Question
In: Biology
Sarah, a forty-nine-year-old Anglo woman, visits her physician complaining of weight loss, sweating, listlessness, and flu-like...
Sarah, a forty-nine-year-old Anglo woman, visits her physician
complaining of weight loss, sweating, listlessness, and flu-like
symptoms (fever, headache, scratchy throat, generalized body ache).
After checking her history the physician notes that Sarah is
married, has four children, and no previous history of chronic
illness. Her weight has decreased 15 pounds over the past three
months and she presents with a temperature of 101 degrees F, a
slightly elevated pulse (85 beats per minute), normal blood
pressure (112/78 mm Hg), and slightly labored breathing. Sarah has
a negative family history of cardiovascular and respiratory
diseases. All of her family members are living and are free of
cardiovascular or respiratory diseases. Sarah does not smoke and is
current on all immunizations. She does report that she developed
these symptoms a few days after visiting a friend whose son was
home with a cold. After a chest X-ray and physical examination of
Sarah’s ear, nose, and throat, the physician confirms the diagnosis
and prescribes bed rest, aspirin, and a nasal decongestant. The
physician also cautions Sarah from returning to her normal
activities until she has been afebrile for a minimum of 24 hours.
Sarah’s condition continues to worsen such that a week later she
returns to her physician’s office. She has pain on the left side of
her chest, is coughing more frequently and her sputum has a yellow
color. Her respiratory rate is 32 breaths per minute and her
breathing is labored. Her blood pressure is unchanged and does not
demonstrate postural changes. Breath sounds indicate inspiratory
rales and a chest X-ray indicates a dense infiltrate within the
lungs. Physical examination reveals lymphadenopathy. The physician
suspects pneumonia and orders laboratory tests on Sarah’s blood and
sputum. The results of the sputum tests indicate the presence of
gram-positive diplococci and polymorphonucleocytes that are too
numerous to count. What concerns the physician, however, are the
results of Sarah’s blood test. Her blood tests indicate leukopenia,
anemia, and thrombocytopenia. In addition, the differential
leukocyte count indicates that the concentration of helper T cells
has decreased. The physician now suspects that Sarah has been
infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and that she
has developed pneumonia as a result of the immune suppression. In
reviewing her history, the physician notes that Sarah has been
married for the past 30 years and does not admit to any
extramarital affairs. She has not received any blood transfusions
or blood products and does not use intravenous drugs. She is a
self-employed certified public accountant and has not visited any
countries with high incidences of HIV infection. Upon further
discussion, Sarah does mention to the physician that she and her
husband were separated a few years ago for approximately 6 months
as a result of his extramarital affair. The physician asks Sarah if
he can run another test to determine whether or not she has
contacted HIV and asks Sarah to talk to her husband about being
tested for HIV as well. The physician also begins treating Sarah
for pneumonia that has developed and asks her to return the next
day for the results of the HIV test.
The next day Sarah and her husband return to the physician’s office
and the physician confirms that the enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent
assay confirms that Sarah is HIV positive. The physician does
mention that a second more sensitive test will be conducted to
confirm this finding, however, he is doubtful that the result will
indicate a false positive in the first test. Her husband admits to
having numerous extramarital affairs with both women and men and
consents to a blood test to determine his HIV status, which
subsequently is positive. The physician then discusses the
replicative cycle of HIV, the concept of a retrovirus, and
treatment options with both Sarah and her husband. Sarah
immediately starts on a regimen of protease inhibitors and
nucleoside analogs (azidothymidine, AZT, and ddI). In addition, the
physician discusses with Sarah and her husband the necessity of
practicing "safe sex" even though both are HIV positive and the
importance of not exposing themselves to opportunistic diseases. In
addition, he mentions that some of the drugs they will be taking to
minimize viral replication may cause nausea. He cautions them to
take all medications as scheduled and to return to his office at
the first sign of any disorder. He also reiterates that this
disease can not be transferred by casual contact, but can be
transferred through an exchange of body fluids (blood, semen, and
vaginal secretions). Answer the following questions about this
case.
