Question
In: Physics
What is drift velocity?
What is drift velocity?
Solutions
Expert Solution
The drift velocity is the flow velocity that a particle, such as an electron, attains due to an electric field. It can also be referred to as axial drift velocity. In general, an electron will propagate randomly in a conductor at the Fermi velocity. An applied electric field will give this random motion a small net flow velocity in one direction.
In a semiconductor, the two main carrier scattering mechanisms are ionized impurity scattering and lattice scattering.
Because current is proportional to drift velocity, which in a resistive material is, in turn, proportional to the magnitude of an external electric field, Ohm's law can be explained in terms of drift velocity.
The most elementary expression of Ohm's law is:
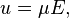
- Thus valence electrons of atom becomes the conduction electrons of the metals
- At room temperature,these conduction electrons moves randomly inside the conductor more or less like a gas molecule
- During motion,these conduction electrons collide with ions(remaining positive charged atom after the valence electrons move away) again and again and there direction of motion changes after each and every collision.
- As a results of these collisions atoms moves in a zig-zag path
- Since in a conductor there are large number of elctrons moving randomly inside the conductor.Hence they have not net motion in any particular direction.Since the number of electrons crossing an imaginary area ΔA from left to right inside the conductor very nearly equals the number of electron crossing the same area element from right to left in a given interval of time leaving flow of electric current through that area nearly equals to zero
- Now when we applied some P.D using a battery across the two ends of the conductor,then an electric field sets up inside the conductor
- After each collision electrons starts fresh in random direction ,again get accelerated and loose their gained Kinetic energy in another collision
- This extra velocity gained by the electrons is lost in subsequent collison and the processes continued till the electron reach positive end of the conductor
- Under the effect of electric field inside the conductor ,free electrons have random thermal velocities due to the room tmeperature and small velocities with which they drift towards the positive end of the conductor.
- if τ is the average time between two successive collisions and
E is the strength of applied electric field then force on electron
due to applied electric field is
F=eE
Where e is the amount of charge on electron - if m is the mass of electron ,then acceleration produced is
given by
a=eE/m - Since electron is acclerated for an average time interval
τ,additional velocity acquired by the electron is
vd=aτ
or vd=(eE/m)τ (3)
This small velocity imposed on the random motion of electrons in a conductor on the application of electric field is known as drift velocity - This drift velocity is defined as the velocity with which free electrons gets drifted towards the positive end of the conductor under the influence of externally applied electric field
Related Solutions
What is drift velocity?
Compare the thermal velocity with the drift velocity of electrons in one mole of a divalent...
What is Genetic drift? and Examples of genetic drift
a) In a Gunn diode oscillator, the electron drift velocity was found to be 107 cm/sec...
Please qualitatively describe drift velocity and why it opposes the relative motion of a conductor and a magnet.
Bob and 2 students of his drift by Dave at velocity vH in the x-direction. He...
State how directions of the electric field, current, drift velocity, and current density related?
1 What is genetic drift? 2 In what way can a genetic bottleneck lead to genetic drift in population?
What is meant by a shift and a drift mutation in viruses?
What is the difference between genetic drift and founder effect?
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 genius_generous answered 2 years ago
genius_generous answered 2 years ago