Question
In: Computer Science
I have a list of things for review in C programming, could you please give me...
I have a list of things for review in C programming, could you please give me an example and a brief explanation for each question... Thank you very much
- 9. Apply pointer arithmetic to C code
- 10. Explain how multiple files can be organized and run in C, as well as what (recommended) content can be placed in header files
- 11. Explain how a link list can be created (i.e. what the nodes are and what components or syntax can be used to create the nodes)
Solutions
Expert Solution
NOTE: PROGRAMS ARE WRITTEN IN C LANGUAGE.
ALL PROGRAMS ARE DONE IN DEV-C++5.11 SOFTWARE. THEY ARE FULLY TESTED AND RUNNING PERFECTLY.
HERE ALL THREE 9), 10) 11) QUESTIONS ARE SOLVED IN DETAILS.
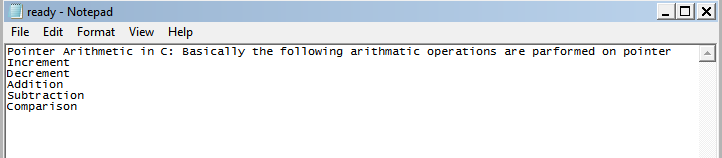
9) Apply pointer arithmetic to C code
Pointer Arithmetic in C: Basically the
following arethmatic operations are performed on pointer
Increment
Decrement
Addition
Subtraction
Comparison
PROGRAM
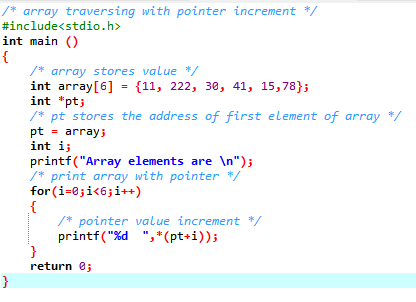
/* array traversing with pointer increment
*/
#include<stdio.h>
int main ()
{
/* array stores value */
int array[6] = {11, 222, 30, 41, 15,78};
int *pt;
/* pt stores the address of first element of array */
pt = array;
int i;
printf("Array elements are \n");
/* print array with pointer */
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
/* pointer value increment */
printf("%d ",*(pt+i));
}
return 0;
}
SCREEN SHOT
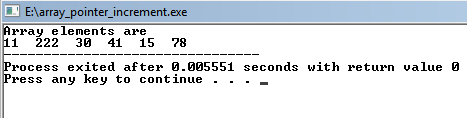
OUTPUT
PROGRAM
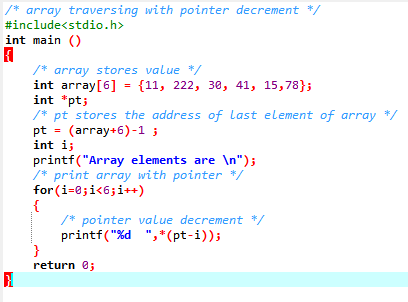
/* array traversing with pointer decrement
*/
#include<stdio.h>
int main ()
{
/* array stores value */
int array[6] = {11, 222, 30, 41, 15,78};
int *pt;
/* pt stores the address of last element of array */
pt = (array+6)-1 ;
int i;
printf("Array elements are \n");
/* print array with pointer */
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
/* pointer value decrement */
printf("%d ",*(pt-i));
}
return 0;
}
SCREEN SHOT
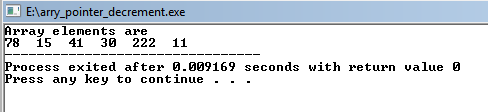
OUTPUT
PROGRAM
/* pointer subtraction and addition*/
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num=100;
/* pointer to integer */
int *p;
/*stores the address of num variable */
p=#
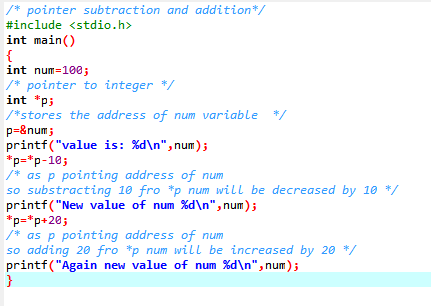
printf("value is: %d\n",num);
*p=*p-10;
/* as p pointing address of num
so substracting 10 fro *p num will be decreased by 10 */
printf("New value of num %d\n",num);
*p=*p+20;
/* as p pointing address of num
so adding 20 fro *p num will be increased by 20 */
printf("Again new value of num %d\n",num);
}
SCREEN SHOT
OUTPUT
10) Explain how multiple files can be organized and run in C, as well as what (recommended) content can be placed in header files
Here multiple files are created and organized through header file, created by use. Here "file.h" is created header file, where the multiple files information are stored and are used in .c file .
