Question
In: Chemistry
Define and provide examples of the following terms (a) aromatic (b) hydrophilic (c) combustion (d) methylene...
Define and provide examples of the following terms
(a) aromatic (b) hydrophilic (c) combustion
(d) methylene group (e) methyl group (f) common name
(g) IUPAC name (h) conformations (i) Newman projection
(j) eclipsed (k) staggered (l) gauche conformation
(m) anti conformation (n) catalytic cracking (o) cis-trans isomers of a ring
(p) chair conformation (q) boat conformation (r) distorted boat
(s) half chair conformation (t) axial position (u) equatorial position
(v) chair-chair interconversion (w) fused ring system (x) bridged bicyclic compound
(y) bridgehead carbon atoms
Solutions
Expert Solution
a - Aromatic :
A aromatic compound refers to an
organic compound which has (2n + 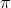 )electrons with cyclic conjugate structure.
)electrons with cyclic conjugate structure.
The molecule should be flat.
Example : Benzene and napthalene.
b - Hydrophilic :
If a compound is readily dissolved in water and water solvents , then it is called as a hydrophilic molecule.
Most of the polar groups which resembles H -OH are hydrophilic, such as alcohols (R-OH) and carboxylic acid (CO-OH)
Other examples of hydrophilic group are : -NH , -NO2 , -CN etc.
c- Combustion :
Combustion is a chemical reaction between oxygen and a substance which gives up heat and light.
All combustion reactions are exothermic.
Examples :
i- Combustion of methane to give CO2 and water.
CH4 + O2 -------> CO2 +
H2O , 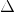 H = -ve
H = -ve
ii- Rusting of Iron
3Fe + 4O2 -------> Fe3O4
d- Methylene group:
Methylene group is apart of a molecule that is connected to the rest of the part by two single bond.
(CH2= or -CH2-)
Example :i- CH3 - CH=CH2 (propene)
Here =CH2 is the methylene group
ii- CH3-CH2-CH3 (propane)
Here -CH2- is the methylene group
Related Solutions
Define the following terms: A- portfolio B- Diversification C- Correlation D- Beta
Define the following terms: a. Cardinalities b. Weak Entity Types c. Categorization d. Aggregation
Define each of the following terms: a. Will. b. Estate. c. Intestate. d. Probate laws. e....
Define the following terms with Examples (a) Total rate of return (b) Capital gain (c) Dividend...
Define the following terms with examples (a) Absolute return (b) Nominal rate of return (c) Real...
Define and describe the following terms: a. Gastriliths: b. X-organ: c. Sinus gland: d. &n
1. Define the following terms: a. Complex Compound b. Complex ion c. Ligand d. Differentiate between...
Define the following terms (a) leading strand (b) lagging strand (c) template strand (d) coding strand
Define the following terms: (a) simple random sampling, (b) systematic sampling, (c) systematic random sampling, (d)...
1. Briefly define the following terms: a. Explicit costs b. Implicit costs c. Normal profit d....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 2 months ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 2 months ago