Question
In: Computer Science
Update the following C code and write the function : void sln_stutter(sln_list* li); that modifies the...
Update the following C code and write the function :
void sln_stutter(sln_list* li);
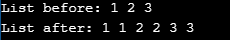
that modifies the list li so that it each element is duplicated. For example the list with elements [1,2,3] would after this function call become the list [1,1,2,2,3,3].
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
struct sln_node {
struct sln_node* next;
int key;
};
struct sln_list {
struct sln_node* head;
};
typedef struct sln_node sln_node;
typedef struct sln_list sln_list;
static sln_node* freelist = NULL;
/* Internal bookkeeping functions for the free list of nodes. */
sln_node* sln_allocate_node() {
sln_node* n;
if(freelist == NULL) {
freelist = malloc(sizeof(sln_node));
freelist->next = NULL;
}
n = freelist;
freelist = n->next;
n->next = NULL;
return n;
}
void sln_release_node(sln_node* n) {
n->next = freelist;
freelist = n;
}
void sln_release_freelist() {
sln_node* n;
while(freelist != NULL) {
n = freelist;
freelist = freelist->next;
free(n);
}
}
/* Create a new singly-linked list. */
sln_list* sln_create() {
sln_list* list = malloc(sizeof(sln_list));
list->head = NULL;
return list;
}
/* Release the list and all its nodes. */
void sln_release(sln_list* list) {
sln_node* n = list->head;
sln_node* m;
while(n != NULL) {
m = n->next;
sln_release_node(n);
n = m;
}
free(list);
}
/* Insert a new element to the list. */
void sln_insert(sln_list* list, int key) {
sln_node* n = sln_allocate_node();
n->key = key;
n->next = list->head;
list->head = n;
}
/* Check if the list contains the given element. Returns 1 or 0. */
int sln_contains(sln_list* list, int key) {
sln_node* n = list->head;
while(n != NULL && n->key != key) {
n = n->next;
}
return (n == NULL)? 0: 1;
}
/* Remove the first occurrence of the given element from the list.
Returns 1 if an element was removed, 0 otherwise. */
int sln_remove(sln_list* list, int key) {
sln_node* n;
sln_node* m;
n = list->head;
if(n == NULL) { return 0; }
if(n->key == key) {
list->head = n->next;
sln_release_node(n);
return 1;
}
while(n->next != NULL && n->next->key != key) {
n = n->next;
}
if(n->next != NULL) {
m = n->next;
n->next = m->next;
sln_release_node(m);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Solutions
Expert Solution
The logic is explained in code comments added to make program complete. No comments added or changes made in existing attached code.
Complete code:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
struct sln_node {
struct sln_node* next;
int key;
};
struct sln_list {
struct sln_node* head;
};
typedef struct sln_node sln_node;
typedef struct sln_list sln_list;
static sln_node* freelist = NULL;
/* Internal bookkeeping functions for the free list of nodes.
*/
sln_node* sln_allocate_node() {
sln_node* n;
if(freelist == NULL) {
freelist = malloc(sizeof(sln_node));
freelist->next = NULL;
}
n = freelist;
freelist = n->next;
n->next = NULL;
return n;
}
void sln_release_node(sln_node* n) {
n->next = freelist;
freelist = n;
}
void sln_release_freelist() {
sln_node* n;
while(freelist != NULL) {
n = freelist;
freelist = freelist->next;
free(n);
}
}
/* Create a new singly-linked list. */
sln_list* sln_create() {
sln_list* list = malloc(sizeof(sln_list));
list->head = NULL;
return list;
}
/* Release the list and all its nodes. */
void sln_release(sln_list* list) {
sln_node* n = list->head;
sln_node* m;
while(n != NULL) {
m = n->next;
sln_release_node(n);
n = m;
}
free(list);
}
/* Insert a new element to the list. */
void sln_insert(sln_list* list, int key) {
sln_node* n = sln_allocate_node();
n->key = key;
n->next = list->head;
list->head = n;
}
/* Check if the list contains the given element. Returns 1 or 0.
*/
int sln_contains(sln_list* list, int key) {
sln_node* n = list->head;
while(n != NULL && n->key != key) {
n = n->next;
}
return (n == NULL)? 0: 1;
}
/* Remove the first occurrence of the given element from the
list.
