Question
In: Computer Science
#1: Write a program that optionally accepts an address and a port from the command line....
- #1: Write a program that optionally accepts an address and a port from the command line. If there is no address/port on the command line, it should create a TCP socket and print the address (i.e. server mode). If there is an address/port, it should connect to it (i.e. client mode). Once the connections are set up, each side should enter a loop of receive, print what it received, then send a message. The message should be “ping” from the client and “pong” from the server.
Hints:
You will need to pick a port for the server – something over 1024.
Ensure that you open your firewall to let the signal through.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Herewith I am providing a C program to demonstrate the given client-server environment.
server.c
#include<stdio.h>
//This header file contains declarations used in most input and
output and is typically included in all C programs.
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
// The header file socket.h includes a number of definitions of
structures needed for sockets.
#include<netinet/in.h>
//The header file in.h contains constants and structures needed for
internet domain addresses
#include<sys/types.h>
//This header file contains definitions of a number of data types
used in system calls. These types are used in the next two include
files.
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
void error(const char *msg)
{
perror(msg);
exit(1);
}
if(argc<2)
{error("\nPort number not provided, program terminated\n");}
int sock, newsock, n, port, i;
char buffer[200];
struct sockaddr_in address;
socklen_t len;
len = sizeof(address);
bzero((char *)&address, sizeof(address));
if((sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0))==0)
error("\nERROR: Socket not created\n");
port = atoi(argv[1]);
address.sin_family = AF_INET;
address.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
address.sin_port = htons(port);
bind(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&address, sizeof(address));
listen(sock, 3);
newsock = accept(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&address,
&len);
if(newsock<0)
error("ERROR: Accept");
/*
bzero(buffer, 200);
n = read(newsock, buffer, 200);
if(n<0)
error("ERROR: READING");
printf("\nClient: %s", buffer);
*/
do{
bzero(buffer, 200);
n = read(newsock, buffer, 200);
if(n<0)
error("ERROR: READING");
printf("\nClient: %s", buffer);
bzero(buffer, 200);
fgets(buffer, 200, stdin);
n = write(newsock, buffer, strlen(buffer));
if(n<0)
error("ERROR: WRITING");
printf("\nMe: %s",buffer);
i = strncmp(buffer,"Bye", 3);
if(i==0)
break;
}while(1);
close(newsock);
close(sock);
return 0;
}
client.c
#include<stdio.h>
//This header file contains declarations used in most input and
output and is typically included in all C programs.
