Question
In: Statistics and Probability
MacroHard Corp
MRP, EOQ and JIT. MacroHard Corp produces J-Pods, music players that can download thousands of songs. MacroHard forecasts that demand in 2010 will be 48,000 J-Pods. The variable production cost of each J-Pod is $50. Due to the large $50,000 cost per setup, MacroHard plans to produce J-Pods once a month in batches of 4,000 each. The carrying cost of a unit in inventory is $20 per year
1. Using an MRP system, what is the annual cost of producing and carrying J-Pods in inventory? (Assume that on average, half of the units produced in a month are in inventory.)
2. A new manager at MacroHard has suggested that the company use the EGG model to determine the optimal batch size to produce. (To use the EGG model, MacroHard needs to treat the setup cost in the same way it would treat ordering cost in a traditional EGG model.) Determine the optimal batch size and number of batches. Round up the number of batches to the nearest whole number. What would be the annual cost of producing and carrying J-Pods in inventory if it uses the optimal batch size?
3.MacroHard is also considering switching from an MRP system to a JIT system. This will result in producing to demand in batch sizes of 500 J-Pods. The frequency of production batches will force MacroHard to reduce setup time and will result in a reduction in setup cost. The new setup cost will be $5,000 per setup. What is the annual cost of producing and carrying J-Pods in inventory under the JIT system?
4. Compare the models analyzed in the previous parts of the problem. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each?
Solutions
Expert Solution
MRP, EOQ, and JIT.
1.
Under a MRP system:
Annual cost of producing and carrying J-Pods in inventory
= Variable production cost + Setup cost + Carrying cost
= $50 × 48,000 + ($50,000 × 12 months) + [$20 × (4,000 ÷ 2)]
= $2,400,000 + 600,000 + 40,000 = $3,040,000
2.
Using an EOQ model to determine batch size:
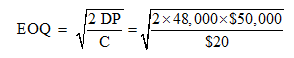
= 15,492 J-Pods per batch
Production of 48,000 per year divided by a batch size of 15,492 would imply J-Pods would be produce 3.1 batches per year. Rounding this up to the nearest whole number yields 4 batches per year.
Annual Cost of producing and carrying J-Pods in inventory
= Variable production cost + Setup cost + Carrying cost
= $50 × 48,000 + ($50,000 × 4) + [$20 × (15,492 ÷ 2)]
= $2,400,000 + 200,000 + 154,920 = $2,754,920
3.
Under a JIT system
Annual Cost of producing and carrying J-Pods in inventory
= Variable production cost + Setup cost + Carrying cost
= $50 × 48,000 + ($5,000 × 96 a) + [$20 × (500 ÷ 2)]
= $2,400,000 + 480,000 + 5,000 = $2,885,000
a production of 48,000 per year divided by a batch size of 500 would imply 96 setups per year.
4.
The EOQ system resulted in the lowest costs, despite the fact that carrying costs were lower for the JIT model. However, the EOQ model, in this case, limits production to only once every four months. This would not allow managers to react quickly to changing market demand or economic conditions. The JIT model provides management with much more flexibility. JIT systems might also lead managers to improve processes, reduce costs and increase quality.
The EOQ system resulted in the lowest costs, despite the fact that carrying costs were lower for the JIT model. However, the EOQ model, in this case, limits production to only once every four months. This would not allow managers to react quickly to changing market demand or economic conditions. The JIT model provides management with much more flexibility. JIT systems might also lead managers to improve processes, reduce costs and increase quality.
Related Solutions
A Corp. owns 80% of B Corp. The Consolidated Financial Statements of A Corp. for 2018...
Cable Corp. has entered into a transaction with Land Corp. Cable Corp will give its equipment...
DaimlerChrysler Corp.
Derozan Corp. manufactured equipment at a cost of $167,770 and leased it to B Corp. on...
AT Corp. opened for business on April 1st. Listed below are the transactions for AT Corp....
On January 1, 2012, P Corp acquired 80% of the outstanding common stock of S Corp for $820,000. On January 1, 2018, P Corp sold $120,000 of land to S Corp for cash.
Calculate the MIRR of the following project. Corp. ABC's initial investment cost is $180, and Corp....
ACCT Corp. is a manufacturer of truck trailers. On 1 January 2020, ACCT Corp. leased a...
Clement Corp., a pharmaceutical manufacturer, licensed a drug patent to Global Corp. for royalties of 5%...
ACCT Corp. is a manufacturer of truck trailers. On 1 January 2020, ACCT Corp. leased a...
- Can you please Describe your actions as the Manager, and how you would manage the project...
- Suppose we have a collection of n different subsets of the set { 1, 2, ...,...
- def read_list(): """ This function should ask the user for a series of integer values (until...
- If two slits are separated by .25cm and the slit to screen is 1m, what is...
- Determine the oxidation number (oxidation state) for the indicated element in each of the following compounds....
- What is the difference between product and production risk? How can they be mitigated?
- C# 1. Create an Employee class with two fields: idNum and hourlyWage. The Employee constructor requires...
 Raffay answered 3 years ago
Raffay answered 3 years ago