Here the example program is "read data from one file and
write to another file where the vowels
will be converted to upper case".
PROGRAM OF .c FILE
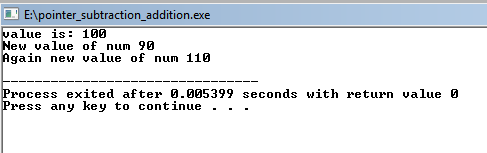
/* read data from one file and write to another file
where the vowels
will be converted to upper case */
#include<stdio.h>
/* include header file */
#include "file.h"
int main()
{
char ch;
/* file pointer fo,fi*/
FILE *fi,*fo;
char in[100],out[100];
/* take file names from header file "file.h" */
/* file_param will take input and output file name
from "file.h" header */
file_param(in,out);
/* open file */
fi=fopen(in,"r");
fo=fopen(out,"w");
/* read individual character of file from where to
read */
while( (ch = getc(fi)) != EOF)
{
/* convert vowels from lower case to upper case
and write in new file */
if(ch=='a' ) ch='A';
if(ch=='e' ) ch='E';
if(ch=='i' ) ch='I';
if(ch=='o' ) ch='O';
if(ch=='u' ) ch='U';
fprintf(fo,"%c",ch);
}
printf("New file is created with upper case vowels");
/* close both files */
fclose(fi);
fclose(fo);
return 0;
}
SCREEN SHOT OF .c FILE
PROGRAM OF "file.h"
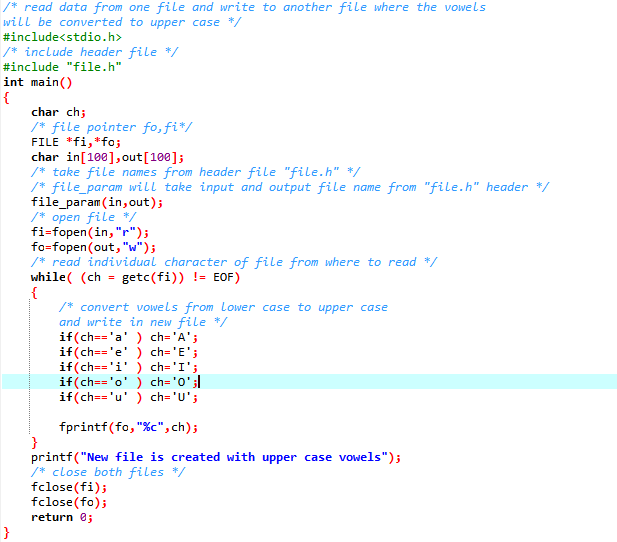
#include<string.h>
/* file_param will take two file names */
file_param(char input[], char output[])
{
strcpy(input,"ready.txt");
strcpy(output,"new_file.txt");
}
SCREEN SHOT OF "file.h"
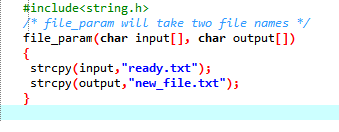
OUTPUT
THE FILE ready.txt IS READ BY PROGRAM
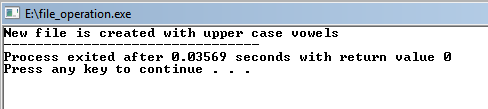
CREATED FILE IS new_file.txt, WHERE VOWELS OF LOWER CASE ARE CONVERTED TO UPPER CASE

11) Explain how a link list can be created (i.e. what the nodes are and what components or syntax can be used to create the nodes)
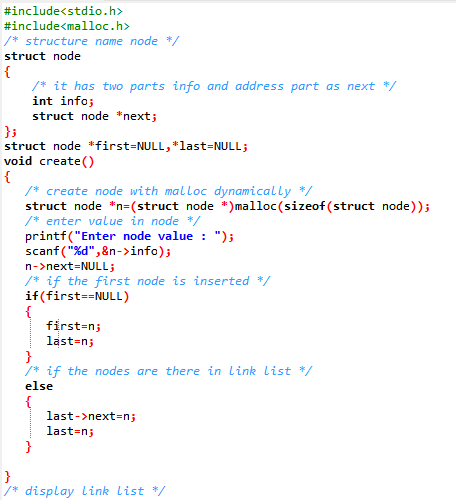
In link list the nodes are created
with structure representation. here
struct node
{
/* it has two parts info and address part as next
*/
int info;
struct node *next;
};
the structure has 2 parts. Through the structure basically, a node
is identified with two parts.
