Question
In: Chemistry
Propanone is a liquid
Propanone is a liquid. It has the structure
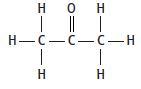
The equation for the complete combustion of propanone is:
CH3COCH3(l) + 4O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
a. Use the following bond energies (in kJ mol–1) to calculate a value for the standard enthalpy change of this reaction:
E(C — C) = +347
E(C — H) = +413
E(O — O) = +496
E(C — O) = +805
E(O — H) = +465
b. Suggest why it would be more accurate to use bond energies that are not average bond energies in this calculation.
c. The standard enthalpy change of combustion of propanone is –1816.5 kJ mol–1. Suggest why this value differs from the value obtained using bond energies.
d. The standard enthalpy change of formation of propanone is –248 kJ mol–1.
i. Define the term standard enthalpy change of formation.
ii. Write the equation that describes the standard enthalpy change of formation of propanone.
iii. Explain why the enthalpy change of formation of propanone cannot be found by a single experiment.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Given −C−H=415kJ/mol C−C=350KJ/mol
C=0=730KJ/mol O−O=495KJ/mol
H−H=435KJ/mol ΔH
sub
of C=720KJ/mol
C(s)→C(g)−ΔH=720KJ/mol
O
∣∣
3C(g)+3H
2
(g)+
2
1
O
2
(g)→CH
3
−C−CH
3
Heat of formation of Acetone = [Bond energy of formation of bond]
+ [Bond energy of dissociation of bond]
=[6(C−H)+2(C−C)+1(C=0)]
+[3{C(s)→C(g)}+3(H−H)+
2
1
(0−0)]
=−[6×415+2×350+1×730]
+[3×720+3×435+
2
1
×495]
=−[2490+700+730]
+[2160+1305+2475]
=−3920KJ+37125KJ
=−207.5KJ/mol
∴ Heat of formation of acetone is −207.5KJ/mol
solution.
−[2490+700+730]
+[2160+1305+2475]
=−3920KJ+37125KJ
=−207.5KJ/mol
∴ Heat of formation of acetone is −207.5KJ/mol
solution.
Related Solutions
Order the following compounds in descending order of frequency for the carbonyl band. 1) 2-propanone, methanal,...
The pKa values of acetone and 1-phenyl-2-propanone are 26.5 and 19.8 respectively. Use electronic factors to...
1) Compare the solubility in water of similar size compounds like pentane, 1-propanol, and propanone. Which...
A vessel contains a mixture of equimolar liquid benzene and liquid toluene that is in equilibrium...
nitromethane CH3NO2 is a good fuel it is liquid at ordinary temperatures when the liquid is...
Many techniques exist to measure the surface energy between a liquid and a liquid or a...
At 300K, the vapor pressure of pure liquid A and liquid B are 37.33 kPa and...
If a small stream of liquid A was strongly deflected by a charged object, liquid B...
Why is it Important to determine the liquid limits of soil and how limits liquid of...
Give an example of a vapor-liquid phase diagram and explain the difference in liquid and vapor...
- 2. a. Choose all of the following that apply to DynamoDB: (a) DynamoDB is part of...
- I asked this question before, but I'm wondering if there are any other ways to do...
- Can you please Describe your actions as the Manager, and how you would manage the project...
- Suppose we have a collection of n different subsets of the set { 1, 2, ...,...
- def read_list(): """ This function should ask the user for a series of integer values (until...
- If two slits are separated by .25cm and the slit to screen is 1m, what is...
- Determine the oxidation number (oxidation state) for the indicated element in each of the following compounds....
 Raffay answered 3 years ago
Raffay answered 3 years ago