Question
In: Economics
1.1 For each of the following events, ceteris paribus, explain whether the production possibility frontier shifts...
1.1 For each of the following events, ceteris paribus, explain whether the production possibility frontier shifts inward, shifts outward or remains unchanged. Use a single diagram to motivate your answer.
1.1.1 The discovery of coal.
1.1.2 Training for workers that increases the amount of a good that can be produced per worker.
1.1.3 A shift in preference for one good compared to the other good.
1.1.4 Invention of a new process of production that reduces the resources necessary to produce a good.
1.2 “Market structure refers to the nature and degree of competition in the market for goods and services. There are a number of determinants of market structures for a particular good.” In terms of the statement above, discuss the following determinants for the four main types of market structures.
1.2.1 Nature of product
1.2.2 Entry and exit conditions
1.2.3 Economies of scale
Solutions
Expert Solution
Ans) 1) PPC shows the possible combination of goods that can be produced in an economy, given the existing resources and technology. Reasons for shift in PPC are÷
- Change in technology.
- Change in existing resources.
A) Discovery of coal means that there is addition to the existing resources. This means that there can be more output and hence PPC will shift outwards.
B) Training increases human resource. This will again lead to outward shift in PPC.
C) Shift in preferences do not lead to any change in PPC. It will simply lead to movement along PPC.
D) Again, the invention which reduces the consumption of resources is improvement in technology. This will again lead to outward shift in PPC.
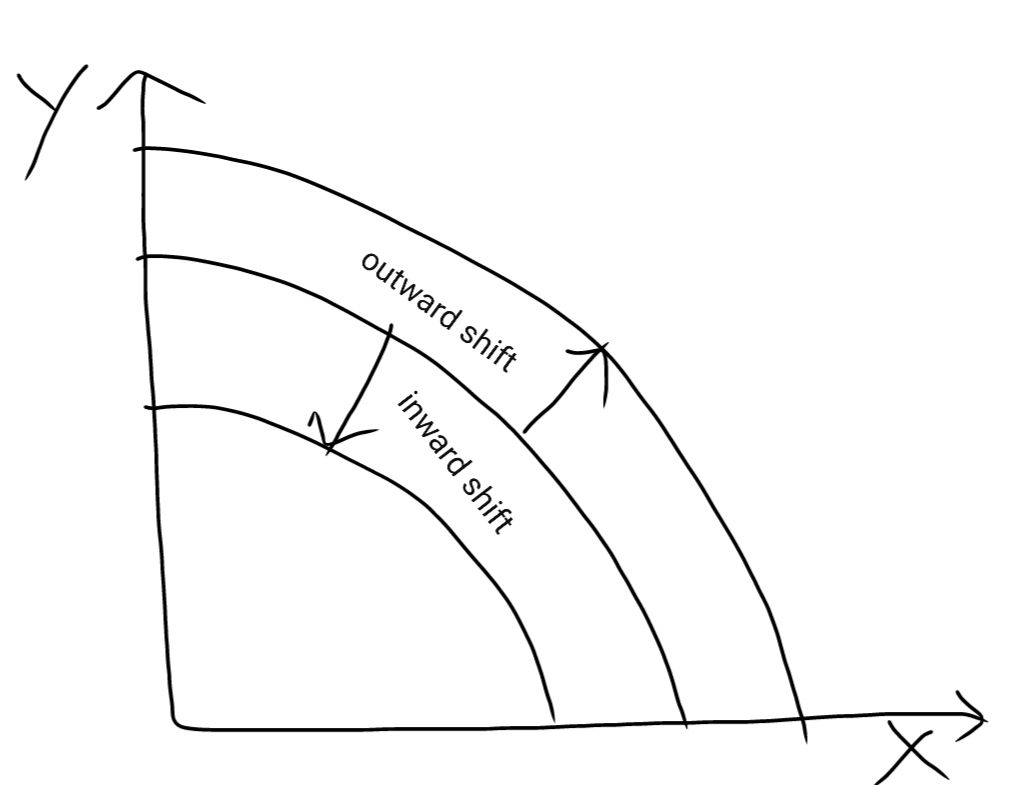
(PPC will shift inside if for eg- there is war, disease, decrease in technology etc.)
2) Perfect competition ÷ perfect competition is when there are many sellers selling homogeneous products. There is free entry and exit in the market. And there is no economies of scale in perfect competition. Eg- vegetable market
Monopolistic competition ÷ In monopolistic competition there are many sellers selling homogeneous but differentiated products. There is no or very less barrier to entry and exit. Here, the economies of scale is not fully exploited. Eg- clothing industry
Oligopoly ÷ in oligopoly there are few large sellers selling homogeneous products. There is significant barrier to entry and exit. Oligopoly can take advantage of economies of scale. Eg- cigarette
Monopoly ÷ in monopoly there is single seller selling unique product. There is high barrier to entry and exit. Economies of scale is achieved in monopoly.
(Economies of scale is reducing ATC by producing more quantity of goods. )
Related Solutions
QUESTION ONE [30] 1.1 For each of the following events, ceteris paribus, explain whether the production...
QUESTION ONE [30] 1.1 Explain the purpose of the production possibility frontier as a basic economic...
Graphically illustrate how each of the following events, ceteris paribus, will affect the competitive market. (Start...
1.1 With the aid of a full y labelled diagram, draw a Production Possibility Frontier for...
Write whether or not each situation would lengthen or shorten a contract, ceteris paribus. a) a...
Explain whether each of the following events shifts the aggregate-demand curve. For each event that does...
I. Explain whether each of the following events shifts the AS, LRAS, AD, both, or neither....
) Explain whether each of the following events shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve, the aggregate...
QUESTION ONE [30] 1.1 “The production possibility frontier (PPF) for two goods represents all possible combinations...
Graphically derive and interpret a PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY FRONTIER
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 Rahul Sunny answered 2 months ago
Rahul Sunny answered 2 months ago