Question
In: Chemistry
3.0ml of starch solution+ 3.0ml amylase added after 50 minute, what color is it after iodine,...
3.0ml of starch solution+ 3.0ml amylase added after 50 minute, what color is it after iodine, what the amount of starch, what color is it after adding Benedict's test, what amount of maltose and enzymes activity?
3.0ml of starch + 3.0ml amylase added, what color is it after iodine, what the amount of starch, what color is it after adding Benedict's test, what amount of maltose and enzymes activity?
3.0ml of starch + 4 drops of 2.0M HCl+ 3.0ml amylase,
what color is it after iodine, what the amount of starch, what
color is it after adding Benedict's test, what amount of maltose
and enzymes activity?
incubate on ice 3.0ml of starch + 3.0ml amylase added, what color is it after iodine, what the amount of starch, what color is it after adding Benedict's test, what amount of maltose and enzymes activity?
Solutions
Expert Solution
Explanation:
Given conditions are -
- 3.0 ml of starch + 3.0 ml amylase added, what is the color after iodine is added? Amount of Starch? what color is seen after adding Benedict's test, what amount of maltose and enzymes activity?
- 3.0 ml of starch + 4 drops of 2.0 M
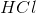 + 3.0 ml amylase, what is the color after iodine is added? what
color is seen after adding Benedict's test, what amount of maltose
and enzymes activity?
+ 3.0 ml amylase, what is the color after iodine is added? what
color is seen after adding Benedict's test, what amount of maltose
and enzymes activity?
- To test the presence of starch iodine test is the best. It changes the brown color to blue/black color when added to the starch. They form a complex.
- Benedict’s test are performed when reducing sugars are present giving brick-red precipitate while starch is a non reducing sugar hence it will not give any color to Benedict’s test. And there is no change in the amount of starch as the precipitate formation indicates the amount of reducing sugar present in it.
- Amylase when reacts to the starch it acts as an enzyme to
catalyze the breakdown of starch. Amylase reacts with starch and
breaks the two glucose molecules that are linked together(
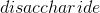 maltose). As the reaction proceeds, the presence of starch will be
less than the maltose sugar.
maltose). As the reaction proceeds, the presence of starch will be
less than the maltose sugar. - Now, when reaction of amylase with starch is carried out by using iodine iodine test we will observe that after the reaction of with starch forming a dark brown/purple color the the color of the solution will become lighter and lighter as the amylase breaks down starch, less and less starch will be present.
- Also the amount of enzyme used is more important. Less enzyme is used then high amount of starch is used that means the complex formation is high. If the color is more light the amylase enzyme activity is high.
The another condition is that why 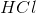 is added or used during the reaction. the reason for this is -
is added or used during the reaction. the reason for this is -
- The acid helps to stop the enzymatic reaction of amylase and iodine reacts with starch to give blue color.
Related Solutions
B. Permeability of starch and iodine Data table: Color of starch solution in bag at start...
1. What normally happens when iodine is added to starch? 2.Tube 2 contained starch at the...
Data 1. What color did you get when you mixed iodine and starch? Remember to make...
Starch hydrolysis What result would you expect if glucose had been added to the starch agar...
1)What color would a Gram-negative cell be if we skipped the iodine? What color would a...
Why would CuSO4 have a blue color after the iron reagent is added? Yes, the answer...
You added sodium sulfate solution to well A1 and observed a color change. Select the answer...
Calculate the pH of a solution after 10.0mL of .1M NaOH is added to 40mL of...
By adding heat to a test tube containing distilled water, amylase, and Benedict's Solution, what will...
Twenty grams of soil was added to 50 mL of water. After mixing, the suspension was...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
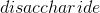 maltose). As the reaction proceeds, the presence of starch will be
less than the maltose sugar.
maltose). As the reaction proceeds, the presence of starch will be
less than the maltose sugar. queen_honey_blossom answered 2 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 2 years ago