1. Why was HIV not initially considered as a possible cause for the
symptoms Sarah presented with?
2. Why did Sarah’s symptoms worsen and develop into
pneumonia?
3. Identify the specific types of leukocytes and the function of
each cell.
4. Why does HIV specifically affect one type of leukocyte?
5. Why can protease inhibitors and nucleoside analogs be used in
minimizing the replication of the HIV virus?
Solutions
Expert Solution
ANS (3)- SPECIFIC TYPES OF LEUKOCYTES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS-
- BASOPHIL---> It is a type of White blood cells whose work to produce heparin, which is the chemical used to prevent the blood clotting too quikly and secondly basophil produces the histamine which promotes blood flow to tissues, hence contributes in immune system.
- EOSINOPHIL---> These contribute to the immune system by the following actions-
- Plays major role in prevention of viral infection.
- These are important molecules in asthma which mediates the allergic reaction.
- Majorly works as destruction of antibody-covered pathogens.
- NEUTROPHIL--> They involves in phagocytosis of antibody-covered pathogens and hence contribute to immune system by protecting the body from the affect of pathogens.
- MONOCYTE-----> These are the cells that convered into macrophages.
- MACROPHAGE---> They trigger the immune response as triggering the phagocytosis of pathogens and activates the T cell .
- B lymphocyte------> They are the important cells of immune system because they are differenciated into memory cell are involved in the production of antibodies that mjaorly reduces the affect of pathogenic organism.
- T lymphocyte-----> These are the cells that actually causes the death of a pathogenic cell that causes the infection. It involves in stimulation of B cell production and also helps in natural killer cell develpoment.
- NATURAL KILLER CELL---> These are the lymphocytes of same family as T and B cells .These cells causes the destruction of pathogenic cells and are also able to recognize and destroy the cancer cells.
- DENDRITIC CELLS ----> These are the type of
leukocytes that forms the bridge between innate and adaptive
immunity responses and these are the antigen presenting cells that
presents the pathogens to lymphocyte cells.
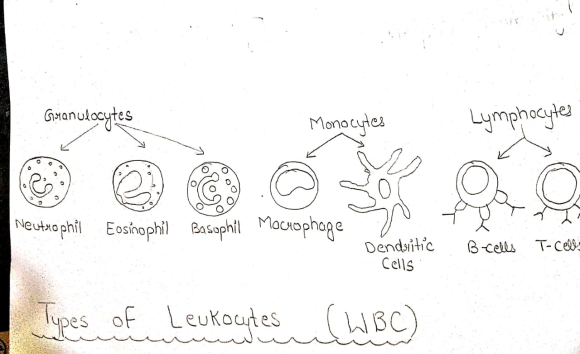
Gavanulocytes Monocytes . Lymphocytes Neutrophil Eosinophil Basophil Macrophage Dendslitic Cells B-cells T-Cews Types of Leukoutes (WBC)
Related Solutions
A 53-year-old woman visited her primary care physician complaining of a burning pain in the epigastrium...
A 63 year old male visits his primary care physician complaining of fatigue and shortness of...
72 year old man, complaining of flu like symptoms, but without a fever.He also has a...
A report by the Gallup Poll stated that on average a woman visits her physician 5.8...
A 33-year-old male patient visits his primary care physician complaining of right buttock and right leg...
An obese 58-year-old woman is seen by her physician. Her chief complaint is perineal itching and...
A 26-year-old woman in graduate school visits the family physician because for the past 3–4 months...
A 43-year-old woman presented to her family physician with a two-year history of fatigue, diarrhea, and...
A 60-year-old woman came to her physician because she was having problems with urination. Her previous...
Gina, a 44-year-old mother of eight children, visited her physician complaining of a “bearing down” sensation...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...

 gladiator answered 3 years ago
gladiator answered 3 years ago