirportCharge());
}
/*
* getter method to determine number of days for which
car is rented
*/
public Long noOdDays(){
return
Duration.between(timein,timeout).plusMinutes(23 *
60).toDays();
}
/*
* getter method to get Reciept
*/
public void printReceipt(){
System.out.println("------ E Z – R
I D E R-----");
System.out.println("
Rental Receipt ");
System.out.println("Customer : "+
c.getName());
System.out.println("Driver License
: "+c.getLicenseNo());
System.out.println("Telephone
:"+c.getTelephoneNo());
System.out.println("Credit Card :
"+c.getCreditCardType()+" "+c.getCreditCardNo());
System.out.println("Vehicle :
"+v.getModel());
System.out.println("Tag #
:"+v.getStatetag()+" "+v.getTagno());
System.out.println("Rent Class
:"+v.getRentalClass().getName());
System.out.println("Daily Rate : $
"+v.getRentalClass().getDailyRate());
System.out.println("Weekly Rate : $
"+v.getRentalClass().getWeeklyRate());
System.out.println("Date/Time Out :
"+getTimeout());
System.out.println("Date/Time In :
"+getTimein());
System.out.println("Rental Charge :
$ "+this.getRentalCharge());
System.out.println("Airport Tax : $
"+this.getAirportCharge());
System.out.println("Sales Tax : $
"+this.getSalesTax());
System.out.println("Total : $
"+this.getTotal());
}
}
5) Main.java with main() function
package package1;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method
stub
Customer customer = new
Customer("John Jones",12343,"724-555-8345","VISA",new
Long(123456780),"New York");
RentalClass rentalClass = new
RentalClass("Luxury Sedan" , 95.00, 545.00);
Vehicle vehicle = new
Vehicle("Mercedes 350E","PA","342399",rentalClass);
RentalAgreement rentalAgreement =
new RentalAgreement(LocalDateTime.of(2017,1,10, 8, 45), customer,
vehicle);
rentalAgreement.setTimeout(LocalDateTime.of(2017,1,12, 8,
45));
rentalAgreement.printReceipt();
}
}
please find the screenshot of the output
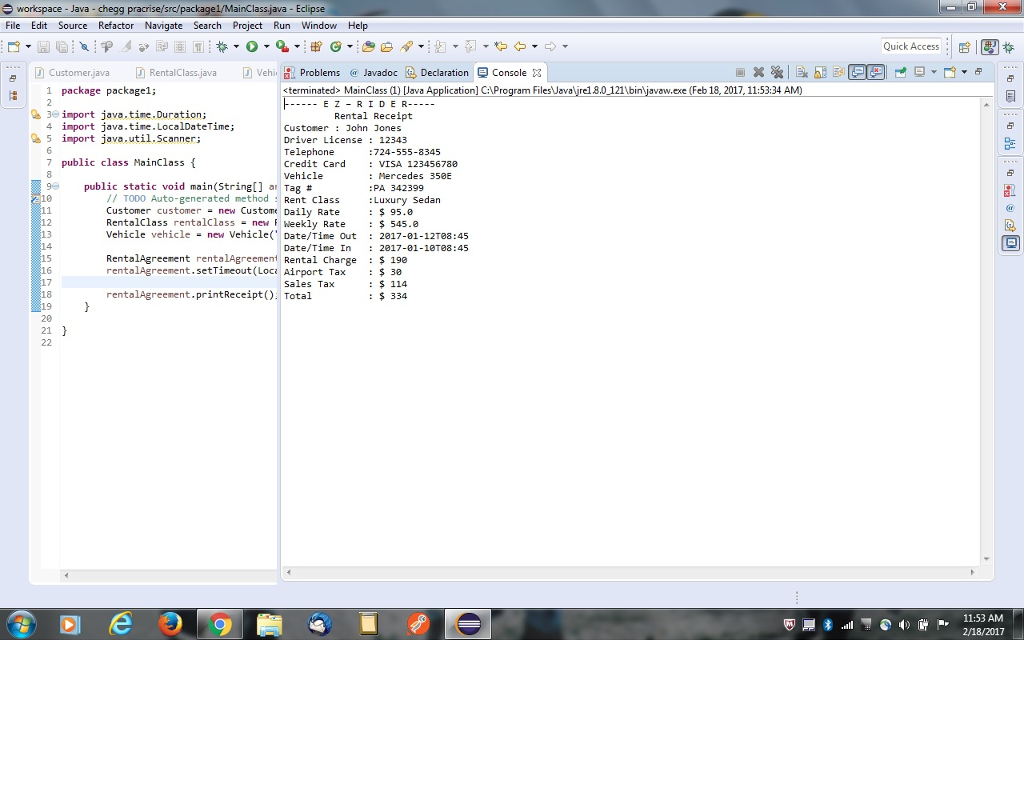
Related Solutions
Please answer the questions as soon as possible. Thanks in advance. Please explain in brief in...
Please give a detailed explanation, not just the answer. Thanks in advance! Use the data in...
Please use very basic level of bluej thanks (please dont use advance techniques ) Write a...
please provide me the tips to produce defect-free membrane (with references) Thanks in advance
please answer it ASAP, Its URGENT!!! Thanks in advance Describe the entire path of the blood...
WILL RATE HIGHLY!!! Please answer both questions with as much background as possible, thanks in advance!...
Please try to answer as soon as possible. Thanks in advance. Answer the questions true, false...
Paraphrase the following. please try not to make it short. needs urgently.. thanks in advance. i...
please read questions and the bottom of the case study and post resources as well please...
Design and implement a C++ program read in a whole line of characters as the input...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 venereology answered 2 months ago
venereology answered 2 months ago