Question
In: Physics
(a) Calculate the angular momentum of Venus due to its orbital motion about the Sun. In...
(a) Calculate the angular momentum of Venus due to its orbital
motion about the Sun. In your calculation, use
1.080 1011 m as the average Venus-Sun
distance and 1.940 107s as the period of
Venus in its orbit.
kg·m2/s
(b) Assume that Venus's angular momentum is described by Bohr's
assumption . Determine the corresponding quantum number.
(c) By what fraction would one have to increase the radius of
Venus's circular orbit in order to raise the quantum number by
1?
Solutions
Expert Solution
(a)
given that
r = 1.080  1011
1011
T = time period = 1.940  107
107
m = 4. 867  1024 kg
1024 kg
angular momentum is given as


 Kg m2 /s
Kg m2 /s
(b) now if the angular momentum is defined by bohr `s assumption than
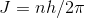
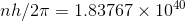
- where h = plank`s constant = 6.6
 10 -34 J S
10 -34 J S 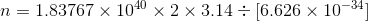
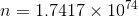 where n = corresponding quantum number .
where n = corresponding quantum number .
(c) -
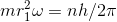 ........................(1)
........................(1)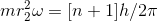 ................(2)
................(2)- deviding equation 2 & 1 we have
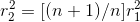
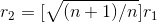 ANSWER
ANSWER
Related Solutions
1. Calculate the angular momentum of the Sun and compare it to the sum angular momentum...
1. Calculate the
angular momentum of the Sun and compare it to the sum angular
momentum of the planets (of their orbits only).
An electron has spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum. For the 4 d electron in...
An electron has spin angular momentum and orbital angular
momentum. For the 4 d electron in scandium, what
percent of its total orbital angular momentum is its spin angular
momentum in the z direction?
An electron has spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum. For the 3.00 d electron in...
An electron has spin angular momentum and orbital angular
momentum.
For the 3.00 d electron in scandium, what percent of
its total orbital angular momentum is its spin angular momentum in
the z direction?
a) Calculate, in units ofℏ, the magnitude of the maximum total (orbital+spin) angular momentum for an...
a) Calculate, in units ofℏ, the magnitude of the maximum total
(orbital+spin) angular momentum for an electron in a hydrogen atom
for states with a principal quantum number of 5.
b) An electron initially in a 4p state decays to a lower energy
state. Which energy state is forbidden? (pick one): 1s, 2s, 3d, or
2p? Why?
c) What is the total number of electrons that can occupy a
subshell for a given amount of orbital angular momentum l? Write...
a) Calculate, in units of ℏ, the magnitude of the maximum total (orbital+spin) angular momentum for...
a) Calculate, in units of ℏ, the magnitude of the maximum total
(orbital+spin) angular momentum for an electron in a hydrogen atom
for states with a principal quantum number of 5.
b) An electron initially in a 4p state decays to a lower energy
state. Which energy state is forbidden? (pick one): 1s, 2s, 3d, or
2p? Why?
c) What is the total number of electrons that can occupy a
subshell for a given amount of orbital angular momentum l?...
Calculate the coupled eigenstates that result from the coupling of orbital angular momentum ?=2 with spin...
Calculate the coupled eigenstates that result from the coupling
of orbital angular momentum ?=2 with spin angular momentum
?=1/2.
HINT: You may freely use results from Ch. 7 in N. Zettili’s
book, including results from the solved problems. Simply quote
exactly which result you are using each time.
given an electron has orbital angular momentum and spin angular momentum, l and s respectively. given...
given an electron has orbital angular momentum and spin angular
momentum, l and s respectively.
given the following relations:
[lx,ly] = ih(bar)lz , [ly,lz] = ih(bar)lx , [lz,lx] =
ih(bar)ly
[sx,sy]= ih(bar) sz , [sy,sz] = ih(bar)sx , [sz, sy\ =
ih(bar)sy
(a) prove first that for an arbitary operator A, B that
AB=BA+[A,B]
(b) show that [lx,l^2] = 0 where l^2 = l*l = lx^2 + ly^2 +
lz^2
(c) show that similarly, [ly,l^2]=0 and [lz,l^2]=0
(d)given that the...
The orbital angular momentum is a 3D vector. For an electron at a state associated with...
The orbital angular momentum is a 3D vector. For an electron at
a state associated with quantum numbers (?, ?, ??), the magnitude
of the orbital angular momentum is √?(? + 1) ℏ. The orbital angular
momentum measured along the z axis, however, will be exactly ??ℏ.
For a real orbital that combines two complex orbitals associated
with two different ?? values, a measurement along the z axis will
result in either of the two ?? values with an equal...
With the sun at the origin, compute the total angular momentum of the earth, and compare...
With the sun at the origin, compute the total angular momentum
of the earth, and compare the magnitude of the contributions from
the angular momentum of the center of mass and the angular momentum
about the center of mass. You can make simplifying assumptions,
like that the orbit is circular, that the earth is perfect sphere,
etc.
If an electron in an atom has an orbital angular momentum with ml = 4, what...
If an electron in an atom has an orbital angular momentum with
ml = 4, what are the components (a) Lorb,z and (b) μorb,z? If the
atom is in an external magnetic field that has magnitude 44 mT and
is directed along the z axis, what are (c) the potential energy
Uorb associated with the electron's orbital magnetic dipole moment
and (d) the magnitude of the potential energy Uspin associated with
the electron's spin magnetic dipole moment? If, instead, the...
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
ADVERTISEMENT
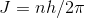
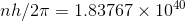
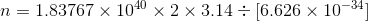
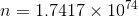 where n = corresponding quantum number .
where n = corresponding quantum number .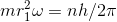 ........................(1)
........................(1)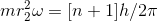 ................(2)
................(2)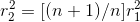
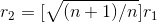 ANSWER
ANSWER genius_generous answered 3 years ago
genius_generous answered 3 years ago