Question
In: Chemistry
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 4.0
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 4.0
Solutions
Expert Solution
Diprotic acid refers to acid that dissociates to give two H+ ion.
First, write down chemical equations. There will be two steps since this is "di"protic acid.
1. H2A >> H+ + HA-
2. HA- >> H+ + A2-
Then, write down expressions for Ka.
(1st equation)
1. 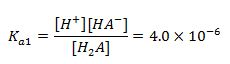
(2nd equation)
2. 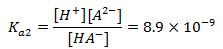
As you can observe, there are four unknowns, i.e., [H2A], [H+], [HA-], and [A2-]. We already have two equations so we need two more to solve this. We can generate two more equations by making assumptions.
We can base one assumption on the fact that the value of Ka1 for this acid is a lot times larger than the value of Ka2.
This means that only a small fraction of the HA- ions formed in the first step go on to dissociate in the second step. If this is true, most of the H+ ions in this solution come from the dissociation of H2A, and most of the HA- ions formed in this reaction remain in solution. As a result, we can assume that the H+ and HA- ion concentrations are more or less equal.
(3rd equation)
|
First assumption: |
[H+]=[HA-] |
We need one more equation, and therefore one more assumption. Since H2A is a weak acid, we can assume that most of the H2A that dissolves in water will still be present when the solution reaches equilibrium. In other words, we can assume that the equilibrium concentration of H2A is approximately equal to the initial concentration of 0.0700 M.
(4th equation)
|
Second assumption: |
[H2A] =CH2A=0.07 M |
We now have four equations for the four unknowns.
Using the 1st,3rd and 4th equations...
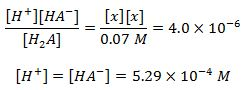
Using the 2nd equation and the computed value above..The answers to the question "equilibrium concentrations of H2A and A2-" are encircled in red below.
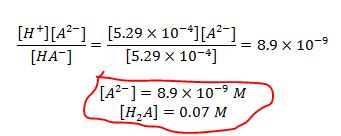
We need to validate if our assumptions are correct. Our first assumption was that the dissociation of H2A is small compared to the initial concentration.. Comparing the concentration of [H+] computed and initial concentration given...
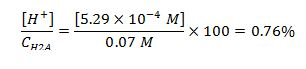
Result above shows that indeed a very small amount, 0.76%, dissociated to H+.
Answering the question "pH of acid solution"..
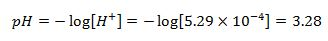
Related Solutions
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 2.8
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 3.2 × 10^-6 and Ka2 = 8.0 ×...
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 2.5 × 10-6 and Ka2 = 5.5 ×...
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 3.3 × 10-6 and Ka2 = 8.2 ×...
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 3.4 × 10-6 and Ka2 = 8.2 ×...
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 3.1 × 10-6 and Ka2 = 6.6 ×...
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 2.8 × 10-6 and Ka2 = 8.7 ×...
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 2.2 × 10-6 and Ka2 = 8.3 ×...
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 3.1 × 10-6 and Ka2 = 5.4 ×...
For the diprotic weak acid H2A, Ka1 = 3.0 × 10^-6 and Ka2 = 7.6 ×...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 queen_honey_blossom answered 1 year ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 1 year ago