1. data part : here is denoted by integer info.
2. address part : here it is denoted by pointer next.
here two dummy pointers first and last are taken to point the first
and last node of the link list respectively.
i) Initially they are NULL, means no nodes are there.
ii) After that for first node insertion, first and last pointer
will take the address of first created node.
iii) In case of link list with allrady inserted node, if new node
is inserted, then pointer last will point the address of new
node.
it is given through following code as
/* first node is created */
if(first==NULL)
{
first=n;
last=n;
}
/* if the nodes are there in link list */
else
{
last->next=n;
last=n;
}
PROGRAM
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
/* structure name node */
struct node
{
/* it has two parts info and address part as next
*/
int info;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *first=NULL,*last=NULL;
void create()
{
/* create node with malloc dynamically */
struct node *n=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* enter value in node */
printf("Enter node value : ");
scanf("%d",&n->info);
n->next=NULL;
/* if the first node is inserted */
if(first==NULL)
{
first=n;
last=n;
}
/* if the nodes are there in link list */
else
{
last->next=n;
last=n;
}
}
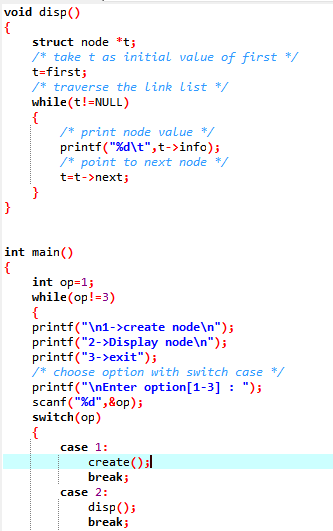
/* display link list */
void disp()
{
struct node *t;
/* take t as initial value of first */
t=first;
/* traverse the link list */
while(t!=NULL)
{
/* print node value */
printf("%d\t",t->info);
/* point to next node */
t=t->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int op=1;
while(op!=3)
{
printf("\n1->create node\n");
printf("2->Display node\n");
printf("3->exit");
/* choose option with switch case */
printf("\nEnter option[1-3] : ");
scanf("%d",&op);
switch(op)
{
case 1:
create();
break;
case 2:
disp();
break;
case 3:
printf("\nExit
from program\n");
break;
default:
printf("Give
correct choice[1-3]\n: ");
}
}
return 0;
}
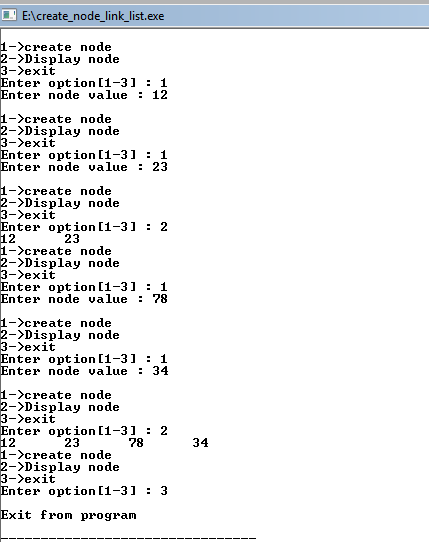
SCREEN SHOT
OUTPUT
Related Solutions
I was stuck on the following review problem on hypothesis testing. Could you please guide me...
I was stuck on the following review problem on hypothesis testing. Could you please guide me...
I am stuck on the following review problem on confidence intervals. Could you please guide me...
I am stuck on the following review problem on confidence intervals. Could you please guide me...
Could you please give me step-by-step on how to solve this. Thank you! I believe that...
I need for you to look at a couple of things and give me some guidance....
This is C++ there are intruction and descriptions. Please give me the answer because I understand...
This exercise I will list a series of words I want you to give me both...
client education for the disease pellagra. if you could please give me an outline for a...
can you please give me short answers only 4 or 5 sentence and please could you...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 venereology answered 2 months ago
venereology answered 2 months ago