Question
In: Physics
Two 50 ?? long, thin parallel straight wires (grey) are connected at their ends by metal...
Two 50 ?? long, thin parallel straight wires (grey) are connected at their ends by metal springs. The mass of each thin wire is 1.0 ?. The upper wire is connected to the ceiling by (non-conducting) stiff rods. Each spring has an equilibrium length of 5.0 ?? and a spring constant of ? = 0.50 ?/?. A steady current ? runs clockwise through the wire-spring loop as indicated by the arrow. At equilibrium, the lower rod hangs at a level 6.0 ?? below the upper wire. Find the magnitude of the current. You may ignore the magnetic fields generated by the springs, and you may approximate the magnetic fields generated by the wires as those from long, straight wires
Solutions
Expert Solution
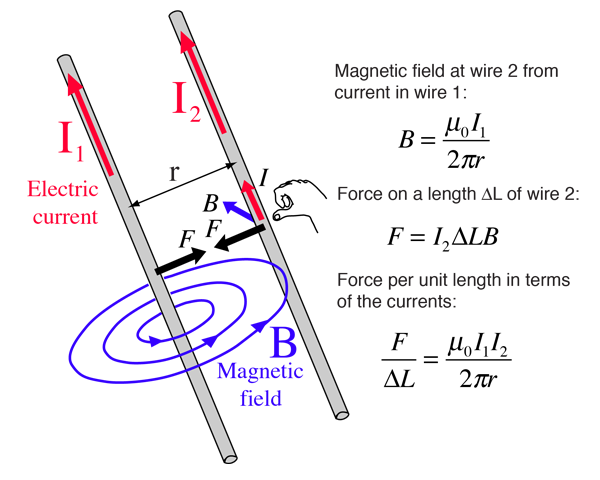
As you can see above if two parallel wires carry current in same direction they attract each other but in our case, they are in opposite directions Hence they repel.
The forces acting are
Magnetic repulsion will act downwards
Weight will act downwards
spring force will act upwards (wire is held)
Balancing them
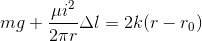
Here r0 is natural length of spring and r is given as 6cm.
m = 1gram dl = 50cm
Thus calculating individually
mg = 0.0098 N
2k(r-r0) = 2k(1cm) = 0.01N
Thus leaving us magnetic force = 2k(r-r0) - mg= 0.0002N
mu/2pi = 2 * 10^-7
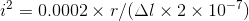
Thus
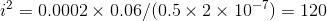
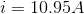
Please Upvote if you like the answer...
Related Solutions
Two long straight parallel wires are oriented north-south. Both wires carry constant current due North and...
Chapter 29, Problem 009 Two long straight wires are parallel and 8.6 cm apart. They are...
Two long, straight, parallel wires are separated by 0.50 m and lie in the X-Y plane....
1. Imagine two very long, parallel, straight wires carrying a current, I, in equal but opposite...
Two long thin parallel wires 13.0 cm apart carry 25-A currents in the same direction. Part...
Two long straight parallel wires are 11 cm apart. Wire A carries 2.0-A current. Wire B's...
Two long parallel wires are placed side by side on a horizontal table. The wires carry...
Three long straight parallel wires are each carrying a steady current I in the same direction....
Two long, straight wires are perpendicular to the plane of the paper and at a distance...
Two resistors 30 Ω and 50 Ω are connected in parallel and this parallel arrangement is...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 genius_generous answered 4 months ago
genius_generous answered 4 months ago