Question
In: Chemistry
Draw the structures of organic compounds A and B. Indicate stereochemistry where applicable.
Draw the structures of organic compounds A and B. Indicate stereochemistry where applicable.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
This problem is based on the concept of alkynes. Alkynes are the class of organic compounds containing carbon-carbon triple bonds. Alkyne is converted into higher alkyne on reaction with haloalkane in the presence of a base. The reduction of alkyne to alkene can be made in the presence of Lindlar's catalyst.
Fundamentals
Alkynes that have hydrogen attached to triple bonded carbon are termed as terminal alkynes. The other alkynes are referred to as nonterminal alkynes or internal alkynes. Non-terminal alkynes are more stable and have more boiling points than the corresponding terminal alkynes.
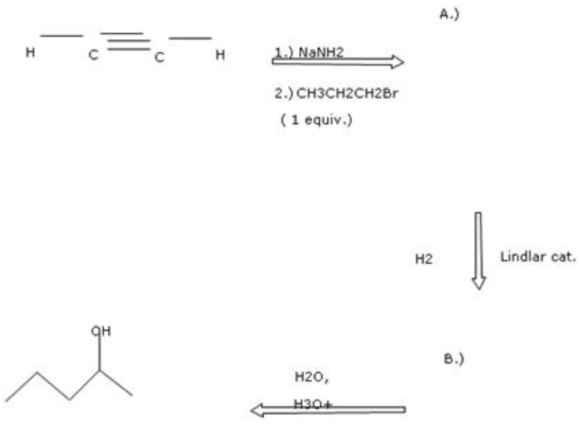
(1) Ethyne, which is a terminal alkyne, reacts with sodamide to give acetylides, which in reaction with haloalkane produce higher alkyne, which is pent-1-yne.
The reaction of acetylene with propyl bromide in the presence of sodamide is written as follows:
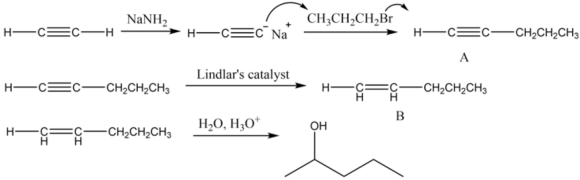
Part 1 The structure of organic compound \(A\) is as follows:
$$ \mathrm{H} \longrightarrow \mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{C} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{CH}_{3} $$
(2)
The hydrogenation of alkynes can be easily carried out using deactivated catalysts such as Lindlar's catalyst to produce cis alkene. The Lindlar's catalyst is \(\mathrm{Pd} / \mathrm{CaCO}_{3}\) in lead acetate poisoned with a small amount of quinoline. The acid-catalyzed reaction of water with alkenes results in the formation of alcohol. The alcohol formed here is 2 pentanol. The addition of water molecule takes place according to Markonikov's rule, which states that highly substituted alkenes are predominantly formed.
The reaction of pent-1-yne with Lindlar's catalyst is as follows:
The alkene formed from the above reaction gives alcohol on hydrolysis as follows:
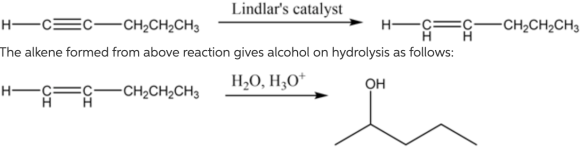
Part 2 The structure of organic compound \(B\) is as follows:![]()
Related Solutions
Draw the structures of organic compounds A and B. Omit all of the byproducts.
Draw Lewis structures for the following compounds.
Draw the condensed and Lewis structures for each of the following compounds (include lone pairs where...
what are the names and structures of the major organic compounds anticipated to be obtained in...
Predict the relative stereochemistry of each product and draw the predicted structures for cinnamic acid, cis-stilbene,...
What does R/S stereochemistry indicate?
Starting with appropriate unlabeled organic compounds, show syntheses of each of the following: (a) Draw the...
Draw the structures of the organic products in each reaction of the following two-step synthesis.
Draw Lewis structures for each of the following compounds. In each case, specify the number of...
Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following compounds. Also calculate the formal charge for each...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago