Question
In: Chemistry
Choose 3 journal articles you think will be useful as references for your formal lab report...
Choose 3 journal articles you think will be useful as references for your formal lab report paper. You may use review articles or research articles. You might try typing in a keyword for your topic and the word “review”. Obtain copies either from the library or from an on-line resource. In the space provided below, explain in no more than 5 sentences per article why you feel the article you have selected is appropriate for your paper. Just because your key word appears in the title does not automatically mean the paper will be useful for your report. Briefly state how you will use it in your report. Attach a copy of each article to the assignment before handing it in. Directions on how to access electronic journals through the University of Houston Library are at the end of this document. If you cannot download an article you desire directly from the PubMed website, try through the University of Houston Library electronic journals collection. If the university does not have the electronic version on file, you will have to go to the library and copy it on a copy machine (the old-fashioned way). If you cannot obtain a copy of the article, you can place a request through interlibrary loan at the service desk at the library or you will need to find another article.
in Crystallography
you can chose any subject you want :)
Solutions
Expert Solution
Crystallography is the science of determining and studies of arrangement of atoms in the crystalline solids.A 3D translationaly periodic arrangement of atoms in space is called a crystal.Lets make the report on the structural makeup of the diamond which isolates it from other crystalline structure.
The Crucial Role Of Crystallography on Diamond Research:-
References:-
1Earth science: Crystallography's journey to the deep Earth by Thomas Duffy 26 February 2014 published in NATURE:-
Diamonds are found under the earth at high-pressure and temperature.Samples of minerals less than 50 micrometres across are compressed between the tips of gem-quality diamonds.researchers fire lasers or X-rays through the diamonds at the samples, to heat them and to investigate their structures using crystallographic methods.
The diamond anvil cell is the primary tool for high-pressure and temperature mineral studies. Samples of minerals less than 50 micrometres across are compressed between the tips of gem-quality diamonds. Then researchers fire lasers or X-rays through the diamonds at the samples, to heat them and to investigate their structures using crystallographic methods.The picture that has emerged is that the main minerals found in the upper mantle — olivine, pyroxene and garnet — undergo a series of phase transitions to denser forms with increasing dept.
2.Volume 106, Number 6, November–December 2001 Journal of Research of the National Institute of Standards and Technology [J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 106, 889–920 (2001)] High Pressure X-Ray Crystallography With the Diamond Cell at NIST/NBS
Scientists in the Crystallography Section at NIST/NBS made several outstanding contributions which greatly promoted the development and advancement of high pressure x-ray crystallography during the second-half of the 20th century. These milestone achievements or “firsts” included: (1) the invention of the lever-arm type diamond anvil cell (DAC) in 1958; (2) the development of DAC technology for powder x-ray diffraction at high pressure in 1960; (3) the introduction of DAC methodology for single crystal x-ray diffraction at high pressure in 1964; (4) the invention of the optical fluorescence ruby method of pressure measurement in 1971; and (5) the discovery of hydrostatic pressure-transmitting media useful to unprecedented pressures for that time.
3.The crucial role of crystallography in diamond research BYFabrizio Nestola
Diamond Light Source Annual Review
The 2011 Diamond Annual Review, which highlights some of the world-class research recently undertaken at Diamond Light Source is now available from their website. The report includes a contribution from Prof. Paul Beer covering some of the fascinating interlocked structures determined from data collected using the Small Molecule Beamline, I19, as part of the Oxford Block Allocation Group (BAG). Highlights of their work include a novel halogen bonded rotaxane and the first reported crystal structure of a “handcuff catenane”.
