Question
In: Biology
COVID-19 belongs to the genera Beta-coronavirus. Compare and contrast the genomic and phenotypic structure between COVID-19...
COVID-19 belongs to the genera Beta-coronavirus. Compare and contrast the genomic and phenotypic structure between COVID-19 and one other member of the Beta-coronavirus genera, along with their associated pathogenesis?
Solutions
Expert Solution
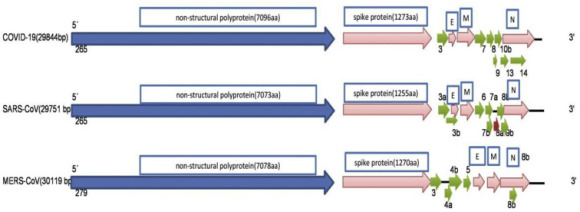
Coronaviruses are involved in human and vertebrate's diseases.Coronaviruses are members of the subfamily Coronavirinae in the family Coronaviridae and the order Nidovirales. COVID-19 is a spherical or pleomorphic enveloped particles containing single-stranded (positive-sense) RNA associated with a nucleoprotein within a capsid comprised of matrix protein. The envelope bears club-shaped glycoprotein projections. Some coronaviruses also contain a hem agglutinin-esterase protein (HE)4 . Coronaviruses possess the largest genomes (26.4–31.7 kb) among all known RNA viruses, with G + C contents varying from 32% to 43%.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1) is a strain of virus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS).It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which infects the epithelial cells within the lungs. The virus enters the host cell by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. It infects humans, bats, and palm civets. SARS-CoV-2 is the third highly pathogenic coronavirus to emerge and spread in human populations. Phylogenetic analyses showed that, as SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 is a member of the Sarbecovirus subgenus (genus Betacoronavirus)
Related Solutions
Describe the basic structure of the coronavirus, SARS-CoV2. What is the difference between SARS-CoV2 and COVID-19?...
Compare and contrast the biological pathways and epidemiology of the novel corona virus (Covid 19) with...
Compare and contrast the biological pathways and epidemiology of the novel corona virus (Covid 19) with...
Compare and contrast events of the current COVID-19 Pandemic with that of one or more pandemics in history.
Question: • Compare and contrast Donald Trumps approach to Covid-19 with the approach taken by Jacinder...
Prompt: Coronavirus (Covid-19) is an enveloped virus. Enveloped viruses like Covid-19 are referred to as being...
By now, you know all bout CORONAVIRUS (COVID-19) as a pandemic threat to the world. COVID-19...
Describe the structure of the COVID-19 virus
COVID-19 The recent outbreak of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) has introduced new challenges to the business environment....
COVID-19 is a contagious disease caused by a newly discovered coronavirus.
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
 gladiator answered 3 months ago
gladiator answered 3 months ago