Question
In: Chemistry
Calculate the diffusion coefficient of N2 at 100 Pa, 100 kPa an 20 MPa (temperature T...
Calculate the diffusion coefficient of N2 at 100 Pa, 100 kPa an 20 MPa (temperature T = 20 degrees celsius).
Solutions
Expert Solution
(a)
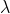 = kT /
(2^0.5)
= kT /
(2^0.5)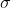 p)
p)
=> 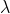 = [(1.381 x
10^-23 J K^-1) (293 K)] / [(2^0.5) (0.36 x 10^-18m^2) (100 Pa)]
= [(1.381 x
10^-23 J K^-1) (293 K)] / [(2^0.5) (0.36 x 10^-18m^2) (100 Pa)]
[We know J/K = Kg m2 s^-1 and Pa = Kg m^-1 s^-2
= 7.94 x 10^-5 m
---------------------------
Average speed = (8RT / 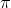 M)^0.5
M)^0.5
= (8 x 8.314 J K^-1 mol^-1 x 293 K / 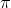 28 x 10^-3 Kg
mol)^0.5
28 x 10^-3 Kg
mol)^0.5
[We know J L^-1 mol^-1 = kg m^2 s^-1]
= (221543.86 m/s)^0.5
= 470.68 m/s
--------------------------
Diffusion D = 1/3 (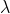 C)
C)
= 1/3 ( 7.94 x 10^-5 m) (470.68 m /s)
= 0.0125 m^2/s
-------------------------------------------------------
b) at 100 k Pa = 100 x 10^3 Pa
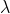 = kT /
(2^0.5)
= kT /
(2^0.5)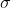 p)
p)
=> 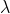 = [(1.381 x
10^-23 J K^-1) (293 K)] / [(2^0.5) (0.36 x 10^-18m^2) (100 x 10^3
Pa)]
= [(1.381 x
10^-23 J K^-1) (293 K)] / [(2^0.5) (0.36 x 10^-18m^2) (100 x 10^3
Pa)]
[We know J/K = Kg m2 s^-1 and Pa = Kg m^-1 s^-2
= 7.94 x 10^-8 m
D= (1/3)(7.94 x 10^-8 m) (470.68 m/s)
= 1.245 x 10^-5 m^2/s
---------------------------------------------------------
c) at 20 MPa = 20 x 10^6 Pa
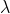 = kT /
(2^0.5)
= kT /
(2^0.5)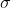 p)
p)
=> 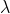 = [(1.381 x
10^-23 J K^-1) (293 K)] / [(2^0.5) (0.36 x 10^-18m^2) (20 x 10^6
Pa)]
= [(1.381 x
10^-23 J K^-1) (293 K)] / [(2^0.5) (0.36 x 10^-18m^2) (20 x 10^6
Pa)]
[We know J/K = Kg m2 s^-1 and Pa = Kg m^-1 s^-2
= 3.974 x 10^-10 m
D= (1/3)(3.974 x 10^-10 m) (470.68 m/s)
= 6.23 x 10^-8 m^2/s
Related Solutions
4.14 (a) Calculate the diffusion coefficient for oxygen ions in a pure ZrO2 electrolyte at T...
Water is flowing in a compressor steadily at 20 kPa and 40 oC to 1.7 MPa...
Nitrogen undergoes an isothermal process from 100 kPa to 500 kPa, T = 300K. How much...
A mass of 0.07 kg of air at a temperature of 30°C and pressure 100 kPa...
Air is at 100 kPa and 150°C, and undergoes a constant pressure process. The final temperature...
Independent Samples T-test 1. If n1 = 100 and n2 = 100, determine the critical value...
calculate the coefficient of isothermal compressibility of a gas at 440 psia and temperature of 80...
0.5 kg of a gas at temperature t1=20?C and pressure p1=0.1 MPa was contained in a...
Air enters an adiabatic compressor at 100 kPa (absolute) and 20 ºC at a rate of...
Calculate the diffusion constant of argon at 20°C and at the following pressures. Take σ =...
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 4 months ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 4 months ago