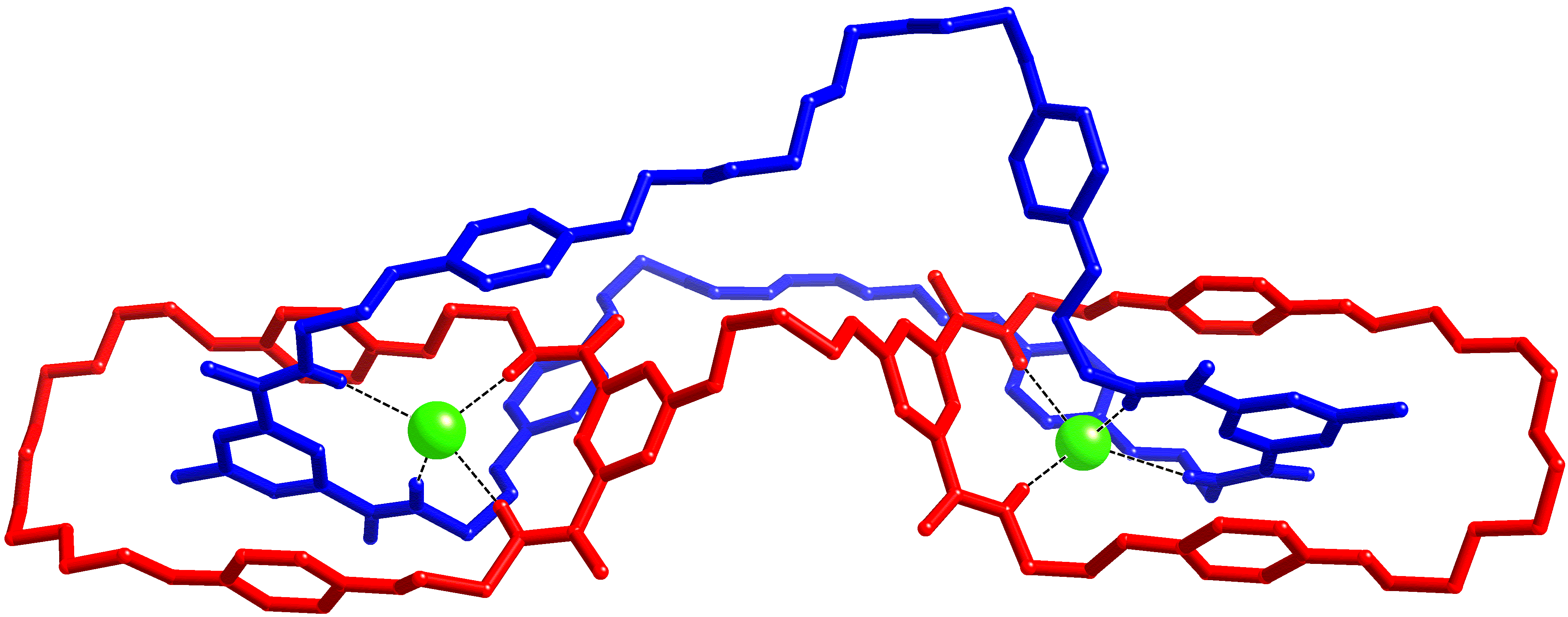
Structure of a handcuff catenane
All these article i have referred to understand the crystal structure of the diamond and its atomic position and arrangement.It also suggest us it is the environmenal condition i.e high temperature and pressure which is responsible for the extraordinary charcter of the diamond which is one of the hardest and shinest material on Earth.
Related Solutions
The 3D printing formal lab report ?
Your answers to this assignment should include references to recently published journal articles or books, media...
In formal chemistry lab report. How to address there is a 20mins waiting period between...
You are required to use at least 3 different ACADEMICALLY credible articles/books/websites as references. You can...
You are required to use at least 3 different ACADEMICALLY credible articles/books/websites as references. You can...
Using a minimum of 3 approved sources (articles from major news outlets, academic journal articles, NOT...
Make a 2 report page: Refer to your textbook and other scholar literature references that you...
Write a report about Non-parametric Tests and refere to your references
Go to the Internet and locate one journal articles in your area of interest which is...
Individually, students will read 3-5 journal / research articles that pertain to marketing a service (as...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 queen_honey_blossom answered 4 months ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 4 months ago