Question
In: Electrical Engineering
Design a distribution system simply explain with figure how electricity is transferred from Generating point to...
Design a distribution system
simply explain with figure how electricity is transferred from Generating point to homes.
Solutions
Expert Solution
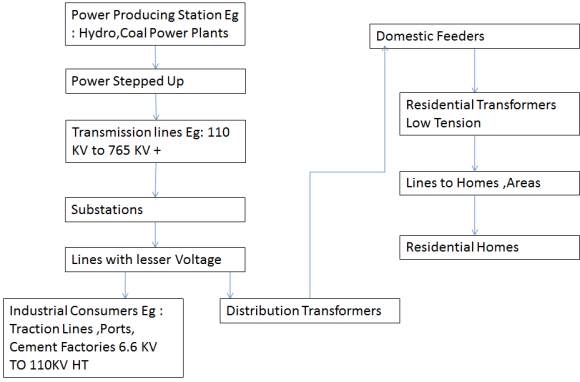
Power Production & Distribution :
1.Electricity is generated from large generating stations like Steam (Coal) , hydroelectric, nuclear power plants. Also through Wind, Solar, Geo thermal power plants etc.
2. The same generated power can't be directly utilized since they are at long distance from consumers at remote locations.
3. To decrease losses, the power generated is stepped up to higher voltages like 220KV,465KV ,765KV etc.
4. The main principle of stepping up voltage is decreasing size of conductors (Wire size) and line losses. More current increases losses hence by stepping current is reduced.
5. Then the power reaches various substations where the voltage is lowered. Substations are ranging from 11KV,33KV,110KV,220KV,465KV,765KV and even 1000KV +HT substations. Usually 200KV + Substations will employed after generating stations. There will be many substations before reaching domestic and industrial consumers.
6. Industrial consumers uses power in range of 415V, 6.6KV to 110KV system.
7. Through Transmission and distribution lines and various substations having power quality equipment and transformer. Power reaches to various feeders for house supplies.
8. This supply is fed to each homes through proper tappings. From then to residential wiring system
Transformers used in distributions are called distribution transformer since they increase current levels and decrease voltage.
9. The entire system is called power grid. Power grids are locations where transient stability and power quality parameters are achieved .
Nowadays Microgrids are in practice to localize , these grids control power system parameters and also efficient in maintaining demand-supply model.
Related Solutions
Explain the difference in how energy is transferred by mechanical waves and how it is transferred...
Explain how a nervous signal originates and then is transferred from the stimulus to the receiving...
Recall the truncated distribution function F* and the algorithm for generating from it, as given in...
Design an ECBM system with methane recovery, electricity generation, and carbon sequestration for a coal field...
9. Explain what two types of proteins are transferred from the cytosol to the ER. How...
a. Expound on the desirable design of wholesale electricity markets. Explain the risk of market power...
Explain how to convert solar energy to electricity?.
1- Explain your understanding of the how the action potential (the electricity) passes from the motor...
choose a product and illustrate and explain all the processes from pre-design to packaging and distribution.
Explain how should the company account for transferred receivables.
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
 Manojponduru answered 1 year ago
Manojponduru answered 1 year ago