Question
In: Chemistry
Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of the following amounts of 0.0577 M...
Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of the following amounts of 0.0577 M HNO3 to a 80.0 mL solution of 0.0750 M aziridine. The pKa of aziridinium is 8.04
a) 0.00 mL of HNO3 b) 7.72 mL of HNO3 c) Volume of HNO3 equal to half the equivalence point volume d) 99 mL of HNO3
e) Volume of HNO3 equal to the equivalence point f) 107 mL of HNO3
Solutions
Expert Solution
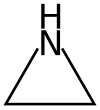 aziridine is C2H5N
aziridine is C2H5N
pKa Aziridine) = 8.04 so -log Ka = 8.04 Therefore Ka = 10^-8.04
OH - ion conc = (Ka*C)^1/2 = (0.0750*10^-8.04)^1/2 = 2.6154*10^-5
a)
Moles of H+ ion - moles of OH - ion = 0.0577*0.00/1000 - 2.6154*80/1000 (because moles = molarity * volume)
= 0 - 0.2090
= - o.2092
so OH- ionare in excess , = + .2092
so pOH = = -log (OH-) = - log(0.2092) = 0.6794
pH = 14 - pH = 14 - 0.6794 = 13.32
b)
moles of H+ ion - moles of OH-
= 0.0577*7.72/1000 - 2.6654*10^-5 * 80/1000
= 4.454*10^-4 - 2.09232*10^-6
= 4.433*10^-4 = excess H+ ion conc
pH = - log (H+ ion conc 0 - log(4.433*10^-4) = 3.3533
d)
moles of H+ ions - moles of OH-
= 0.0577*99/1000 - 2.6154*10^-5*80/1000
= 5.7123*10^-3 - 2.09*10^-6
so excess of H+ ion conc = 5.71020*10^-3
pH = - log (H+ ion conc = - log(5.71021*10^-3) = =2.2433
f)
moles of H+ ions - moles of OH- ions
= 0.0577*107/1000 - 2.6154*10^-5 *80/1000
= 6.1739*10^-3 - 2.09232*10^-6
= 6.1718*10^-3 = excess H+ ions
so pH = - log H+ ion conc = - log(6.1718*10^-3) = +2.2096
e)
At equivalence point
pH = 14 + log (Ca*Cb(Kw) /(Ca+Cb)*Ka ) ^1/2
= 14 + log (0.0577*2.6154*10^-5 * 10^-14 /(0.0577+2.6154*10^-5 ) * 10^-8.04 )^1/2
= 14 + log (1.509*10^-20/5.2647*10^-10)^1/2 = 14-10.5426 = 3.457
c )
At half equivalence point
pH = pKa + log base/acid
But base = acid = 1 say
so pH = pKa + log 1/1
pKa + log 1 = pKa + 0 = 8.04 +0 = 8.04
Related Solutions
Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of the following amounts of 0.0615 M...
Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of the following amounts of 0.0602 M...
Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of the following amounts of 0.0656 M...
Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of the following amounts of 0.0536 M...
Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of the following amounts of 0.0649 M...
Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of the following amounts of 0.0568 M...
Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of the following amounts of 0.0656 M...
Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of each of the given amounts of...
calculate the pH of a solution that results from the addition of the following amounts of...
Calculate the pH of a buffer solution after the addition of 20.0 mL of 0.200 M...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 10 months ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 10 months ago