Returns 1 if an element was removed, 0 otherwise. */
int sln_remove(sln_list* list, int key) {
sln_node* n;
sln_node* m;
n = list->head;
if(n == NULL) { return 0; }
if(n->key == key) {
list->head = n->next;
sln_release_node(n);
return 1;
}
while(n->next != NULL && n->next->key != key)
{
n = n->next;
}
if(n->next != NULL) {
m = n->next;
n->next = m->next;
sln_release_node(m);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
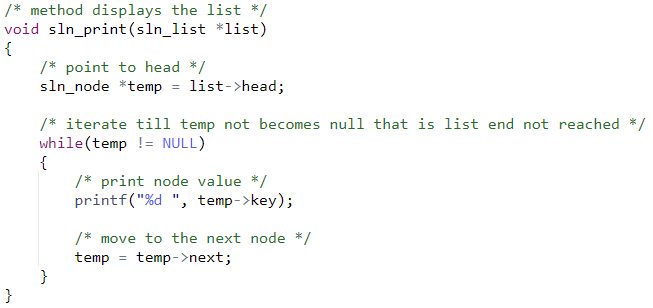
/* method displays the list */
void sln_print(sln_list *list)
{
/* point to head */
sln_node *temp = list->head;
/* iterate till temp not becomes null that is list end not reached
*/
while(temp != NULL)
{
/* print node value */
printf("%d ", temp->key);
/* move to the next node */
temp = temp->next;
}
}
/* modifies the list li so that it each element is
duplicated. For example the
list with elements [1,2,3] would after this function call become
the
list [1,1,2,2,3,3] */
void sln_stutter(sln_list* li)
{
/* make temporary varibale and make it point to head of the list
*/
sln_node *node = li->head;
/* iterte till the end of the list not reached */
while(node != NULL)
{
/* create temporary node */
sln_node* tempNode = sln_allocate_node();
/* assign the current node value as tempNode value */
tempNode->key = node->key;
/*the new node points to the next node of the curent node in the
list*/
tempNode->next = node->next;
/* current node next will point to new node */
node->next = tempNode;
/* make node points to the next element in the list which is next
node
to the new node added */
node = tempNode->next;
}
}
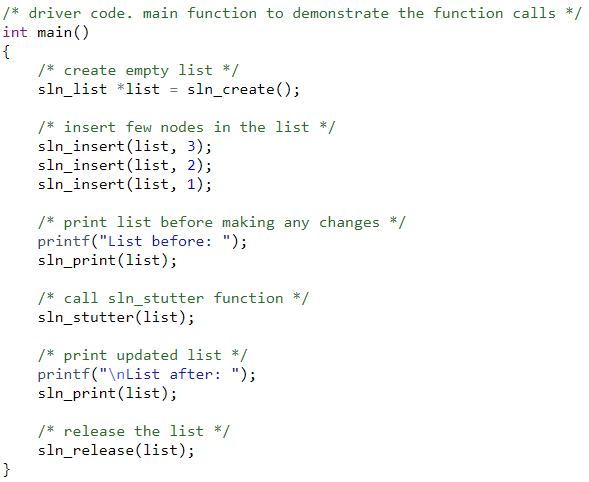
/* driver code. main function to demonstrate the
function calls */
int main()
{
/* create empty list */
sln_list *list = sln_create();
/* insert few nodes in the list */
sln_insert(list, 3);
sln_insert(list, 2);
sln_insert(list, 1);
/* print list before making any changes */
printf("List before: ");
sln_print(list);
/* call sln_stutter function */
sln_stutter(list);
/* print updated list */
printf("\nList after: ");
sln_print(list);
/* release the list */
sln_release(list);
}

Output from Sample Run:
Related Solutions
C++ Write the C++ code for a void function that prompts the user to enter a...
Using c++, write a program that will display your name as a void function then will...
In c++ language, write a void function GetYear that prompts for and inputs the year the...
4, Make the table project with C++. Write a function with the following interface: void multiplyTable(int...
Write c code program for the following Write a function, circle, which takes the radius of...
(In c++ language) 1A) Write a void function GetYear that prompts for and inputs the year...
Write C++ code according to this prompt: void print10LeapYears() gets a Gregorian year and prints the...
In C++ Complete the following code without the use of auto. Write a function, getAverages, that...
*Code in C* Write a function that checks if a number is a perfect cube. Write...
Please write the code in c++ Write a function with one input parameter that is a...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 venereology answered 2 months ago
venereology answered 2 months ago