Question
In: Physics
A photon of wavelength 0.65037 nm strikes a free electron that is initially at rest. The...
A photon of wavelength 0.65037 nm strikes a free electron that is initially at rest. The photon is scattered straight backward. What is the speed of the recoil electron after the collision?
Solutions
Expert Solution
When a gamma ray photon collides with an electron, Compton scattering occurs. Compton scattering is a type of elastic scattering that results in a change in the photon's wavelength called a Compton shift sure to its transfer of energy and momentum to the electron. The Compton shift depends entirely on the scattering angle, so a photon scattered in a given direction will always have the same change in its wavelength.
In Compton scattering, the change in the wavelength of the incident photon depends only on the scattering angle
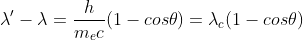
where 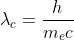
is the Compton wavelength for an electron.
This means that the final wavelength of the photon is,
= 6.98896 × 10-11 m
where there angle is 180° since the photon scattered backwards and the wavelength of the photon is given.
By the conservation of energy, because Compton scattering is elastic, the energy lost by the photon is gained by the electron.
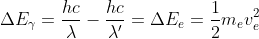
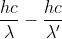
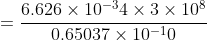
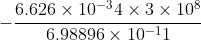
J
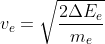
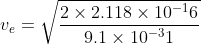 =
2.16 × 107 m/s
=
2.16 × 107 m/s
Related Solutions
An X-ray photon with a wavelength of 0.120 nm scatters from a free electron at rest....
Compton Scattering.A photon of wavelength λcollides elastically with a free electron (initially at rest) of mass...
An X-ray photon with a wavelength of 0.979 nm strikes a surface. The emitted electron has...
An X-ray photon of wavelength 0.958 nm strikes a surface. The emitted electron has a kinetic...
An incident x-ray photon is scattered from a free electron that is initially at rest. The...
A 3100 TeV photon strikes an electron at rest and scatters by an angle of 120°....
An electron in the hydrogen atom falls from the 2p to 1s state and a photon is emitted. What is the wavelength of the emitted photon (in nm)?
A photon moving in the +x-direction, scatters off a free stationary electron. The wavelength of the...
A photon moving in the +x-direction, scatters off a free stationary electron. The wavelength of the...
A photon, moving in the +x-direction, scatters off a free stationary electron. The wavelength of the...
- C PROGRAMMIMG I want to check if my 2 input is a number or not all...
- In long paragraphs answer the questions below: Discuss the key components (where, when, what) and causes...
- Sinkal Co. was formed on January 1, 2018 as a wholly owned foreign subsidiary of a...
- Larry’s best friend, Garfield, owns a lasagna factory. Garfield’s financial skills are not very strong, so...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
 genius_generous answered 1 year ago
genius_generous answered 1 year ago