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<netdb.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
// The header file socket.h includes a number of definitions of
structures needed for sockets.
#include<netinet/in.h>
//The header file in.h contains constants and structures needed for
internet domain addresses
#include<sys/types.h>
// This header file contains definitions of a number of data types
used in system calls. These types are used in the next two include
files.
void error(const char* msg)
{
perror(msg);
exit(1);
}
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
if(argc<2)
error("\nIP address, Port number not provided\n");
if(argc<3)
error("\nPort number not provided\n");
int sock, n, port, i;
struct sockaddr_in server;
struct hostent *address;
char buffer[200];
socklen_t len;
len = sizeof(server);
bzero((char *)&server, sizeof(server));
sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
//int socket(domain, type, protocol)
if(sock<0)
error("Socket Could Not Be Created\n");
else
printf("Socket Created Succesfully\n");
port = atoi(argv[2]);
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_port = htons(port);
address = gethostbyname(argv[1]);
bcopy((char *)address->h_addr,
(char*)&server.sin_addr.s_addr, address->h_length);
//inet_pton(&server, , &server.s_addr);
n = connect(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&server, len);
if(n<0)
error("ERROR: Connect");
do{
bzero(buffer, 200);
fgets(buffer, 200, stdin);
n = write(sock, buffer, strlen(buffer));
if(n<0)
error("ERROR: WRITING");
printf("\nMe: %s", buffer);
bzero(buffer, 200);
n = read(sock, buffer, 200);
if(n<0)
error("ERROR: READING");
printf("\nServer: %s", buffer);
i = strncmp(buffer,"Bye", 3);
if(i==0)
break;
}while(1);
close(sock);
return 0;
}
Output screenshot
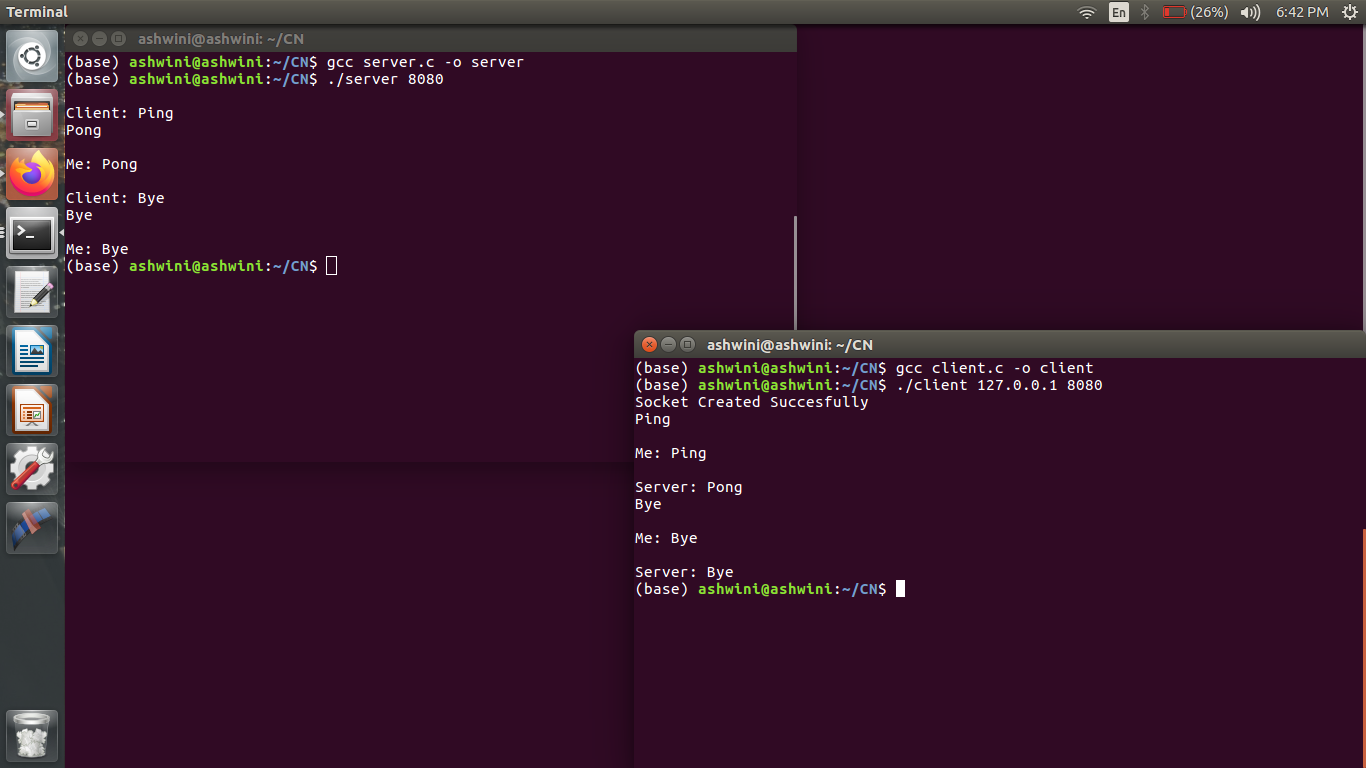
Related Solutions
Write a C program that accepts a port number as a command line argument, and starts...
Write a C program that accepts a port number as a command line argument, and starts...
program c Write a program called filesearch that accepts two command-line arguments: A string A filename...
A C program that accepts a single command line argument and converts it in to binary...
Write a Java application that accepts a bar code as a command line parameter and prints...
The program should be able to do the following: In Java accepts one command line parameter....
The Java program should be able to do the following: accepts one command line parameter. The...
Write a program that takes an integer N from the command line and uses StdRandom.uniform() to...
Use C++ to write a program that reads in a binary string from the command line...
Write a Java program which reads a positive integer from the command line, then displays the...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 venereology answered 3 months ago
venereology answered 3 months ago