Question
In: Chemistry
Consider the following reaction. 2NO2(g)⇌N2O4(g) When the system is at equilibrium, it contains NO2 at a...
Consider the following reaction. 2NO2(g)⇌N2O4(g) When the system is at equilibrium, it contains NO2 at a pressure of 0.722 atm, and N2O4 at a pressure of 0.0521 atm. The volume of the container is then reduced to half its original volume. What is the pressure of each gas after equilibrium is reestablished?
PNO2= ?? atm
PN2O4= ?? atm
Solutions
Expert Solution
P1V1 = P2V2 or P1/P2 = V2/V1 when the volume is reduced to half i.e V2 = 0.5 V1 , P1 / P2 = 0.5 = 1/2
P2 = 2 P1
So when the volume is reduced to half, the pressure will be doubled and it is assumed under isothermal condition.
The equation is
2 NO2 (g) 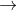 N2O4
(g)
Total P
N2O4
(g)
Total P
equillibrium pressure 0.722 atm 0.0521 atm 0.722 + 0.0521 = 0.7741 atm
Total Pressure = PNO2 + PN2O4
When reducing the volume to half
the total pressure is doubled A atm B atm 2 x 0.7741 = 1.5482 atm
A + B = 1.5482 atm
Where A and B are the new equillibrium pressure of NO2 and N2O4 respectively
Kp of the reaction at the given equillibrium pressures = [PN2O4] / [PNO2] 2
= 0.0521 / 0.7222 atm-1
= 0.1 atm-1
Kp under the new equillibrium conditions is given by
Kp = B / A2 but Kp = 0.1 atm-1
therefore 0.1 = B / A2 but A + B = 1.5482 atm and hencer B = [1.5482 - A] atm
0.1 = [1.5482 -A]/ A2
01 A2 = 1.5482 - A
or 0.1 A2 + A - 1.5482 = 0 This is quadratic equation in A can be solved
using the standard formula
x = [ - b 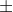
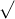 (b2 - 4 ac) ] / 2a
(b2 - 4 ac) ] / 2a
A =[ -1 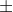
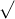 (
1 - 4 (0.1)(-1.5482)] / 0.2
(
1 - 4 (0.1)(-1.5482)] / 0.2
The pressure cannot be negative and hence we take only the positive
value of 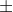 .
.
A =[ -1 + 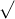 (1.61928) ] /0.2
(1.61928) ] /0.2
= [ -1 + 1.2725] / 0.2
= 0.2725/0.2 = 1.3625 atm therefore B = 1.5482 - 1.3625 = 0.1857 atm
PNO2 = 1.3625 atm
PN2O4 = 0.1857 atm
Related Solutions
Consider the reaction N2O4 (g) ? 2 NO2 (g). At equilibrium, a 2.00-L reaction vessel contains...
Consider the reaction: 2 NO2 (g) ⇌ N2O4 (g) The ΔGf° for NO2 (g) = 52...
The equilibrium constant (KP) is 0.16 at a particular temperature for the reaction: N2O4(g) ⇌ 2NO2(g)...
Consider the reaction: 2 NO2(g) → N2O4(g) Calculate ΔG (in kJ/mol) at 298°K if the equilibrium...
Consider the following equilibrium: N2O4(g)?2NO2(g) Thermodynamic data on these gases are given in Appendix C in...
The degree of dissociation, α, for the following reaction: N2O4(g) <--> 2NO2(g) is 0.655 at 298...
For the following reaction, Kc = 0.513 at 500 K. N2O4(g)⇌2NO2(g) If a reaction vessel initially...
The following system is at equilibrium with [N2O4] = 0.55 M and [NO2] = 0.25 M....
Consider the reaction: NO2 (g) + CO (g) ---> CO2 (g) + NO (g) The equilibrium...
The value of Kc for the reaction: N2O4(g) ↔ 2NO2 (g) is 0.21 at 373K. If...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 months ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 months ago