Question
In: Biology
How can an obligate aerobe still grow without oxygen by carrying out anaerobic respiration? this lab...
How can an obligate aerobe still grow without oxygen by carrying out anaerobic respiration?
this lab is about nitrate reduction and how it is one form of anaerobic respiration.
Solutions
Expert Solution
solution
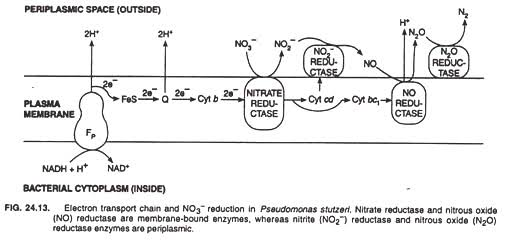
- Obligate aerobes are live in the presence of oxygen only but some bacterial strain can utilize NO3 instead of O2 as an electron acceptor to proceed anaerobic respiration.
- Enzyme Nitrate reductase (on inner membrane) is responsible for nitrate reduction in obligate aerobe to start anaerobic respiration.
- Nitrate is a molecule having high reduction potential act as terminal electron acceptor in many anaerobic bacteria.
Related Solutions
Lab 4: Cellular Respiration Anaerobic Respiration What are the two kinds of anaerobic respiration? What are...
Lab 4: Cellular Respiration Anaerobic Respiration What are the
two kinds of anaerobic respiration? What are the byproducts of each
type? Aerobic Respiration vs. Anaerobic Respiration What do they
have in common? How are they different?
Lab 5: Enzymes and Standard Curve To what extent can changing an
enzyme's environment affect its functionality? Experimental design
Be able to understand how to use a standard curve to find out an
unknown concentration of glucose using absorbance values.
explain how photosynthesis can occur without the production of oxygen, and how respiration can occur without...
explain how photosynthesis can occur without the production of
oxygen, and how respiration can occur without requiring
oxygen
You are studying a bacterial strain that is an obligate aerobe. The bacteria can do some...
You are studying a bacterial strain that is an obligate aerobe.
The bacteria can do some fermentation and produce lactic acid as an
end product, but normally only when starved for oxygen and can’t
survive on fermentation alone. Your rival dumps a chemical into
your prize culture. This chemical binds to the first protein in the
electron transport chain, locking it into a fully reduced and
inhibited state permanently. Describe the predicted consequences of
this poison on the function of...
1.) Compare aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration and fermentation. How are the processes similar? How are they...
1.) Compare aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration and
fermentation. How are the processes similar? How are they
different? How do these processes determine which environment the
organism can live in?
[Key terms to use in answer: electron transport chain,
cytochrome, ATP, glucose, glycolysis, obligate aerobe, facultative
anaerobe, microaerophile, obligate anaerobe, oxidase, catalase,
peroxidase, CO 2 , organic acids and alcohols,
alternative substrates (other than glucose)]
2.) Using your knowledge of DNA recombination events to complete
the following:
(Use the following terminology...
Yeast make alcohol in the absence of oxygen by a process called fermentation (i.e., anaerobic respiration)....
Yeast make alcohol in the absence of oxygen by a process called
fermentation (i.e., anaerobic respiration). Complete fermentation
of one of the sugar glucose (C6 H12
O6) will generate two moles of ethanol (C2
H6 O), two moles of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas,
and tow moles of the important molecule ATP (C10
H16 N5 O13 P3), using
in cellular transfers. You perform an experiment to make alcohol,
so you set up an anaerobic fermentation system using yeast. You add
135...
1. How can anaerobic microorganisms grow on the skin or in the mouth, both which are...
1. How can anaerobic microorganisms grow on the skin or in the
mouth, both which are exposed to air?
2. Why do many gram positive microbes that grow on the skin,
such as S. Epidermis grow poorly or not at all in the gut?
how does mitochondria get oxygen in anaerobic conditions?
how does mitochondria get oxygen in anaerobic conditions?
Compare and contrast aerobic respiration versus anaerobic respiration. Explain the (1) electron transport system and how...
Compare and contrast aerobic respiration versus anaerobic
respiration. Explain the (1) electron transport system and how many
ATP are produced, (2) where the electrons go (the final electron
acceptor), and (3) give an example of an organism that carries out
aerobic respiration and an example of an organism that uses
anaerobic respiration.
A student carrying out out a Spectrophotmetric dtermination of copper in Brass lab experiment was in...
A student carrying out out a Spectrophotmetric dtermination of
copper in Brass lab experiment was in a hurry to finish. The
student decided to omit the filtering step of the procedure because
the brass solution did not appear very cloudy. It turned out that
there was tin in the sample.
a) Did the omission of the filtering step cause a high or low
result? Briefly explain.
b) Also during the filtering process some of the brass solution
is absorbed by...
Bacteria can perform aerobic and anaerobic respiration depending on their enzymes and metabolic needs. A student...
Bacteria can perform aerobic and anaerobic respiration depending
on their enzymes and metabolic needs. A student argued that aerobic
and anaerobic respiration should produce the same amount of ATP. He
reasoned that they both use basically the same process; only the
terminal electron acceptor is different. What is the primary error
in this student’s argument? Think about the different organisms in
the body and in nature. Discuss how some produce their energy by
anaerobic and aerobic metabolism. Discuss what would...
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
ADVERTISEMENT

 gladiator answered 3 years ago
gladiator answered 3 years ago