Question
In: Physics
If the momentum of a particle is doubled, what happens to its de Broglie wavelength? it...
If the momentum of a particle is doubled, what happens to its de Broglie wavelength?
it decreases by a factor of 2-1/2
it doubles
it halves
it becomes slightly less than half
it slightly more than doubles
Solutions
Expert Solution
Ans: it halves
Because According to formula of de Broglie wavelength - wavelength is inversly proportional to momentum.
In some situations, light behaves like a wave, while in others, it behaves like particles. The particles of light are called photons, and they can be thought of as both waves and particles. Louis de Broglie developed a formula to relate this dual wave and particle behavior. It can also be applied to other particles, like electrons and protons. The formula relates the wavelength to the momentum of a wave/particle.
For particles with mass (electrons, protons, etc., but not photons), there is another form of the de Broglie wavelength formula. At non-relativistic speeds, the momentum of a particle is equal to its rest mass, m, multiplied by its velocity, v.
The unit of the de Broglie wavelength is meters (m), though it
is often very small, and so expressed in nanometers (1 nm =
10(-9) m), or Angstroms (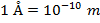 ).
).
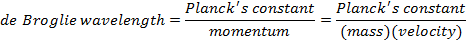
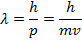
λ = the de Broglie wavelength (m)
h = Planck's constant (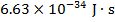 )
)
p = momentum of a particle (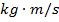 )
)
m = mass of a particle (kg)
v = velocity of a particle (m/s)
Related Solutions
The de Broglie wavelength of a proton in a particle accelerator is 1.81 × 10-14 m....
1. For what kinetic energy is the de Broglie wavelength of an electron equal to its...
An electron has a de Broglie wavelength of 235 nm .What is the speed of the...
a) Derive an expression for the de Broglie wavelength of an electron in the Bohr model...
Explain what physicists mean when they say that the de Broglie wavelength relates to the probability...
In this example we will apply the concept of the de Broglie wavelength to neutrons. Find...
The mass of an electron is 9.11×10−31 kg. If the de Broglie wavelength for an electron...
Calculate the de Broglie wavelength of (a) a 0.715 keV electron (mass = 9.109 × 10-31...
5. (5) (a) Describe the de Broglie Model (also known as the de Broglie-Bohr Model) of...
Describe dual nature of matter? Write de Broglie wavelength and frequency? Explain the electron microscope? Write...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 genius_generous answered 1 year ago
genius_generous answered 1 year ago